Quickstart: Add voice calling to your app
Get started with Azure Communication Services by using the Calling SDK to add voice and video calling to your app.
In this quickstart, you learn how to start a call using the Azure Communication Services Calling SDK for Windows.
You can download the sample app from GitHub.
Prerequisites
To complete this tutorial, you need the following prerequisites:
An Azure account with an active subscription. Create an account for free.
Install Visual Studio 2022 with Universal Windows Platform development workload.
A deployed Communication Services resource. Create a Communication Services resource. You need to record your connection string for this quickstart.
A User Access Token for your Azure Communication Service. You can also use the Azure CLI and run the command with your connection string to create a user and an access token.
az communication identity token issue --scope voip --connection-string "yourConnectionString"For details, see Use Azure CLI to Create and Manage Access Tokens.
Setting up
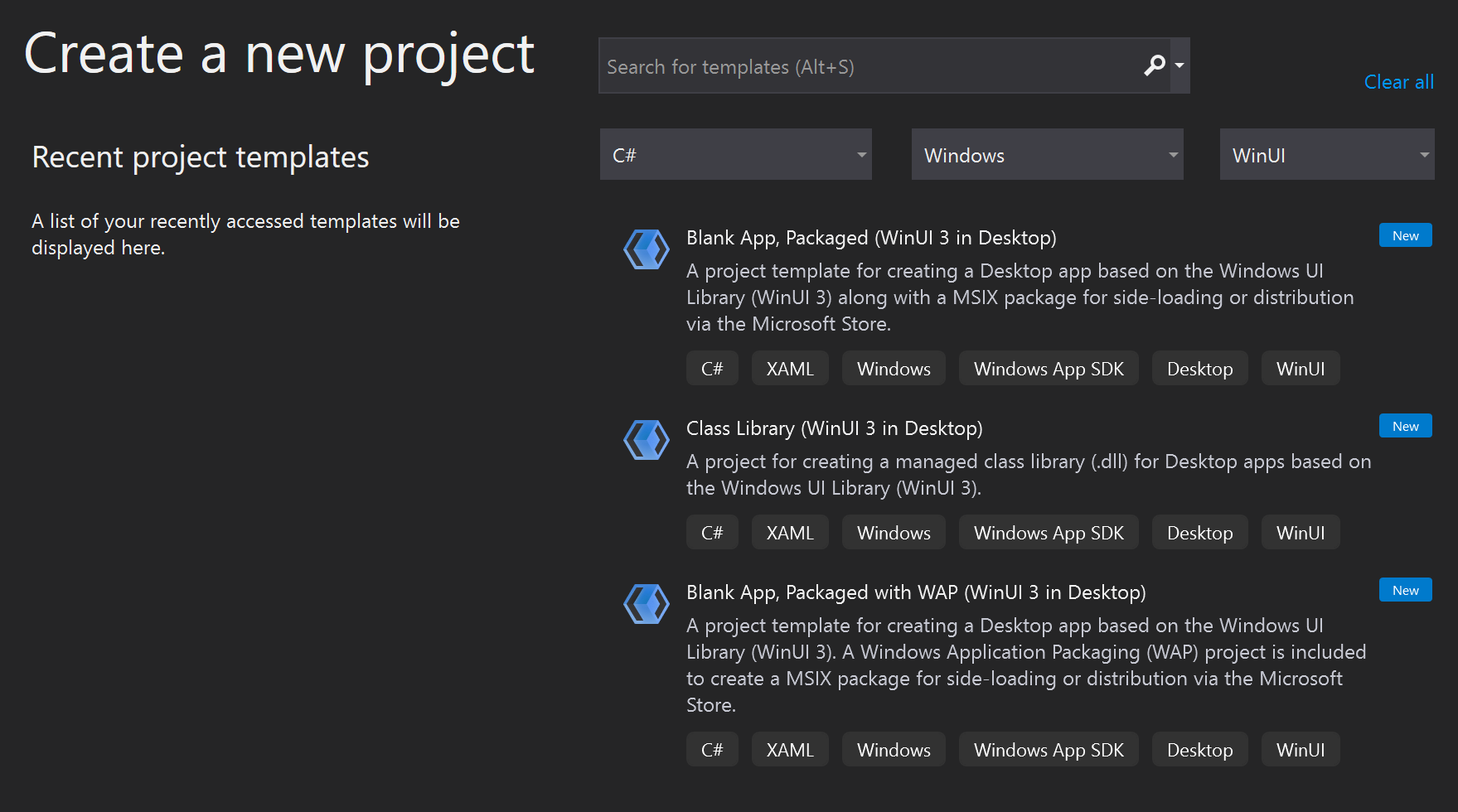
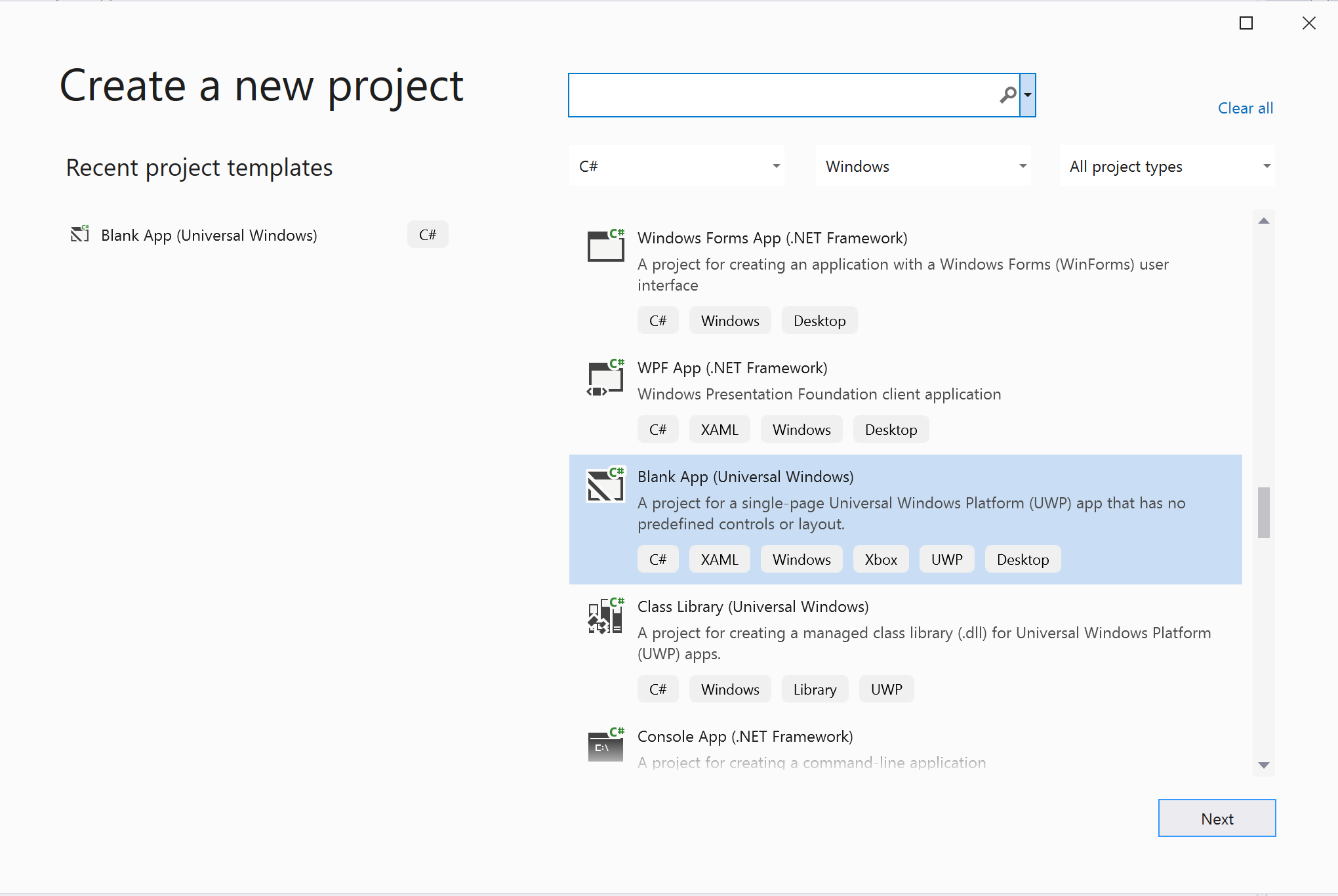
Creating the project
In Visual Studio, create a new project with the Blank App (Universal Windows) template to set up a single-page Universal Windows Platform (UWP) app.
Install the package
Right select your project and go to Manage Nuget Packages to install Azure.Communication.Calling.WindowsClient 1.4.0 or superior. Make sure Include Prerelease is checked if you want to see the versions for public preview.
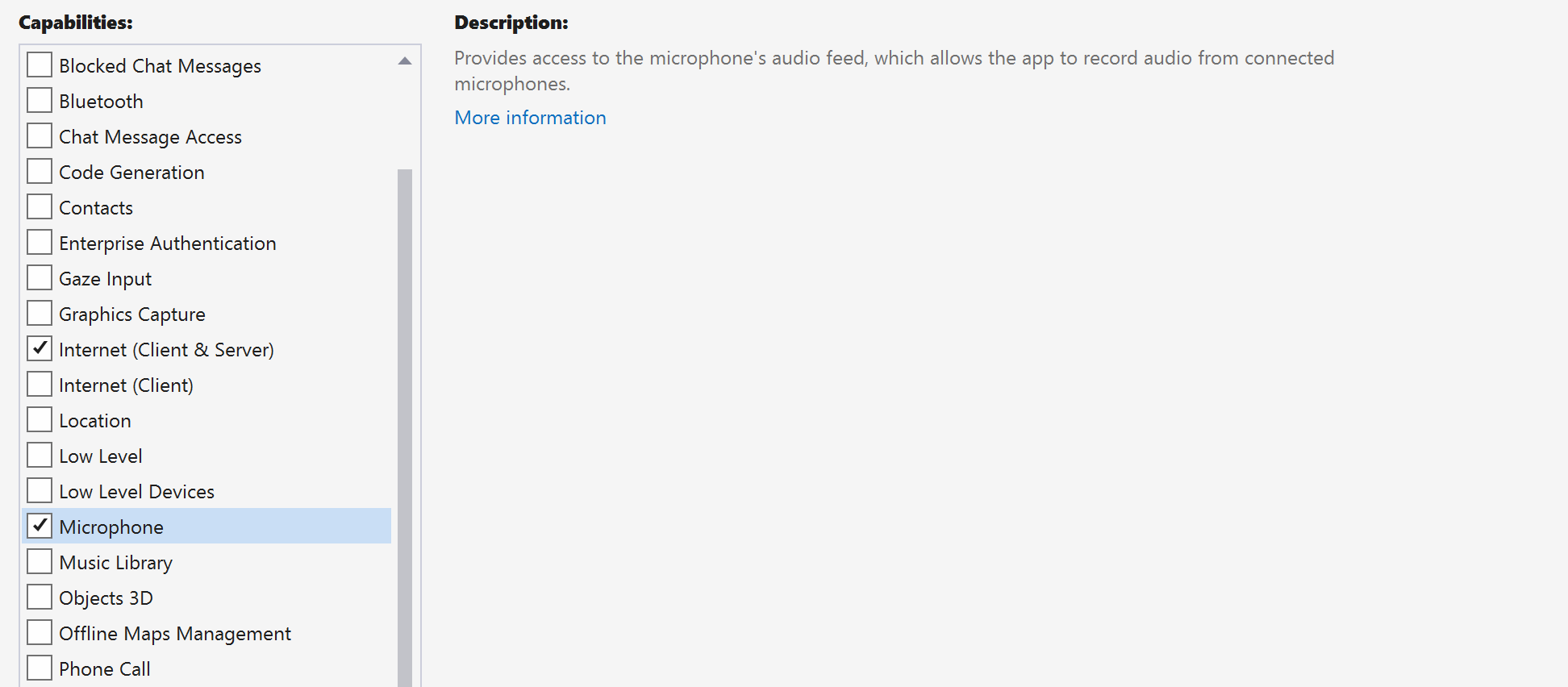
Request access
Go to Package.appxmanifest and select Capabilities.
