Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
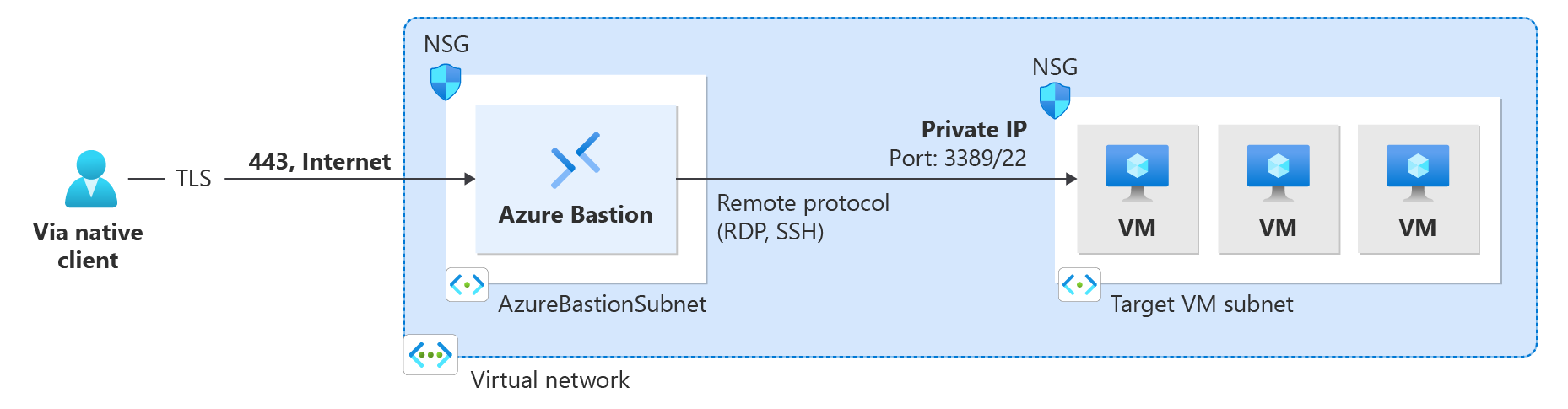
This article helps you connect via Azure Bastion to a VM in virtual network using the native client on your local Linux computer. The native client feature lets you connect to your target VMs via Bastion using Azure CLI, and expands your sign-in options to include local SSH key pair and Microsoft Entra ID. For more information and steps to configure Bastion for native client connections, see Configure Bastion for native client connections. Connections via native client require the Bastion Standard SKU or higher.
After you've configured Bastion for native client support, you can connect to a VM using a native Linux client. The method you use to connect depends on both the client you're connecting from, and the VM you're connecting to. The following list shows some of the available ways you can connect from a Linux native client. See Connect to VMs for the full list showing available client connection/feature combinations.
- Connect to a Linux VM using az network bastion ssh.
- Connect to a Windows VM using az network bastion tunnel.
- Connect to any VM using az network bastion tunnel.
- Transfer files to your target VM over SSH using az network bastion tunnel.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, verify that you have the following prerequisites:
- The latest version of the CLI commands (version 2.32 or later) is installed. You can update your CLI for Bastion using
az extension update --name bastion. For information about installing the CLI commands, see Install the Azure CLI and Get Started with Azure CLI. - Azure Bastion is already deployed and configured for your virtual network. For steps, see Configure Bastion for native client connections.
- A virtual machine in the virtual network.
- The VM's Resource ID. The Resource ID can be easily located in the Azure portal. Go to the Overview page for your VM and select the JSON View link to open the Resource JSON. Copy the Resource ID at the top of the page to your clipboard to use later when connecting to your VM.
- If you plan to sign in to your virtual machine using your Microsoft Entra credentials, make sure your virtual machine is set up using one of the following methods:
- Enable Microsoft Entra sign-in for a Windows VM or Linux VM.
- Configure your Windows VM to be Microsoft Entra joined.
- Configure your Windows VM to be Microsoft Entra hybrid joined.
Verify roles and ports
Verify that the following roles and ports are configured in order to connect to the VM.
Required roles
Reader role on the virtual machine.
Reader role on the NIC with private IP of the virtual machine.
Reader role on the Azure Bastion resource.
Virtual Machine Administrator Login or Virtual Machine User Login role, if you’re using the Microsoft Entra sign-in method. You only need to do this if you're enabling Microsoft Entra login using the processes outlined in one of these articles:
Ports
To connect to a Linux VM using native client support, you must have the following ports open on your Linux VM:
- Inbound port: SSH (22) or
- Inbound port: Custom value (you’ll then need to specify this custom port when you connect to the VM via Azure Bastion)
To connect to a Windows VM using native client support, you must have the following ports open on your Windows VM:
- Inbound port: RDP (3389) or
- Inbound port: Custom value (you’ll then need to specify this custom port when you connect to the VM via Azure Bastion)
To learn about how to best configure NSGs with Azure Bastion, see Working with NSG access and Azure Bastion.
