What is a voice assistant?
By using voice assistants with the Speech service, developers can create natural, human-like, conversational interfaces for their applications and experiences. The voice assistant service provides fast, reliable interaction between a device and an assistant implementation.
Choose an assistant solution
The first step in creating a voice assistant is to decide what you want it to do. Speech service provides multiple, complementary solutions for crafting assistant interactions. You might want your application to support an open-ended conversation with phrases such as "I need to go to Seattle" or "What kind of pizza can I order?" For flexibility and versatility, you can add voice in and voice out capabilities to a bot by using Azure AI Bot Service with the Direct Line Speech channel.
If you aren't yet sure what you want your assistant to do, we recommend Direct Line Speech as the best option. It offers integration with a rich set of tools and authoring aids, such as the Virtual Assistant solution and enterprise template and the QnA Maker service, to build on common patterns and use your existing knowledge sources.
Reference architecture for building a voice assistant by using the Speech SDK
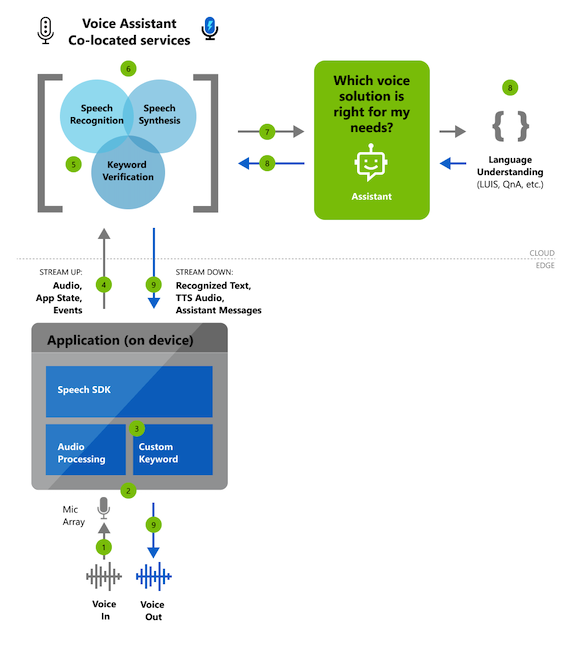
Core features
Whether you choose Direct Line Speech or another solution to create your assistant interactions, you can use a rich set of customization features to customize your assistant to your brand, product, and personality.
| Category | Features |
|---|---|
| Custom keyword | Users can start conversations with assistants by using a custom keyword such as "Hey Contoso." An app does this with a custom keyword engine in the Speech SDK, which you can configure by going to Get started with custom keywords. Voice assistants can use service-side keyword verification to improve the accuracy of the keyword activation (versus using the device alone). |
| Speech to text | Voice assistants convert real-time audio into recognized text by using speech to text from the Speech service. This text is available, as it's transcribed, to both your assistant implementation and your client application. |
| Text to speech | Textual responses from your assistant are synthesized through text to speech from the Speech service. This synthesis is then made available to your client application as an audio stream. Microsoft offers the ability to build your own custom, high-quality Neural Text to speech (Neural TTS) voice that gives a voice to your brand. |
Get started with voice assistants
We offer the following quickstart article that's designed to have you running code in less than 10 minutes: Quickstart: Create a custom voice assistant by using Direct Line Speech
Sample code and tutorials
Sample code for creating a voice assistant is available on GitHub. The samples cover the client application for connecting to your assistant in several popular programming languages.
- Voice assistant samples on GitHub
- Tutorial: Voice-enable an assistant that's built by using Azure AI Bot Service with the C# Speech SDK
Customization
Voice assistants that you build by using Speech service can use a full range of customization options.
Note
Customization options vary by language and locale. To learn more, see Supported languages.
Next steps
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for