Check Internet (Client) and Internet (Client & Server) to gain inbound and outbound access to the Internet. Check Microphone to access the audio feed of the microphone, and Webcam to access the video feed of the camera.
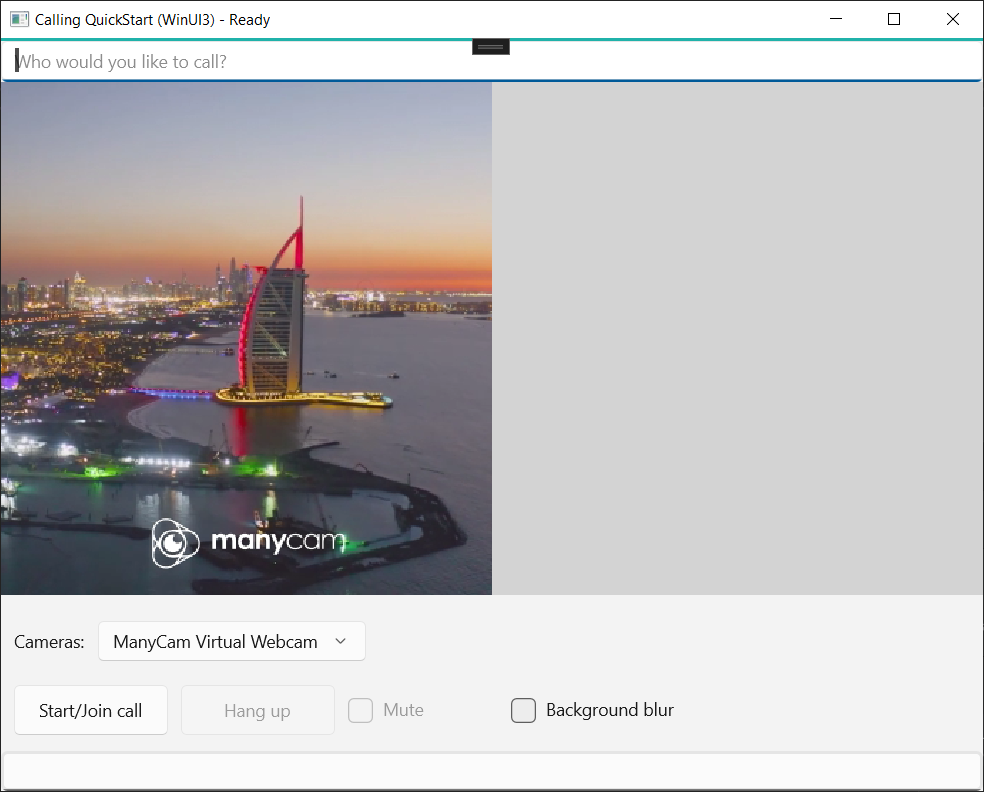
Set up the app framework
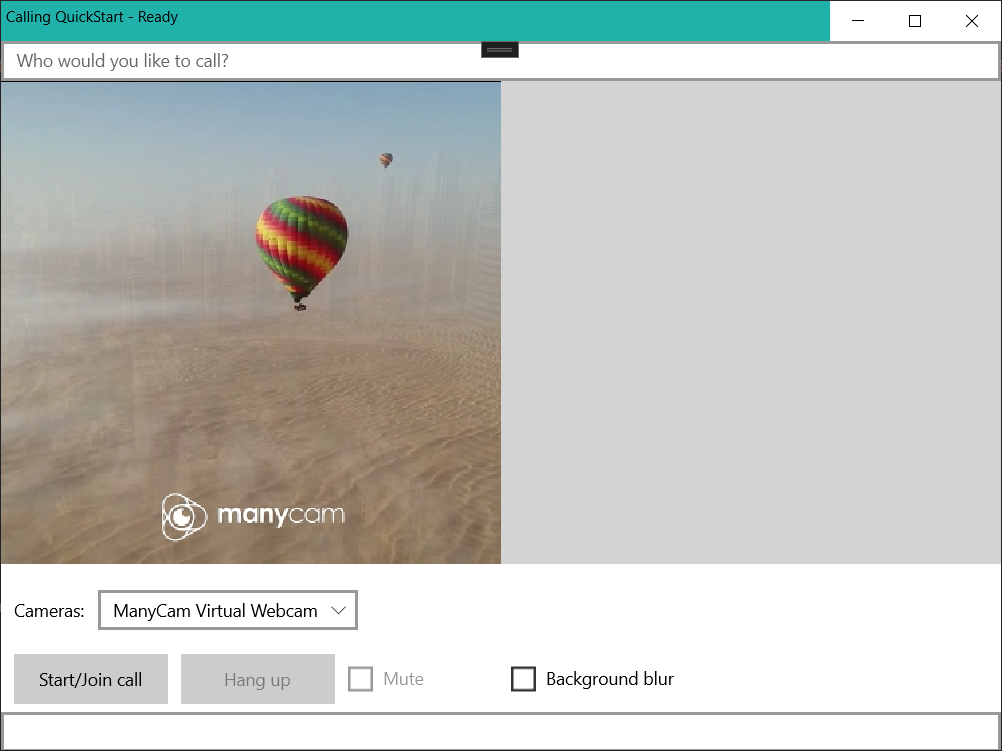
We need to configure a basic layout to attach our logic. In order to place an outbound call, we need a TextBox to provide the User ID of the callee. We also need a Start/Join call button and a Hang up button. A Mute and a BackgroundBlur checkboxes are also included in this sample to demonstrate the features of toggling audio states and video effects.
Open the MainPage.xaml of your project and add the Grid node to your Page:
<Page
x:Class="CallingQuickstart.MainPage"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:local="using:CallingQuickstart"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Background="{ThemeResource ApplicationPageBackgroundThemeBrush}" Width="800" Height="600">
<!-- Don't forget to replace ‘CallingQuickstart’ with your project’s name -->
<Grid>
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition Height="16*"/>
<RowDefinition Height="30*"/>
<RowDefinition Height="200*"/>
<RowDefinition Height="60*"/>
<RowDefinition Height="16*"/>
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<TextBox Grid.Row="1" x:Name="CalleeTextBox" PlaceholderText="Who would you like to call?" TextWrapping="Wrap" VerticalAlignment="Center" Height="30" Margin="10,10,10,10" />
<Grid x:Name="AppTitleBar" Background="LightSeaGreen">
<TextBlock x:Name="QuickstartTitle" Text="Calling Quickstart sample title bar" Style="{StaticResource CaptionTextBlockStyle}" Padding="7,7,0,0"/>
</Grid>
<Grid Grid.Row="2">
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition/>
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<ColumnDefinition Width="*"/>
<ColumnDefinition Width="*"/>
</Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<MediaPlayerElement x:Name="LocalVideo" HorizontalAlignment="Center" Stretch="UniformToFill" Grid.Column="0" VerticalAlignment="Center" AutoPlay="True" />
<MediaPlayerElement x:Name="RemoteVideo" HorizontalAlignment="Center" Stretch="UniformToFill" Grid.Column="1" VerticalAlignment="Center" AutoPlay="True" />
</Grid>
<StackPanel Grid.Row="3" Orientation="Vertical" Grid.RowSpan="2">
<StackPanel Orientation="Horizontal">
<Button x:Name="CallButton" Content="Start/Join call" Click="CallButton_Click" VerticalAlignment="Center" Margin="10,0,0,0" Height="40" Width="123"/>
<Button x:Name="HangupButton" Content="Hang up" Click="HangupButton_Click" VerticalAlignment="Center" Margin="10,0,0,0" Height="40" Width="123"/>
<CheckBox x:Name="MuteLocal" Content="Mute" Margin="10,0,0,0" Click="MuteLocal_Click" Width="74"/>
</StackPanel>
</StackPanel>
<TextBox Grid.Row="5" x:Name="Stats" Text="" TextWrapping="Wrap" VerticalAlignment="Center" Height="30" Margin="0,2,0,0" BorderThickness="2" IsReadOnly="True" Foreground="LightSlateGray" />
</Grid>
</Page>
Open the MainPage.xaml.cs and replace the content with following implementation:
using Azure.Communication.Calling.WindowsClient;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Windows.ApplicationModel;
using Windows.ApplicationModel.Core;
using Windows.Media.Core;
using Windows.Networking.PushNotifications;
using Windows.UI;
using Windows.UI.ViewManagement;
using Windows.UI.Xaml;
using Windows.UI.Xaml.Controls;
using Windows.UI.Xaml.Media;
using Windows.UI.Xaml.Navigation;
namespace CallingQuickstart
{
public sealed partial class MainPage : Page
{
private const string authToken = "<AUTHENTICATION_TOKEN>";
private CallClient callClient;
private CallTokenRefreshOptions callTokenRefreshOptions = new CallTokenRefreshOptions(false);
private CallAgent callAgent;
private CommunicationCall call;
private LocalOutgoingAudioStream micStream;
#region Page initialization
public MainPage()
{
this.InitializeComponent();
// Additional UI customization code goes here
}
protected override async void OnNavigatedTo(NavigationEventArgs e)
{
await InitCallAgentAndDeviceManagerAsync();
base.OnNavigatedTo(e);
}
#endregion
#region UI event handlers
private async void CallButton_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
// Start a call
}
private async void HangupButton_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
// Hang up a call
}
private async void MuteLocal_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
// Toggle mute/unmute audio state of a call
}
#endregion
#region API event handlers
private async void OnIncomingCallAsync(object sender, IncomingCallReceivedEventArgs args)
{
// Handle incoming call event
}
private async void OnStateChangedAsync(object sender, PropertyChangedEventArgs args)
{
// Handle connected and disconnected state change of a call
}
#endregion
#region Helper methods
private async Task InitCallAgentAndDeviceManagerAsync()
{
//Initialize the call agent and search for devices
}
private async Task<CommunicationCall> StartCallAsync(string acsCallee)
{
// Start a call to an Azure Communication Services user using the CallAgent and the callee id
}
#endregion
}
}
Object model
The next table listed the classes and interfaces handle some of the major features of the Azure Communication Services Calling SDK:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
CallClient |
The CallClient is the main entry point to the Calling SDK. |
CallAgent |
The CallAgent is used to start and manage calls. |
CommunicationCall |
The CommunicationCall is used to manage an ongoing call. |
CallTokenCredential |
The CallTokenCredential is used as the token credential to instantiate the CallAgent. |
CallIdentifier |
The CallIdentifier is used to represent the identity of the user, which can be one of the following options: UserCallIdentifier, PhoneNumberCallIdentifier etc. |
Authenticate the client
Initialize a CallAgent instance with a User Access Token that enables us to make and receive calls, and optionally obtain a DeviceManager instance to query for client device configurations.
In the code, replace <AUTHENTICATION_TOKEN> with a User Access Token. Refer to the user access token documentation if you don't already have a token available.