Connect to a Linux VM
The steps in the following sections help you connect to a Linux VM from a Linux native client using the az network bastion command. This extension can be installed by running, az extension add --name bastion.
When you connect using this command, file transfers aren't supported. If you want to transfer files, connect using the az network bastion tunnel command instead.
This command lets you do the following:
- Connect to a Linux VM using SSH.
- Authenticate via Microsoft Entra ID
- Connect to concurrent VM sessions within the virtual network.
To sign in, use one of the following examples. Once you sign in to your target VM, the native client on your computer opens up with your VM session.
SSH key pair
To sign in to your VM using an SSH key pair, use the following example.
az network bastion ssh --name "<BastionName>" --resource-group "<ResourceGroupName>" --target-resource-id "<VMResourceId>" --auth-type "ssh-key" --username "<Username>" --ssh-key "<Filepath>"
Microsoft Entra authentication
If you’re signing in to a Microsoft Entra login-enabled VM, use the following example. For more information, see Azure Linux VMs and Microsoft Entra ID.
az network bastion ssh --name "<BastionName>" --resource-group "<ResourceGroupName>" --target-resource-id "<VMResourceId or VMSSInstanceResourceId>" --auth-type "AAD"
Username/password
If you’re signing in to your VM using a local username and password, use the following example. You’ll then be prompted for the password for the target VM.
az network bastion ssh --name "<BastionName>" --resource-group "<ResourceGroupName>" --target-resource-id "<VMResourceId or VMSSInstanceResourceId>" --auth-type "password" --username "<Username>"
SSH to a Linux VM IP address
You can connect to a VM private IP address instead of the resource ID. Microsoft Entra ID authentication, and custom ports and protocols, aren't supported when using this type of connection. For more information about IP-based connections, see Connect to a VM - IP address.
Using the az network bastion command, replace --target-resource-id with --target-ip-address and the specified IP address to connect to your VM. The following example uses --ssh-key for the authentication method.
az network bastion ssh --name "<BastionName>" --resource-group "<ResourceGroupName>" --target-ip-address "<VMIPAddress>" --auth-type "ssh-key" --username "<Username>" --ssh-key "<Filepath>"
Connect to a VM - tunnel command
The az network bastion tunnel command is another way that you can connect to your VMs. When you use this command, you can do the following:
- Connect from native clients on non-Windows local computers. (For example, a Linux computer.)
- Connect to a VM using SSH or RDP. (The bastion tunnel doesn't relay web servers or hosts.)
- Use the native client of your choice.
- Transfer files to your target VM from your local computer.
Limitations:
- Signing in using an SSH private key stored in Azure Key Vault isn’t supported with this feature. Before signing in to your Linux VM using an SSH key pair, download your private key to a file on your local machine.
- This feature isn't supported on Cloud Shell.
Steps:
Sign in to your Azure account using
az login. If you have more than one subscription, you can view them usingaz account listand select the subscription containing your Bastion resource usingaz account set --subscription "<subscription ID>".Open the tunnel to your target VM. Without root privileges use local port 1024 or above as ports below that are privileged ports only accessible by root.
az network bastion tunnel --name "<BastionName>" --resource-group "<ResourceGroupName>" --target-resource-id "<VMResourceId or VMSSInstanceResourceId>" --resource-port "<TargetVMPort>" --port "<LocalMachinePort>"Connect to your target VM using SSH or RDP, the native client of your choice, and the local machine port you specified in the previous step.
For example, you can use the following command if you have the OpenSSH client installed on your local computer:
ssh <username>@127.0.0.1 -p <LocalMachinePort>
Tunnel to a VM IP address
You can also connect to a VM private IP address, instead of the resource ID. Microsoft Entra ID authentication, and custom ports and protocols, aren't supported when using this type of connection. For more information about IP-based connections, see Connect to a VM - IP address.
Using the az network bastion tunnel command, replace --target-resource-id with --target-ip-address and the specified IP address to connect to your VM.
az network bastion tunnel --name "<BastionName>" --resource-group "<ResourceGroupName>" --target-ip-address "<VMIPAddress>" --resource-port "<TargetVMPort>" --port "<LocalMachinePort>"
Multi-connection tunnel
Add the following to your $HOME.ssh\config.
Host tunneltunnel HostName 127.0.0.1 Port 2222 User mylogin StrictHostKeyChecking=No UserKnownHostsFile=\\.\NULAdd the tunnel connection to your established tunnel connection.
az network bastion tunnel --name mybastion --resource-group myrg --target-resource-id /subscriptions/<mysubscription>/resourceGroups/myrg/providers/Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines/myvm --resource-port 22 --port 22Create an ssh tunnel in the bastion tunnel.
ssh -L 2222:127.0.0.1:22 mylogin@127.0.0.1Use VS Code to connect to your tunnel connection.