Add InitCallAgentAndDeviceManagerAsync function, which bootstraps the SDK. This helper can be customized to meet the requirements of your application.
private async Task InitCallAgentAndDeviceManagerAsync()
{
this.callClient = new CallClient(new CallClientOptions() {
Diagnostics = new CallDiagnosticsOptions() {
// make sure to put your project AppName
AppName = "CallingQuickstart",
AppVersion="1.0",
Tags = new[] { "Calling", "ACS", "Windows" }
}
});
// Set up local audio stream using the first mic enumerated
var deviceManager = await this.callClient.GetDeviceManagerAsync();
var mic = deviceManager?.Microphones?.FirstOrDefault();
micStream = new LocalOutgoingAudioStream();
var tokenCredential = new CallTokenCredential(authToken, callTokenRefreshOptions);
var callAgentOptions = new CallAgentOptions()
{
DisplayName = $"{Environment.MachineName}/{Environment.UserName}",
};
this.callAgent = await this.callClient.CreateCallAgentAsync(tokenCredential, callAgentOptions);
this.callAgent.IncomingCallReceived += OnIncomingCallAsync;
}
Start the call
Once a StartCallOptions object is obtained, CallAgent can be used to initiate the Azure Communication Services call:
private async Task<CommunicationCall> StartCallAsync(string acsCallee)
{
var options = new StartCallOptions();
var call = await this.callAgent.StartCallAsync( new [] { new UserCallIdentifier(acsCallee) }, options);
return call;
}
End a call
End the current call when the Hang up button is clicked. Add the implementation to the HangupButton_Click to end a call, and stop the preview and video streams.
private async void HangupButton_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
var call = this.callAgent?.Calls?.FirstOrDefault();
if (call != null)
{
await call.HangUpAsync(new HangUpOptions() { ForEveryone = false });
}
}
Toggle mute/unmute on audio
Mute the outgoing audio when the Mute button is clicked. Add the implementation to the MuteLocal_Click to mute the call.
private async void MuteLocal_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
var muteCheckbox = sender as CheckBox;
if (muteCheckbox != null)
{
var call = this.callAgent?.Calls?.FirstOrDefault();
if (call != null)
{
if ((bool)muteCheckbox.IsChecked)
{
await call.MuteOutgoingAudioAsync();
}
else
{
await call.UnmuteOutgoingAudioAsync();
}
}
// Update the UI to reflect the state
}
}
Accept an incoming call
IncomingCallReceived event sink is set up in the SDK bootstrap helper InitCallAgentAndDeviceManagerAsync.
this.callAgent.IncomingCallReceived += OnIncomingCallAsync;
Application has an opportunity to configure how the incoming call should be accepted, such as video and audio stream kinds.
private async void OnIncomingCallAsync(object sender, IncomingCallReceivedEventArgs args)
{
var incomingCall = args.IncomingCall;
var acceptCallOptions = new AcceptCallOptions() { };
call = await incomingCall.AcceptAsync(acceptCallOptions);
call.StateChanged += OnStateChangedAsync;
}
Monitor and response to call state change event
StateChanged event on CommunicationCall object is fired when an in progress call transactions from one state to another. Application is offered the opportunities to reflect the state changes on UI or insert business logics.
private async void OnStateChangedAsync(object sender, PropertyChangedEventArgs args)
{
var call = sender as CommunicationCall;
if (call != null)
{
var state = call.State;
// Update the UI
switch (state)
{
case CallState.Connected:
{
await call.StartAudioAsync(micStream);
break;
}
case CallState.Disconnected:
{
call.StateChanged -= OnStateChangedAsync;
call.Dispose();
break;
}
default: break;
}
}
}
Make call button work
Once the Callee ID isn't null or empty, you can start a call.
The call state must be changed using the OnStateChangedAsync action.
private async void CallButton_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
var callString = CalleeTextBox.Text.Trim();
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(callString))
{
call = await StartCallAsync(callString);
call.StateChanged += OnStateChangedAsync;
}
}
Run the code
You can build and run the code on Visual Studio. For solution platforms, we support ARM64, x64, and x86.
You can make an outbound call by providing a user ID in the text field and clicking the Start Call/Join button. Calling 8:echo123 connects you with an echo bot, this feature is great for getting started and verifying your audio devices are working.
In this quickstart, you learn how to start a call using the Azure Communication Services Calling SDK for JavaScript.
Sample code
You can download the sample app from GitHub.
Note
Outbound calling to an Azure Communication Services user can be accessed using the Azure Communication Services UI Library. The UI Library enables developers to add a call client that is VoIP enabled into their application with only a couple lines of code.
Prerequisites
An Azure account with an active subscription. Create an account for free.
You need to have Node.js 18. You can use the msi installer to install it.
An active Communication Services resource. Create a Communication Services resource. You need to record your connection string for this quickstart.
A User Access Token to instantiate the call client. Learn how to create and manage user access tokens. You can also use the Azure CLI and run the command with your connection string to create a user and an access token.
az communication identity token issue --scope voip --connection-string "yourConnectionString"For details, see Use Azure CLI to Create and Manage Access Tokens.
Setting up
Create a new Node.js application
Open your terminal or command window create a new directory for your app, and navigate to it.
mkdir calling-quickstart
cd calling-quickstart
Run npm init -y to create a package.json file with default settings.
npm init -y
Install the package
Use the npm install command to install the Azure Communication Services Calling SDK for JavaScript.
npm install @azure/communication-common --save
npm install @azure/communication-calling --save
The --save option lists the library as a dependency in your package.json file.
Set up the app framework
This quickstart uses Webpack to bundle the application assets. Run the following command to install the webpack, webpack-cli and webpack-dev-server npm packages and list them as development dependencies in your package.json:
npm install copy-webpack-plugin@^11.0.0 webpack@^5.88.2 webpack-cli@^5.1.4 webpack-dev-server@^4.15.1 --save-dev
Here's the html, that we need to add to the index.html file that we created:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Communication Client - Calling Sample</title>
</head>
<body>
<h4>Azure Communication Services</h4>
<h1>Calling Quickstart</h1>
<input
id="token-input"
type="text"
placeholder="User access token"
style="margin-bottom:1em; width: 200px;"
/>
</div>
<button id="token-submit" type="button">
Submit
</button>
<input
id="callee-id-input"
type="text"
placeholder="Who would you like to call?"
style="margin-bottom:1em; width: 200px; display: block;"
/>
<div>
<button id="call-button" type="button" disabled="true">
Start Call
</button>
<button id="accept-call-button" type="button" disabled="true">
Accept Call
</button>
<button id="hang-up-button" type="button" disabled="true">
Hang Up
</button>
</div>
<script src="./main.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
Create a file in the root directory of your project called index.js to contain the application logic for this quickstart. Add the following code to import the calling client and get references to the DOM elements so we can attach our business logic.
import { CallClient } from "@azure/communication-calling";
import { AzureCommunicationTokenCredential } from '@azure/communication-common';
let call;
let incomingCall;
let callAgent;
let deviceManager;
let tokenCredential;
const userToken = document.getElementById("token-input");
const calleeInput = document.getElementById("callee-id-input");
const submitToken = document.getElementById("token-submit");
const callButton = document.getElementById("call-button");
const hangUpButton = document.getElementById("hang-up-button");
const acceptCallButton = document.getElementById('accept-call-button');
Object model
The following classes and interfaces handle some of the major features of the Azure Communication Services Calling SDK:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
CallClient |
The CallClient is the main entry point to the Calling SDK. |
CallAgent |
The CallAgent is used to start and manage calls. |
AzureCommunicationTokenCredential |
The AzureCommunicationTokenCredential class implements the CommunicationTokenCredential interface, which is used to instantiate the CallAgent. |
Authenticate the client
You need to input a valid user access token for your resource into the text field and click 'Submit'. Refer to the user access token documentation if you don't already have a token available. Using the CallClient, initialize a CallAgent instance with a CommunicationTokenCredential that enables to make and receive calls.
Add the following code to app.js:
submitToken.addEventListener("click", async () => {
const callClient = new CallClient();
const userTokenCredential = userToken.value;
try {
tokenCredential = new AzureCommunicationTokenCredential(userTokenCredential);
callAgent = await callClient.createCallAgent(tokenCredential);
deviceManager = await callClient.getDeviceManager();
await deviceManager.askDevicePermission({ audio: true });
callButton.disabled = false;
submitToken.disabled = true;
// Listen for an incoming call to accept.
callAgent.on('incomingCall', async (args) => {
try {
incomingCall = args.incomingCall;
acceptCallButton.disabled = false;
callButton.disabled = true;
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
}
});
} catch(error) {
window.alert("Please submit a valid token!");
}
})
Start a call
Add an event handler to initiate a call when the callButton is clicked:
callButton.addEventListener("click", () => {
// start a call
const userToCall = calleeInput.value;
call = callAgent.startCall(
[{ id: userToCall }],
{}
);
// toggle button states
hangUpButton.disabled = false;
callButton.disabled = true;
});
End a call
Add an event listener to end the current call when the hangUpButton is clicked:
hangUpButton.addEventListener("click", () => {
// end the current call
// The `forEveryone` property ends the call for all call participants.
call.hangUp({ forEveryone: true });
// toggle button states
hangUpButton.disabled = true;
callButton.disabled = false;
submitToken.disabled = false;
acceptCallButton.disabled = true;
});
Accept an incoming call
Add an event listener to accept an incoming call to the acceptCallButton
acceptCallButton.onclick = async () => {
try {
call = await incomingCall.accept();
acceptCallButton.disabled = true;
hangUpButton.disabled = false;
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
}
}
Add the webpack local server code
Create a file in the root directory of your project called webpack.config.js to contain the local server logic for this quickstart. Add the following code to webpack.config.js:
const path = require('path');
const CopyPlugin = require("copy-webpack-plugin");
module.exports = {
mode: 'development',
entry: './index.js',
output: {
filename: 'main.js',
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist'),
},
devServer: {
static: {
directory: path.join(__dirname, './')
},
},
plugins: [
new CopyPlugin({
patterns: [
'./index.html'
]
}),
]
};
Run the code
Use the command npx webpack serve --config webpack.config.js to run your application.
Open your browser and navigate to http://localhost:8080/. You should see the following screen:
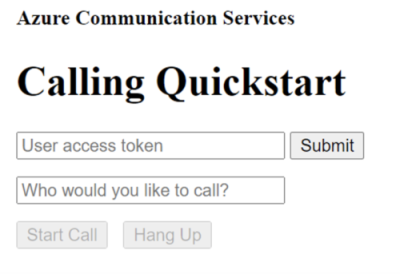
You can make an outbound VOIP call by providing a valid user access token and user ID in the corresponding text fields and clicking the Start Call button.
Calling 8:echo123 connects you with an echo bot, which is great for getting started and verifying your audio devices are working. Pass {id: '8:echo123'} to the CallAgent.startCall() API to call echo bot.
To call an Azure Communication Services communication user, pass {communicationUserId: 'ACS_USER_ID'} to the CallAgent.startCall() API.
In this quickstart, you learn how to start a call using the Azure Communication Services Calling SDK for Android.
Sample Code
You can download the sample app from GitHub.
Prerequisites
An Azure account with an active subscription. Create an account for free.
Android Studio, for creating your Android application.
A deployed Communication Services resource. Create a Communication Services resource. You need to record your connection string for this quickstart.
A User Access Token for your Azure Communication Service. You can also use the Azure CLI and run the command with your connection string to create a user and an access token.
az communication identity token issue --scope voip --connection-string "yourConnectionString"For details, see Use Azure CLI to Create and Manage Access Tokens.
Setting up
Create an Android app with an empty activity
From Android Studio, select Start a new Android Studio project.
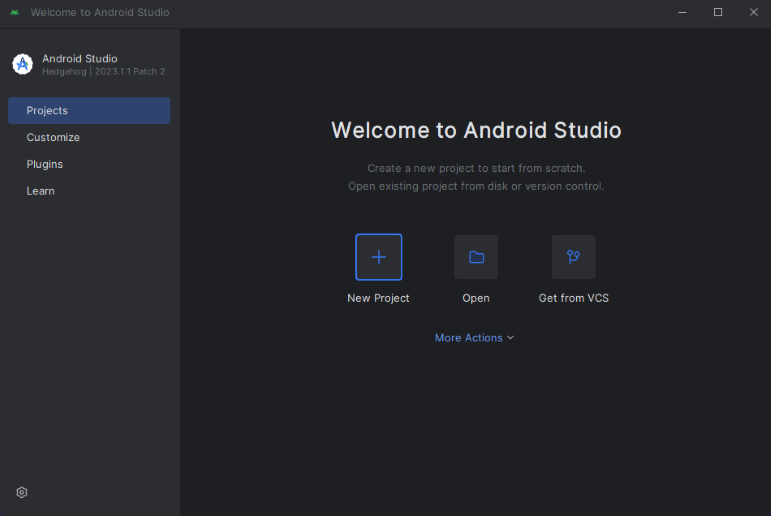
Select "Empty Views Activity" project template under "Phone and Tablet".
Select Minimum SDK of "API 26: Android 8.0 (Oreo)" or greater.

Install the package
Locate your project settings.gradle.kts and make sure to see mavenCentral() at the list of repositories under pluginManagement and dependencyResolutionManagement
pluginManagement {
repositories {
...
mavenCentral()
...
}
}
dependencyResolutionManagement {
repositoriesMode.set(RepositoriesMode.FAIL_ON_PROJECT_REPOS)
repositories {
...
mavenCentral()
}
}
Then, in your module level build.gradle add the following lines to the dependencies and android sections
android {
...
compileOptions {
sourceCompatibility JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8
targetCompatibility JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8
}
}
dependencies {
...
implementation ("com.azure.android:azure-communication-calling:2.6.0")
...
}
Add permissions to application manifest
In order to request permissions required to make a call, they must be declared in the Application Manifest (app/src/main/AndroidManifest.xml). Replace the content of file with the following code:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.contoso.acsquickstart">
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_WIFI_STATE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.RECORD_AUDIO" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.CAMERA" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_PHONE_STATE" />
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme">
<!--Our Calling SDK depends on the Apache HTTP SDK.
When targeting Android SDK 28+, this library needs to be explicitly referenced.
See https://developer.android.com/about/versions/pie/android-9.0-changes-28#apache-p-->
<uses-library android:name="org.apache.http.legacy" android:required="false"/>
<activity android:name=".MainActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>
Set up the layout for the app
Two inputs are needed: a text input for the callee ID, and a button for placing the call. These inputs can be added through the designer or by editing the layout xml. Create a button with an ID of call_button and a text input of callee_id. Navigate to (app/src/main/res/layout/activity_main.xml) and replace the content of file with the following code:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<Button
android:id="@+id/call_button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginBottom="16dp"
android:text="Call"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/callee_id"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:ems="10"
android:hint="Callee Id"
android:inputType="textPersonName"
android:minHeight="48dp"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toTopOf="@+id/call_button"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
Create the main activity scaffolding and bindings
With the layout created the bindings can be added as well as the basic scaffolding of the activity. The activity handles requesting runtime permissions, creating the call agent, and placing the call when the button is press ed. Each is covered in its own section. The onCreate method is overridden to invoke getAllPermissions and createAgent and to add the bindings for the call button. This event occurs only once when the activity is created. For more information, on onCreate, see the guide Understand the Activity Lifecycle.
Navigate to MainActivity.java and replace the content with the following code:
package com.contoso.acsquickstart;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import androidx.core.app.ActivityCompat;
import android.media.AudioManager;
import android.Manifest;
import android.content.pm.PackageManager;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.Toast;
import com.azure.android.communication.common.CommunicationUserIdentifier;
import com.azure.android.communication.common.CommunicationTokenCredential;
import com.azure.android.communication.calling.CallAgent;
import com.azure.android.communication.calling.CallClient;
import com.azure.android.communication.calling.StartCallOptions;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private CallAgent callAgent;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
getAllPermissions();
createAgent();
// Bind call button to call `startCall`
Button callButton = findViewById(R.id.call_button);
callButton.setOnClickListener(l -> startCall());
setVolumeControlStream(AudioManager.STREAM_VOICE_CALL);
}
/**
* Request each required permission if the app doesn't already have it.
*/
private void getAllPermissions() {
// See section on requesting permissions
}
/**
* Create the call agent for placing calls
*/
private void createAgent() {
// See section on creating the call agent
}
/**
* Place a call to the callee id provided in `callee_id` text input.
*/
private void startCall() {
// See section on starting the call
}
}
Request permissions at runtime
For Android 6.0 and higher (API level 23) and targetSdkVersion 23 or higher, permissions are granted at runtime instead of when the app is installed. In order to support it, getAllPermissions can be implemented to call ActivityCompat.checkSelfPermission and ActivityCompat.requestPermissions for each required permission.
/**
* Request each required permission if the app doesn't already have it.
*/
private void getAllPermissions() {
String[] requiredPermissions = new String[]{android.Manifest.permission.RECORD_AUDIO, android.Manifest.permission.CAMERA, android.Manifest.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE, Manifest.permission.READ_PHONE_STATE};
ArrayList<String> permissionsToAskFor = new ArrayList<>();
for (String permission : requiredPermissions) {
if (ActivityCompat.checkSelfPermission(this, permission) != PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED) {
permissionsToAskFor.add(permission);
}
}
if (!permissionsToAskFor.isEmpty()) {
ActivityCompat.requestPermissions(this, permissionsToAskFor.toArray(new String[0]), 1);
}
}
Note
When designing your app, consider when these permissions should be requested. Permissions should be requested as they are needed, not ahead of time. For more information, see, the Android Permissions Guide.
Object model
The following classes and interfaces handle some of the major features of the Azure Communication Services Calling SDK:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
allClient |
The CallClient is the main entry point to the Calling SDK. |
CallAgent |
The CallAgent is used to start and manage calls. |
CommunicationTokenCredential |
The CommunicationTokenCredential is used as the token credential to instantiate the CallAgent. |
CommunicationIdentifier |
The CommunicationIdentifier is used as different type of participant that could be part of a call. |
Create an agent from the user access token
With a user token, an authenticated call agent can be instantiated. Generally this token is generated from a service with authentication specific to the application. For more information on user access tokens, check the User Access Tokens guide.
For the quickstart, replace <User_Access_Token> with a user access token generated for your Azure Communication Service resource.
/**
* Create the call agent for placing calls
*/
private void createAgent() {
String userToken = "<User_Access_Token>";
try {
CommunicationTokenCredential credential = new CommunicationTokenCredential(userToken);
callAgent = new CallClient().createCallAgent(getApplicationContext(), credential).get();
} catch (Exception ex) {
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "Failed to create call agent.", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
Start a call using the call agent
Placing the call can be done via the call agent, and just requires providing a list of callee IDs and the call options. For the quickstart, the default call options without video and a single callee ID from the text input are used.
/**
* Place a call to the callee id provided in `callee_id` text input.
*/
private void startCall() {
EditText calleeIdView = findViewById(R.id.callee_id);
String calleeId = calleeIdView.getText().toString();
StartCallOptions options = new StartCallOptions();
callAgent.startCall(
getApplicationContext(),
Arrays.asList(new CommunicationUserIdentifier[]{new CommunicationUserIdentifier(calleeId)}),
options);
}
Launch the app and call the echo bot
The app can now be launched using the "Run App" button on the toolbar (Shift+F10). Verify you're able to place calls by calling 8:echo123. A pre-recorded message plays then repeat your message back to you.

In this quickstart, you learn how to start a call using the Azure Communication Services Calling SDK for iOS.
Sample Code
You can download the sample app from GitHub.
Prerequisites
To complete this tutorial, you need the following prerequisites:
An Azure account with an active subscription. Create an account for free.
A Mac running Xcode, along with a valid developer certificate installed into your Keychain.
A deployed Communication Services resource. Create a Communication Services resource. You need to record your connection string for this quickstart.
A User Access Token for your Azure Communication Service. You can also use the Azure CLI and run the command with your connection string to create a user and an access token.
az communication identity token issue --scope voip --connection-string "yourConnectionString"For details, see Use Azure CLI to Create and Manage Access Tokens.
Setting up
Creating the Xcode project
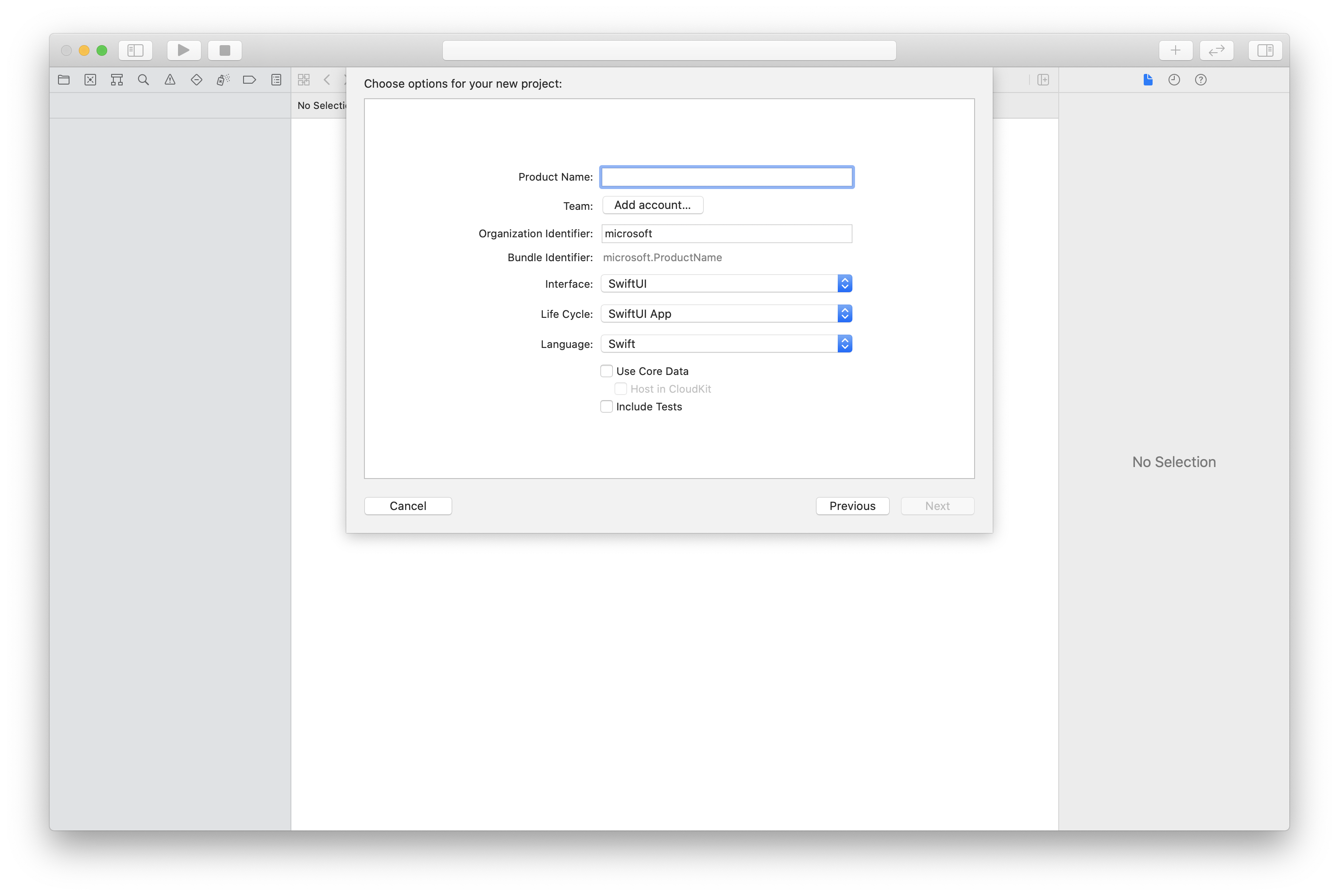
In Xcode, create a new iOS project and select the App template. This tutorial uses the SwiftUI framework, so you should set the Language to Swift and the User Interface to SwiftUI. You're not going to create tests during this quick start. Feel free to uncheck Include Tests.
Install the package and dependencies with CocoaPods
To create a Podfile for your application, open the terminal and navigate to the project folder and run:
pod initAdd the following code to the Podfile and save (make sure that "target" matches the name of your project):
platform :ios, '13.0' use_frameworks! target 'AzureCommunicationCallingSample' do pod 'AzureCommunicationCalling', '~> 1.0.0' endRun
pod install.Open the
.xcworkspacewith Xcode.
Request access to the microphone
In order to access the device's microphone, you need to update your app's Information Property List with an NSMicrophoneUsageDescription. You set the associated value to a string that was included in the dialog the system uses to request access from the user.
Right-click the Info.plist entry of the project tree and select Open As > Source Code. Add the following lines the top level <dict> section, and then save the file.
<key>NSMicrophoneUsageDescription</key>
<string>Need microphone access for VOIP calling.</string>
Set up the app framework
Open your project's ContentView.swift file and add an import declaration to the top of the file to import the AzureCommunicationCalling library. In addition, import AVFoundation, we need this code for audio permission request in the code.
import AzureCommunicationCalling
import AVFoundation
Replace the implementation of the ContentView struct with some simple UI controls that enable a user to initiate and end a call. We attach business logic to these controls in this quickstart.
struct ContentView: View {
@State var callee: String = ""
@State var callClient: CallClient?
@State var callAgent: CallAgent?
@State var call: Call?
var body: some View {
NavigationView {
Form {
Section {
TextField("Who would you like to call?", text: $callee)
Button(action: startCall) {
Text("Start Call")
}.disabled(callAgent == nil)
Button(action: endCall) {
Text("End Call")
}.disabled(call == nil)
}
}
.navigationBarTitle("Calling Quickstart")
}.onAppear {
// Initialize call agent
}
}
func startCall() {
// Ask permissions
AVAudioSession.sharedInstance().requestRecordPermission { (granted) in
if granted {
// Add start call logic
}
}
}
func endCall() {
// Add end call logic
}
}
Object model
The following classes and interfaces handle some of the major features of the Azure Communication Services Calling SDK:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
CallClient |
The CallClient is the main entry point to the Calling SDK. |
CallAgent |
The CallAgent is used to start and manage calls. |
CommunicationTokenCredential |
The CommunicationTokenCredential is used as the token credential to instantiate the CallAgent. |
CommunicationUserIdentifier |
The CommunicationUserIdentifier is used to represent the identity of the user, which can be one of the following options: CommunicationUserIdentifier,PhoneNumberIdentifier or CallingApplication. |
Authenticate the client
Initialize a CallAgent instance with a User Access Token, which enables us to make and receive calls.
In the following code, you need to replace <USER ACCESS TOKEN> with a valid user access token for your resource. Refer to the user access token documentation if you don't already have a token available.
Add the following code to the onAppear callback in ContentView.swift:
var userCredential: CommunicationTokenCredential?
do {
userCredential = try CommunicationTokenCredential(token: "<USER ACCESS TOKEN>")
} catch {
print("ERROR: It was not possible to create user credential.")
return
}
self.callClient = CallClient()
// Creates the call agent
self.callClient?.createCallAgent(userCredential: userCredential!) { (agent, error) in
if error != nil {
print("ERROR: It was not possible to create a call agent.")
return
}
else {
self.callAgent = agent
print("Call agent successfully created.")
}
}
Start a call
The startCall method is set as the action that is performed when the Start Call button is tapped. Update the implementation to start a call with the ASACallAgent:
func startCall()
{
// Ask permissions
AVAudioSession.sharedInstance().requestRecordPermission { (granted) in
if granted {
// start call logic
let callees:[CommunicationIdentifier] = [CommunicationUserIdentifier(self.callee)]
self.callAgent?.startCall(participants: callees, options: StartCallOptions()) { (call, error) in
if (error == nil) {
self.call = call
} else {
print("Failed to get call object")
}
}
}
}
}
You also can use the properties in StartCallOptions to set the initial options for the call (that is, it allows starting the call with the microphone muted).
End a call
Implement the endCall method to end the current call when the End Call button is tapped.
func endCall()
{
self.call!.hangUp(options: HangUpOptions()) { (error) in
if (error != nil) {
print("ERROR: It was not possible to hangup the call.")
}
}
}
Run the code
You can build and run your app on iOS simulator by selecting Product > Run or by using the (⌘-R) keyboard shortcut.
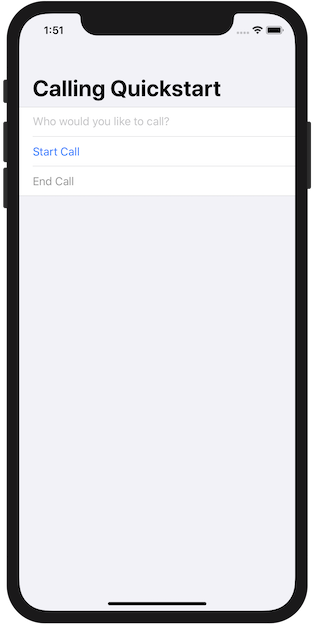
You can make an outbound VOIP call by providing a user ID in the text field and tapping the Start Call button. Calling 8:echo123 connects you with an echo bot, this feature is great for getting started and verifying your audio devices are working.
Note
The first time you make a call, the system will prompt you for access to the microphone. In a production application, you should use the AVAudioSession API to check the permission status and gracefully update your application's behavior when permission is not granted.
In this quickstart, you learn how to start a call using the Azure Communication Services Calling SDK for Unity.
You can download the sample app from GitHub.
Prerequisites
To complete this tutorial, you need the following prerequisites:
An Azure account with an active subscription. Create an account for free.
Install Unity Hub and Unity Editor with Universal Windows Platform development workload.
A deployed Communication Services resource. Create a Communication Services resource. You need to record your connection string for this quickstart.
A User Access Token for your Azure Communication Service. You can also use the Azure CLI and run the command with your connection string to create a user and an access token.
az communication identity token issue --scope voip --connection-string "yourConnectionString"For details, see Use Azure CLI to Create and Manage Access Tokens.
Setting up
Creating the project
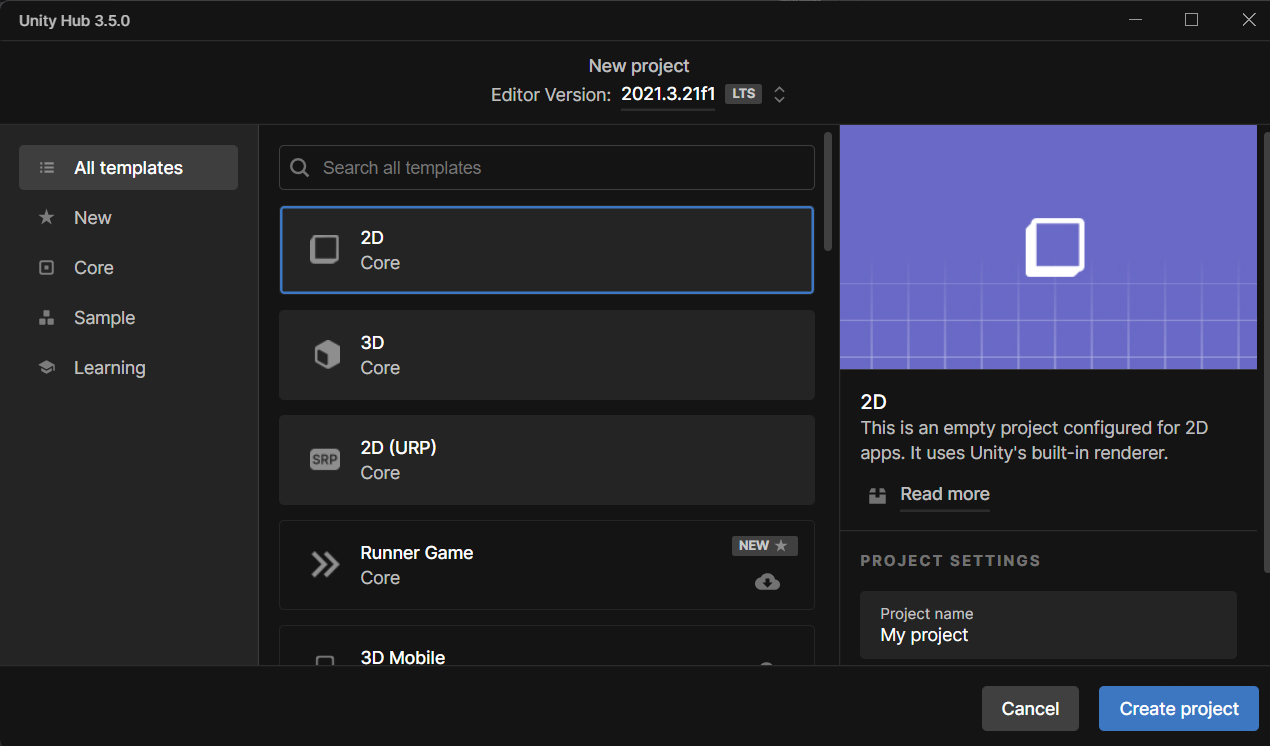
In Unity Hub, create a new project with the 2D Core template to set up the unity project.
Install the package
There are two ways to install the Azure Communication Calling SDK for Unity.
Download the SDK from the public npm feed and import it in Unity Editor's package manager, found under the Windows tab.
Download the Mixed Reality Feature Tool from Microsoft and install it via the mixed reality tool manager.
Set up the app framework
We need to configure a basic layout to attach our logic. In order to place an outbound call, we need a TextBox to provide the User ID of the callee. We also need a Start/Join call button and a Hang up button.
Create a new scene called Main in your project.
Open the Main.unity file and replace the content with following implementation:
Main.Unity Code
Main.unity
%YAML 1.1
%TAG !u! tag:unity3d.com,2011:
--- !u!29 &1
OcclusionCullingSettings:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
serializedVersion: 2
m_OcclusionBakeSettings:
smallestOccluder: 5
smallestHole: 0.25
backfaceThreshold: 100
m_SceneGUID: 00000000000000000000000000000000
m_OcclusionCullingData: {fileID: 0}
--- !u!104 &2
RenderSettings:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
serializedVersion: 9
m_Fog: 0
m_FogColor: {r: 0.5, g: 0.5, b: 0.5, a: 1}
m_FogMode: 3
m_FogDensity: 0.01
m_LinearFogStart: 0
m_LinearFogEnd: 300
m_AmbientSkyColor: {r: 0.212, g: 0.227, b: 0.259, a: 1}
m_AmbientEquatorColor: {r: 0.114, g: 0.125, b: 0.133, a: 1}
m_AmbientGroundColor: {r: 0.047, g: 0.043, b: 0.035, a: 1}
m_AmbientIntensity: 1
m_AmbientMode: 3
m_SubtractiveShadowColor: {r: 0.42, g: 0.478, b: 0.627, a: 1}
m_SkyboxMaterial: {fileID: 0}
m_HaloStrength: 0.5
m_FlareStrength: 1
m_FlareFadeSpeed: 3
m_HaloTexture: {fileID: 0}
m_SpotCookie: {fileID: 10001, guid: 0000000000000000e000000000000000, type: 0}
m_DefaultReflectionMode: 0
m_DefaultReflectionResolution: 128
m_ReflectionBounces: 1
m_ReflectionIntensity: 1
m_CustomReflection: {fileID: 0}
m_Sun: {fileID: 0}
m_IndirectSpecularColor: {r: 0, g: 0, b: 0, a: 1}
m_UseRadianceAmbientProbe: 0
--- !u!157 &3
LightmapSettings:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
serializedVersion: 12
m_GIWorkflowMode: 1
m_GISettings:
serializedVersion: 2
m_BounceScale: 1
m_IndirectOutputScale: 1
m_AlbedoBoost: 1
m_EnvironmentLightingMode: 0
m_EnableBakedLightmaps: 0
m_EnableRealtimeLightmaps: 0
m_LightmapEditorSettings:
serializedVersion: 12
m_Resolution: 2
m_BakeResolution: 40
m_AtlasSize: 1024
m_AO: 0
m_AOMaxDistance: 1
m_CompAOExponent: 1
m_CompAOExponentDirect: 0
m_ExtractAmbientOcclusion: 0
m_Padding: 2
m_LightmapParameters: {fileID: 0}
m_LightmapsBakeMode: 1
m_TextureCompression: 1
m_FinalGather: 0
m_FinalGatherFiltering: 1
m_FinalGatherRayCount: 256
m_ReflectionCompression: 2
m_MixedBakeMode: 2
m_BakeBackend: 0
m_PVRSampling: 1
m_PVRDirectSampleCount: 32
m_PVRSampleCount: 500
m_PVRBounces: 2
m_PVREnvironmentSampleCount: 500
m_PVREnvironmentReferencePointCount: 2048
m_PVRFilteringMode: 2
m_PVRDenoiserTypeDirect: 0
m_PVRDenoiserTypeIndirect: 0
m_PVRDenoiserTypeAO: 0
m_PVRFilterTypeDirect: 0
m_PVRFilterTypeIndirect: 0
m_PVRFilterTypeAO: 0
m_PVREnvironmentMIS: 0
m_PVRCulling: 1
m_PVRFilteringGaussRadiusDirect: 1
m_PVRFilteringGaussRadiusIndirect: 5
m_PVRFilteringGaussRadiusAO: 2
m_PVRFilteringAtrousPositionSigmaDirect: 0.5
m_PVRFilteringAtrousPositionSigmaIndirect: 2
m_PVRFilteringAtrousPositionSigmaAO: 1
m_ExportTrainingData: 0
m_TrainingDataDestination: TrainingData
m_LightProbeSampleCountMultiplier: 4
m_LightingDataAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_LightingSettings: {fileID: 0}
--- !u!196 &4
NavMeshSettings:
serializedVersion: 2
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_BuildSettings:
serializedVersion: 2
agentTypeID: 0
agentRadius: 0.5
agentHeight: 2
agentSlope: 45
agentClimb: 0.4
ledgeDropHeight: 0
maxJumpAcrossDistance: 0
minRegionArea: 2
manualCellSize: 0
cellSize: 0.16666667
manualTileSize: 0
tileSize: 256
accuratePlacement: 0
maxJobWorkers: 0
preserveTilesOutsideBounds: 0
debug:
m_Flags: 0
m_NavMeshData: {fileID: 0}
--- !u!1 &247756367
GameObject:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
serializedVersion: 6
m_Component:
- component: {fileID: 247756370}
- component: {fileID: 247756369}
- component: {fileID: 247756368}
m_Layer: 0
m_Name: EventSystem
m_TagString: Untagged
m_Icon: {fileID: 0}
m_NavMeshLayer: 0
m_StaticEditorFlags: 0
m_IsActive: 1
--- !u!114 &247756368
MonoBehaviour:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_GameObject: {fileID: 247756367}
m_Enabled: 1
m_EditorHideFlags: 0
m_Script: {fileID: 11500000, guid: 4f231c4fb786f3946a6b90b886c48677, type: 3}
m_Name:
m_EditorClassIdentifier:
m_SendPointerHoverToParent: 1
m_HorizontalAxis: Horizontal
m_VerticalAxis: Vertical
m_SubmitButton: Submit
m_CancelButton: Cancel
m_InputActionsPerSecond: 10
m_RepeatDelay: 0.5
m_ForceModuleActive: 0
--- !u!114 &247756369
MonoBehaviour:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_GameObject: {fileID: 247756367}
m_Enabled: 1
m_EditorHideFlags: 0
m_Script: {fileID: 11500000, guid: 76c392e42b5098c458856cdf6ecaaaa1, type: 3}
m_Name:
m_EditorClassIdentifier:
m_FirstSelected: {fileID: 0}
m_sendNavigationEvents: 1
m_DragThreshold: 10
--- !u!4 &247756370
Transform:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_GameObject: {fileID: 247756367}
m_LocalRotation: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0, w: 1}
m_LocalPosition: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0}
m_LocalScale: {x: 1, y: 1, z: 1}
m_ConstrainProportionsScale: 0
m_Children: []
m_Father: {fileID: 0}
m_RootOrder: 2
m_LocalEulerAnglesHint: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0}
--- !u!1 &293984669
GameObject:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
serializedVersion: 6
m_Component:
- component: {fileID: 293984671}
- component: {fileID: 293984670}
m_Layer: 0
m_Name: AppManager
m_TagString: Untagged
m_Icon: {fileID: 0}
m_NavMeshLayer: 0
m_StaticEditorFlags: 0
m_IsActive: 1
--- !u!114 &293984670
MonoBehaviour:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_GameObject: {fileID: 293984669}
m_Enabled: 1
m_EditorHideFlags: 0
m_Script: {fileID: 11500000, guid: 7c7d18b32fdb6b14e857ebb6d9627958, type: 3}
m_Name:
m_EditorClassIdentifier:
callStatus: {fileID: 1529611528}
videoPlayer: {fileID: 0}
--- !u!4 &293984671
Transform:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_GameObject: {fileID: 293984669}
m_LocalRotation: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0, w: 1}
m_LocalPosition: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0}
m_LocalScale: {x: 1, y: 1, z: 1}
m_ConstrainProportionsScale: 0
m_Children: []
m_Father: {fileID: 0}
m_RootOrder: 1
m_LocalEulerAnglesHint: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0}
--- !u!1 &438770860
GameObject:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
serializedVersion: 6
m_Component:
- component: {fileID: 438770861}
- component: {fileID: 438770863}
- component: {fileID: 438770862}
m_Layer: 5
m_Name: Text (TMP)
m_TagString: Untagged
m_Icon: {fileID: 0}
m_NavMeshLayer: 0
m_StaticEditorFlags: 0
m_IsActive: 1
--- !u!224 &438770861
RectTransform:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_GameObject: {fileID: 438770860}
m_LocalRotation: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0, w: 1}
m_LocalPosition: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0}
m_LocalScale: {x: 1, y: 1, z: 1}
m_ConstrainProportionsScale: 0
m_Children: []
m_Father: {fileID: 1732033234}
m_RootOrder: 0
m_LocalEulerAnglesHint: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0}
m_AnchorMin: {x: 0, y: 0}
m_AnchorMax: {x: 1, y: 1}
m_AnchoredPosition: {x: 0, y: 0}
m_SizeDelta: {x: 0, y: 0}
m_Pivot: {x: 0.5, y: 0.5}
--- !u!114 &438770862
MonoBehaviour:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_GameObject: {fileID: 438770860}
m_Enabled: 1
m_EditorHideFlags: 0
m_Script: {fileID: 11500000, guid: f4688fdb7df04437aeb418b961361dc5, type: 3}
m_Name:
m_EditorClassIdentifier:
m_Material: {fileID: 0}
m_Color: {r: 1, g: 1, b: 1, a: 1}
m_RaycastTarget: 1
m_RaycastPadding: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0, w: 0}
m_Maskable: 1
m_OnCullStateChanged:
m_PersistentCalls:
m_Calls: []
m_text: Start Call
m_isRightToLeft: 0
m_fontAsset: {fileID: 11400000, guid: 8f586378b4e144a9851e7b34d9b748ee, type: 2}
m_sharedMaterial: {fileID: 2180264, guid: 8f586378b4e144a9851e7b34d9b748ee, type: 2}
m_fontSharedMaterials: []
m_fontMaterial: {fileID: 0}
m_fontMaterials: []
m_fontColor32:
serializedVersion: 2
rgba: 4281479730
m_fontColor: {r: 0.19607843, g: 0.19607843, b: 0.19607843, a: 1}
m_enableVertexGradient: 0
m_colorMode: 3
m_fontColorGradient:
topLeft: {r: 1, g: 1, b: 1, a: 1}
topRight: {r: 1, g: 1, b: 1, a: 1}
bottomLeft: {r: 1, g: 1, b: 1, a: 1}
bottomRight: {r: 1, g: 1, b: 1, a: 1}
m_fontColorGradientPreset: {fileID: 0}
m_spriteAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_tintAllSprites: 0
m_StyleSheet: {fileID: 0}
m_TextStyleHashCode: -1183493901
m_overrideHtmlColors: 0
m_faceColor:
serializedVersion: 2
rgba: 4294967295
m_fontSize: 24
m_fontSizeBase: 24
m_fontWeight: 400
m_enableAutoSizing: 0
m_fontSizeMin: 18
m_fontSizeMax: 72
m_fontStyle: 0
m_HorizontalAlignment: 2
m_VerticalAlignment: 512
m_textAlignment: 65535
m_characterSpacing: 0
m_wordSpacing: 0
m_lineSpacing: 0
m_lineSpacingMax: 0
m_paragraphSpacing: 0
m_charWidthMaxAdj: 0
m_enableWordWrapping: 1
m_wordWrappingRatios: 0.4
m_overflowMode: 0
m_linkedTextComponent: {fileID: 0}
parentLinkedComponent: {fileID: 0}
m_enableKerning: 1
m_enableExtraPadding: 0
checkPaddingRequired: 0
m_isRichText: 1
m_parseCtrlCharacters: 1
m_isOrthographic: 1
m_isCullingEnabled: 0
m_horizontalMapping: 0
m_verticalMapping: 0
m_uvLineOffset: 0
m_geometrySortingOrder: 0
m_IsTextObjectScaleStatic: 0
m_VertexBufferAutoSizeReduction: 0
m_useMaxVisibleDescender: 1
m_pageToDisplay: 1
m_margin: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0, w: 0}
m_isUsingLegacyAnimationComponent: 0
m_isVolumetricText: 0
m_hasFontAssetChanged: 0
m_baseMaterial: {fileID: 0}
m_maskOffset: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0, w: 0}
--- !u!222 &438770863
CanvasRenderer:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_GameObject: {fileID: 438770860}
m_CullTransparentMesh: 1
--- !u!1 &519420028
GameObject:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
serializedVersion: 6
m_Component:
- component: {fileID: 519420032}
- component: {fileID: 519420031}
- component: {fileID: 519420029}
m_Layer: 0
m_Name: Main Camera
m_TagString: MainCamera
m_Icon: {fileID: 0}
m_NavMeshLayer: 0
m_StaticEditorFlags: 0
m_IsActive: 1
--- !u!81 &519420029
AudioListener:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_GameObject: {fileID: 519420028}
m_Enabled: 1
--- !u!20 &519420031
Camera:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_GameObject: {fileID: 519420028}
m_Enabled: 1
serializedVersion: 2
m_ClearFlags: 2
m_BackGroundColor: {r: 0.19215687, g: 0.3019608, b: 0.4745098, a: 0}
m_projectionMatrixMode: 1
m_GateFitMode: 2
m_FOVAxisMode: 0
m_SensorSize: {x: 36, y: 24}
m_LensShift: {x: 0, y: 0}
m_FocalLength: 50
m_NormalizedViewPortRect:
serializedVersion: 2
x: 0
y: 0
width: 1
height: 1
near clip plane: 0.3
far clip plane: 1000
field of view: 60
orthographic: 1
orthographic size: 5
m_Depth: -1
m_CullingMask:
serializedVersion: 2
m_Bits: 4294967295
m_RenderingPath: -1
m_TargetTexture: {fileID: 0}
m_TargetDisplay: 0
m_TargetEye: 0
m_HDR: 1
m_AllowMSAA: 0
m_AllowDynamicResolution: 0
m_ForceIntoRT: 0
m_OcclusionCulling: 0
m_StereoConvergence: 10
m_StereoSeparation: 0.022
--- !u!4 &519420032
Transform:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_GameObject: {fileID: 519420028}
m_LocalRotation: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0, w: 1}
m_LocalPosition: {x: 0, y: 0, z: -10}
m_LocalScale: {x: 1, y: 1, z: 1}
m_ConstrainProportionsScale: 0
m_Children: []
m_Father: {fileID: 0}
m_RootOrder: 0
m_LocalEulerAnglesHint: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0}
--- !u!1 &857336305
GameObject:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
serializedVersion: 6
m_Component:
- component: {fileID: 857336306}
- component: {fileID: 857336309}
- component: {fileID: 857336308}
- component: {fileID: 857336307}
m_Layer: 5
m_Name: Placeholder
m_TagString: Untagged
m_Icon: {fileID: 0}
m_NavMeshLayer: 0
m_StaticEditorFlags: 0
m_IsActive: 1
--- !u!224 &857336306
RectTransform:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_GameObject: {fileID: 857336305}
m_LocalRotation: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0, w: 1}
m_LocalPosition: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0}
m_LocalScale: {x: 1, y: 1, z: 1}
m_ConstrainProportionsScale: 0
m_Children: []
m_Father: {fileID: 1787936407}
m_RootOrder: 0
m_LocalEulerAnglesHint: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0}
m_AnchorMin: {x: 0, y: 0}
m_AnchorMax: {x: 1, y: 1}
m_AnchoredPosition: {x: 0, y: 0}
m_SizeDelta: {x: 0, y: 0}
m_Pivot: {x: 0.5, y: 0.5}
--- !u!114 &857336307
MonoBehaviour:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_GameObject: {fileID: 857336305}
m_Enabled: 1
m_EditorHideFlags: 0
m_Script: {fileID: 11500000, guid: 306cc8c2b49d7114eaa3623786fc2126, type: 3}
m_Name:
m_EditorClassIdentifier:
m_IgnoreLayout: 1
m_MinWidth: -1
m_MinHeight: -1
m_PreferredWidth: -1
m_PreferredHeight: -1
m_FlexibleWidth: -1
m_FlexibleHeight: -1
m_LayoutPriority: 1
--- !u!114 &857336308
MonoBehaviour:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_GameObject: {fileID: 857336305}
m_Enabled: 1
m_EditorHideFlags: 0
m_Script: {fileID: 11500000, guid: f4688fdb7df04437aeb418b961361dc5, type: 3}
m_Name:
m_EditorClassIdentifier:
m_Material: {fileID: 0}
m_Color: {r: 1, g: 1, b: 1, a: 1}
m_RaycastTarget: 1
m_RaycastPadding: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0, w: 0}
m_Maskable: 1
m_OnCullStateChanged:
m_PersistentCalls:
m_Calls: []
m_text: Who Would you like to call?
m_isRightToLeft: 0
m_fontAsset: {fileID: 11400000, guid: 8f586378b4e144a9851e7b34d9b748ee, type: 2}
m_sharedMaterial: {fileID: 2180264, guid: 8f586378b4e144a9851e7b34d9b748ee, type: 2}
m_fontSharedMaterials: []
m_fontMaterial: {fileID: 0}
m_fontMaterials: []
m_fontColor32:
serializedVersion: 2
rgba: 2150773298
m_fontColor: {r: 0.19607843, g: 0.19607843, b: 0.19607843, a: 0.5}
m_enableVertexGradient: 0
m_colorMode: 3
m_fontColorGradient:
topLeft: {r: 1, g: 1, b: 1, a: 1}
topRight: {r: 1, g: 1, b: 1, a: 1}
bottomLeft: {r: 1, g: 1, b: 1, a: 1}
bottomRight: {r: 1, g: 1, b: 1, a: 1}
m_fontColorGradientPreset: {fileID: 0}
m_spriteAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_tintAllSprites: 0
m_StyleSheet: {fileID: 0}
m_TextStyleHashCode: -1183493901
m_overrideHtmlColors: 0
m_faceColor:
serializedVersion: 2
rgba: 4294967295
m_fontSize: 14
m_fontSizeBase: 14
m_fontWeight: 400
m_enableAutoSizing: 0
m_fontSizeMin: 18
m_fontSizeMax: 72
m_fontStyle: 2
m_HorizontalAlignment: 1
m_VerticalAlignment: 256
m_textAlignment: 65535
m_characterSpacing: 0
m_wordSpacing: 0
m_lineSpacing: 0
m_lineSpacingMax: 0
m_paragraphSpacing: 0
m_charWidthMaxAdj: 0
m_enableWordWrapping: 0
m_wordWrappingRatios: 0.4
m_overflowMode: 0
m_linkedTextComponent: {fileID: 0}
parentLinkedComponent: {fileID: 0}
m_enableKerning: 1
m_enableExtraPadding: 1
checkPaddingRequired: 0
m_isRichText: 1
m_parseCtrlCharacters: 1
m_isOrthographic: 1
m_isCullingEnabled: 0
m_horizontalMapping: 0
m_verticalMapping: 0
m_uvLineOffset: 0
m_geometrySortingOrder: 0
m_IsTextObjectScaleStatic: 0
m_VertexBufferAutoSizeReduction: 0
m_useMaxVisibleDescender: 1
m_pageToDisplay: 1
m_margin: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0, w: 0}
m_isUsingLegacyAnimationComponent: 0
m_isVolumetricText: 0
m_hasFontAssetChanged: 0
m_baseMaterial: {fileID: 0}
m_maskOffset: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0, w: 0}
--- !u!222 &857336309
CanvasRenderer:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_GameObject: {fileID: 857336305}
m_CullTransparentMesh: 1
--- !u!1 &963546686
GameObject:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
serializedVersion: 6
m_Component:
- component: {fileID: 963546687}
- component: {fileID: 963546690}
- component: {fileID: 963546689}
- component: {fileID: 963546688}
m_Layer: 5
m_Name: InputField (TMP)
m_TagString: Untagged
m_Icon: {fileID: 0}
m_NavMeshLayer: 0
m_StaticEditorFlags: 0
m_IsActive: 1
--- !u!224 &963546687
RectTransform:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_GameObject: {fileID: 963546686}
m_LocalRotation: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0, w: 1}
m_LocalPosition: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0}
m_LocalScale: {x: 1, y: 1, z: 1}
m_ConstrainProportionsScale: 0
m_Children:
- {fileID: 1787936407}
m_Father: {fileID: 1843906927}
m_RootOrder: 0
m_LocalEulerAnglesHint: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0}
m_AnchorMin: {x: 0.5, y: 0.5}
m_AnchorMax: {x: 0.5, y: 0.5}
m_AnchoredPosition: {x: 0.00002861, y: 327}
m_SizeDelta: {x: 1337.7578, y: 71.4853}
m_Pivot: {x: 0.5, y: 0.5}
--- !u!114 &963546688
MonoBehaviour:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_GameObject: {fileID: 963546686}
m_Enabled: 1
m_EditorHideFlags: 0
m_Script: {fileID: 11500000, guid: 2da0c512f12947e489f739169773d7ca, type: 3}
m_Name:
m_EditorClassIdentifier:
m_Navigation:
m_Mode: 3
m_WrapAround: 0
m_SelectOnUp: {fileID: 0}
m_SelectOnDown: {fileID: 0}
m_SelectOnLeft: {fileID: 0}
m_SelectOnRight: {fileID: 0}
m_Transition: 1
m_Colors:
m_NormalColor: {r: 1, g: 1, b: 1, a: 1}
m_HighlightedColor: {r: 0.9607843, g: 0.9607843, b: 0.9607843, a: 1}
m_PressedColor: {r: 0.78431374, g: 0.78431374, b: 0.78431374, a: 1}
m_SelectedColor: {r: 0.9607843, g: 0.9607843, b: 0.9607843, a: 1}
m_DisabledColor: {r: 0.78431374, g: 0.78431374, b: 0.78431374, a: 0.5019608}
m_ColorMultiplier: 1
m_FadeDuration: 0.1
m_SpriteState:
m_HighlightedSprite: {fileID: 0}
m_PressedSprite: {fileID: 0}
m_SelectedSprite: {fileID: 0}
m_DisabledSprite: {fileID: 0}
m_AnimationTriggers:
m_NormalTrigger: Normal
m_HighlightedTrigger: Highlighted
m_PressedTrigger: Pressed
m_SelectedTrigger: Selected
m_DisabledTrigger: Disabled
m_Interactable: 1
m_TargetGraphic: {fileID: 963546689}
m_TextViewport: {fileID: 1787936407}
m_TextComponent: {fileID: 1676708954}
m_Placeholder: {fileID: 857336308}
m_VerticalScrollbar: {fileID: 0}
m_VerticalScrollbarEventHandler: {fileID: 0}
m_LayoutGroup: {fileID: 0}
m_ScrollSensitivity: 1
m_ContentType: 0
m_InputType: 0
m_AsteriskChar: 42
m_KeyboardType: 0
m_LineType: 0
m_HideMobileInput: 0
m_HideSoftKeyboard: 0
m_CharacterValidation: 0
m_RegexValue:
m_GlobalPointSize: 14
m_CharacterLimit: 0
m_OnEndEdit:
m_PersistentCalls:
m_Calls: []
m_OnSubmit:
m_PersistentCalls:
m_Calls: []
m_OnSelect:
m_PersistentCalls:
m_Calls: []
m_OnDeselect:
m_PersistentCalls:
m_Calls: []
m_OnTextSelection:
m_PersistentCalls:
m_Calls: []
m_OnEndTextSelection:
m_PersistentCalls:
m_Calls: []
m_OnValueChanged:
m_PersistentCalls:
m_Calls:
- m_Target: {fileID: 293984670}
m_TargetAssemblyTypeName: CallClientHost, Assembly-CSharp
m_MethodName: set_CalleeIdentity
m_Mode: 0
m_Arguments:
m_ObjectArgument: {fileID: 0}
m_ObjectArgumentAssemblyTypeName: UnityEngine.Object, UnityEngine
m_IntArgument: 0
m_FloatArgument: 0
m_StringArgument:
m_BoolArgument: 0
m_CallState: 2
m_OnTouchScreenKeyboardStatusChanged:
m_PersistentCalls:
m_Calls: []
m_CaretColor: {r: 0.19607843, g: 0.19607843, b: 0.19607843, a: 1}
m_CustomCaretColor: 0
m_SelectionColor: {r: 0.65882355, g: 0.80784315, b: 1, a: 0.7529412}
m_Text:
m_CaretBlinkRate: 0.85
m_CaretWidth: 1
m_ReadOnly: 0
m_RichText: 1
m_GlobalFontAsset: {fileID: 11400000, guid: 8f586378b4e144a9851e7b34d9b748ee, type: 2}
m_OnFocusSelectAll: 1
m_ResetOnDeActivation: 1
m_RestoreOriginalTextOnEscape: 1
m_isRichTextEditingAllowed: 0
m_LineLimit: 0
m_InputValidator: {fileID: 0}
--- !u!114 &963546689
MonoBehaviour:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_GameObject: {fileID: 963546686}
m_Enabled: 1
m_EditorHideFlags: 0
m_Script: {fileID: 11500000, guid: fe87c0e1cc204ed48ad3b37840f39efc, type: 3}
m_Name:
m_EditorClassIdentifier:
m_Material: {fileID: 0}
m_Color: {r: 1, g: 1, b: 1, a: 1}
m_RaycastTarget: 1
m_RaycastPadding: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0, w: 0}
m_Maskable: 1
m_OnCullStateChanged:
m_PersistentCalls:
m_Calls: []
m_Sprite: {fileID: 10911, guid: 0000000000000000f000000000000000, type: 0}
m_Type: 1
m_PreserveAspect: 0
m_FillCenter: 1
m_FillMethod: 4
m_FillAmount: 1
m_FillClockwise: 1
m_FillOrigin: 0
m_UseSpriteMesh: 0
m_PixelsPerUnitMultiplier: 1
--- !u!222 &963546690
CanvasRenderer:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_GameObject: {fileID: 963546686}
m_CullTransparentMesh: 1
--- !u!1 &1184525248
GameObject:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
serializedVersion: 6
m_Component:
- component: {fileID: 1184525249}
- component: {fileID: 1184525251}
- component: {fileID: 1184525250}
m_Layer: 5
m_Name: Status Header
m_TagString: Untagged
m_Icon: {fileID: 0}
m_NavMeshLayer: 0
m_StaticEditorFlags: 0
m_IsActive: 1
--- !u!224 &1184525249
RectTransform:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_GameObject: {fileID: 1184525248}
m_LocalRotation: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0, w: 1}
m_LocalPosition: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0}
m_LocalScale: {x: 1, y: 1, z: 1}
m_ConstrainProportionsScale: 0
m_Children: []
m_Father: {fileID: 1843906927}
m_RootOrder: 3
m_LocalEulerAnglesHint: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0}
m_AnchorMin: {x: 0.5, y: 0.5}
m_AnchorMax: {x: 0.5, y: 0.5}
m_AnchoredPosition: {x: -23, y: -303}
m_SizeDelta: {x: 159.05, y: 33.5037}
m_Pivot: {x: 0.5, y: 0.5}
--- !u!114 &1184525250
MonoBehaviour:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_GameObject: {fileID: 1184525248}
m_Enabled: 1
m_EditorHideFlags: 0
m_Script: {fileID: 11500000, guid: f4688fdb7df04437aeb418b961361dc5, type: 3}
m_Name:
m_EditorClassIdentifier:
m_Material: {fileID: 0}
m_Color: {r: 1, g: 1, b: 1, a: 1}
m_RaycastTarget: 1
m_RaycastPadding: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0, w: 0}
m_Maskable: 1
m_OnCullStateChanged:
m_PersistentCalls:
m_Calls: []
m_text: Status
m_isRightToLeft: 0
m_fontAsset: {fileID: 11400000, guid: 8f586378b4e144a9851e7b34d9b748ee, type: 2}
m_sharedMaterial: {fileID: 2180264, guid: 8f586378b4e144a9851e7b34d9b748ee, type: 2}
m_fontSharedMaterials: []
m_fontMaterial: {fileID: 0}
m_fontMaterials: []
m_fontColor32:
serializedVersion: 2
rgba: 4294967295
m_fontColor: {r: 1, g: 1, b: 1, a: 1}
m_enableVertexGradient: 0
m_colorMode: 3
m_fontColorGradient:
topLeft: {r: 1, g: 1, b: 1, a: 1}
topRight: {r: 1, g: 1, b: 1, a: 1}
bottomLeft: {r: 1, g: 1, b: 1, a: 1}
bottomRight: {r: 1, g: 1, b: 1, a: 1}
m_fontColorGradientPreset: {fileID: 0}
m_spriteAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_tintAllSprites: 0
m_StyleSheet: {fileID: 0}
m_TextStyleHashCode: -1183493901
m_overrideHtmlColors: 0
m_faceColor:
serializedVersion: 2
rgba: 4294967295
m_fontSize: 24
m_fontSizeBase: 24
m_fontWeight: 400
m_enableAutoSizing: 0
m_fontSizeMin: 18
m_fontSizeMax: 72
m_fontStyle: 0
m_HorizontalAlignment: 1
m_VerticalAlignment: 256
m_textAlignment: 65535
m_characterSpacing: 0
m_wordSpacing: 0
m_lineSpacing: 0
m_lineSpacingMax: 0
m_paragraphSpacing: 0
m_charWidthMaxAdj: 0
m_enableWordWrapping: 1
m_wordWrappingRatios: 0.4
m_overflowMode: 0
m_linkedTextComponent: {fileID: 0}
parentLinkedComponent: {fileID: 0}
m_enableKerning: 1
m_enableExtraPadding: 0
checkPaddingRequired: 0
m_isRichText: 1
m_parseCtrlCharacters: 1
m_isOrthographic: 1
m_isCullingEnabled: 0
m_horizontalMapping: 0
m_verticalMapping: 0
m_uvLineOffset: 0
m_geometrySortingOrder: 0
m_IsTextObjectScaleStatic: 0
m_VertexBufferAutoSizeReduction: 0
m_useMaxVisibleDescender: 1
m_pageToDisplay: 1
m_margin: {x: 0, y: 2.5243988, z: 10.097656, w: -2.5243645}
m_isUsingLegacyAnimationComponent: 0
m_isVolumetricText: 0
m_hasFontAssetChanged: 0
m_baseMaterial: {fileID: 0}
m_maskOffset: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0, w: 0}
--- !u!222 &1184525251
CanvasRenderer:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_GameObject: {fileID: 1184525248}
m_CullTransparentMesh: 1
--- !u!1 &1332239153
GameObject:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
serializedVersion: 6
m_Component:
- component: {fileID: 1332239154}
- component: {fileID: 1332239157}
- component: {fileID: 1332239156}
- component: {fileID: 1332239155}
m_Layer: 5
m_Name: Hang Up Button
m_TagString: Untagged
m_Icon: {fileID: 0}
m_NavMeshLayer: 0
m_StaticEditorFlags: 0
m_IsActive: 1
--- !u!224 &1332239154
RectTransform:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_GameObject: {fileID: 1332239153}
m_LocalRotation: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0, w: 1}
m_LocalPosition: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0}
m_LocalScale: {x: 1, y: 1, z: 1}
m_ConstrainProportionsScale: 0
m_Children:
- {fileID: 1917486034}
m_Father: {fileID: 1843906927}
m_RootOrder: 2
m_LocalEulerAnglesHint: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0}
m_AnchorMin: {x: 0.5, y: 0.5}
m_AnchorMax: {x: 0.5, y: 0.5}
m_AnchoredPosition: {x: -277, y: -329}
m_SizeDelta: {x: 212.1357, y: 53.698}
m_Pivot: {x: 0.5, y: 0.5}
--- !u!114 &1332239155
MonoBehaviour:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_GameObject: {fileID: 1332239153}
m_Enabled: 1
m_EditorHideFlags: 0
m_Script: {fileID: 11500000, guid: 4e29b1a8efbd4b44bb3f3716e73f07ff, type: 3}
m_Name:
m_EditorClassIdentifier:
m_Navigation:
m_Mode: 3
m_WrapAround: 0
m_SelectOnUp: {fileID: 0}
m_SelectOnDown: {fileID: 0}
m_SelectOnLeft: {fileID: 0}
m_SelectOnRight: {fileID: 0}
m_Transition: 1
m_Colors:
m_NormalColor: {r: 1, g: 1, b: 1, a: 1}
m_HighlightedColor: {r: 0.9607843, g: 0.9607843, b: 0.9607843, a: 1}
m_PressedColor: {r: 0.78431374, g: 0.78431374, b: 0.78431374, a: 1}
m_SelectedColor: {r: 0.9607843, g: 0.9607843, b: 0.9607843, a: 1}
m_DisabledColor: {r: 0.78431374, g: 0.78431374, b: 0.78431374, a: 0.5019608}
m_ColorMultiplier: 1
m_FadeDuration: 0.1
m_SpriteState:
m_HighlightedSprite: {fileID: 0}
m_PressedSprite: {fileID: 0}
m_SelectedSprite: {fileID: 0}
m_DisabledSprite: {fileID: 0}
m_AnimationTriggers:
m_NormalTrigger: Normal
m_HighlightedTrigger: Highlighted
m_PressedTrigger: Pressed
m_SelectedTrigger: Selected
m_DisabledTrigger: Disabled
m_Interactable: 1
m_TargetGraphic: {fileID: 1332239156}
m_OnClick:
m_PersistentCalls:
m_Calls:
- m_Target: {fileID: 293984670}
m_TargetAssemblyTypeName: AppManager, Assembly-CSharp
m_MethodName: HangupButton_Click
m_Mode: 1
m_Arguments:
m_ObjectArgument: {fileID: 0}
m_ObjectArgumentAssemblyTypeName: UnityEngine.Object, UnityEngine
m_IntArgument: 0
m_FloatArgument: 0
m_StringArgument:
m_BoolArgument: 0
m_CallState: 2
--- !u!114 &1332239156
MonoBehaviour:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_GameObject: {fileID: 1332239153}
m_Enabled: 1
m_EditorHideFlags: 0
m_Script: {fileID: 11500000, guid: fe87c0e1cc204ed48ad3b37840f39efc, type: 3}
m_Name:
m_EditorClassIdentifier:
m_Material: {fileID: 0}
m_Color: {r: 1, g: 1, b: 1, a: 1}
m_RaycastTarget: 1
m_RaycastPadding: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0, w: 0}
m_Maskable: 1
m_OnCullStateChanged:
m_PersistentCalls:
m_Calls: []
m_Sprite: {fileID: 10905, guid: 0000000000000000f000000000000000, type: 0}
m_Type: 1
m_PreserveAspect: 0
m_FillCenter: 1
m_FillMethod: 4
m_FillAmount: 1
m_FillClockwise: 1
m_FillOrigin: 0
m_UseSpriteMesh: 0
m_PixelsPerUnitMultiplier: 1
--- !u!222 &1332239157
CanvasRenderer:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_GameObject: {fileID: 1332239153}
m_CullTransparentMesh: 1
--- !u!1 &1529611526
GameObject:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
serializedVersion: 6
m_Component:
- component: {fileID: 1529611527}
- component: {fileID: 1529611529}
- component: {fileID: 1529611528}
m_Layer: 5
m_Name: Status
m_TagString: Untagged
m_Icon: {fileID: 0}
m_NavMeshLayer: 0
m_StaticEditorFlags: 0
m_IsActive: 1
--- !u!224 &1529611527
RectTransform:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_GameObject: {fileID: 1529611526}
m_LocalRotation: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0, w: 1}
m_LocalPosition: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0}
m_LocalScale: {x: 1, y: 1, z: 1}
m_ConstrainProportionsScale: 0
m_Children: []
m_Father: {fileID: 1843906927}
m_RootOrder: 4
m_LocalEulerAnglesHint: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0}
m_AnchorMin: {x: 0.5, y: 0.5}
m_AnchorMax: {x: 0.5, y: 0.5}
m_AnchoredPosition: {x: -2.525, y: -344.75}
m_SizeDelta: {x: 200, y: 50}
m_Pivot: {x: 0.5, y: 0.5}
--- !u!114 &1529611528
MonoBehaviour:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_GameObject: {fileID: 1529611526}
m_Enabled: 1
m_EditorHideFlags: 0
m_Script: {fileID: 11500000, guid: f4688fdb7df04437aeb418b961361dc5, type: 3}
m_Name:
m_EditorClassIdentifier:
m_Material: {fileID: 0}
m_Color: {r: 1, g: 1, b: 1, a: 1}
m_RaycastTarget: 1
m_RaycastPadding: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0, w: 0}
m_Maskable: 1
m_OnCullStateChanged:
m_PersistentCalls:
m_Calls: []
m_text: Disconnected
m_isRightToLeft: 0
m_fontAsset: {fileID: 11400000, guid: 8f586378b4e144a9851e7b34d9b748ee, type: 2}
m_sharedMaterial: {fileID: 2180264, guid: 8f586378b4e144a9851e7b34d9b748ee, type: 2}
m_fontSharedMaterials: []
m_fontMaterial: {fileID: 0}
m_fontMaterials: []
m_fontColor32:
serializedVersion: 2
rgba: 4294967295
m_fontColor: {r: 1, g: 1, b: 1, a: 1}
m_enableVertexGradient: 0
m_colorMode: 3
m_fontColorGradient:
topLeft: {r: 1, g: 1, b: 1, a: 1}
topRight: {r: 1, g: 1, b: 1, a: 1}
bottomLeft: {r: 1, g: 1, b: 1, a: 1}
bottomRight: {r: 1, g: 1, b: 1, a: 1}
m_fontColorGradientPreset: {fileID: 0}
m_spriteAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_tintAllSprites: 0
m_StyleSheet: {fileID: 0}
m_TextStyleHashCode: -1183493901
m_overrideHtmlColors: 0
m_faceColor:
serializedVersion: 2
rgba: 4294967295
m_fontSize: 30
m_fontSizeBase: 30
m_fontWeight: 400
m_enableAutoSizing: 0
m_fontSizeMin: 18
m_fontSizeMax: 72
m_fontStyle: 0
m_HorizontalAlignment: 1
m_VerticalAlignment: 256
m_textAlignment: 65535
m_characterSpacing: 0
m_wordSpacing: 0
m_lineSpacing: 0
m_lineSpacingMax: 0
m_paragraphSpacing: 0
m_charWidthMaxAdj: 0
m_enableWordWrapping: 1
m_wordWrappingRatios: 0.4
m_overflowMode: 0
m_linkedTextComponent: {fileID: 0}
parentLinkedComponent: {fileID: 0}
m_enableKerning: 1
m_enableExtraPadding: 0
checkPaddingRequired: 0
m_isRichText: 1
m_parseCtrlCharacters: 1
m_isOrthographic: 1
m_isCullingEnabled: 0
m_horizontalMapping: 0
m_verticalMapping: 0
m_uvLineOffset: 0
m_geometrySortingOrder: 0
m_IsTextObjectScaleStatic: 0
m_VertexBufferAutoSizeReduction: 0
m_useMaxVisibleDescender: 1
m_pageToDisplay: 1
m_margin: {x: 0, y: 0, z: -25.861023, w: 0}
m_isUsingLegacyAnimationComponent: 0
m_isVolumetricText: 0
m_hasFontAssetChanged: 0
m_baseMaterial: {fileID: 0}
m_maskOffset: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0, w: 0}
--- !u!222 &1529611529
CanvasRenderer:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_GameObject: {fileID: 1529611526}
m_CullTransparentMesh: 1
--- !u!1 &1676708952
GameObject:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
serializedVersion: 6
m_Component:
- component: {fileID: 1676708953}
- component: {fileID: 1676708955}
- component: {fileID: 1676708954}
m_Layer: 5
m_Name: Text
m_TagString: Untagged
m_Icon: {fileID: 0}
m_NavMeshLayer: 0
m_StaticEditorFlags: 0
m_IsActive: 1
--- !u!224 &1676708953
RectTransform:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_GameObject: {fileID: 1676708952}
m_LocalRotation: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0, w: 1}
m_LocalPosition: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0}
m_LocalScale: {x: 1, y: 1, z: 1}
m_ConstrainProportionsScale: 0
m_Children: []
m_Father: {fileID: 1787936407}
m_RootOrder: 1
m_LocalEulerAnglesHint: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0}
m_AnchorMin: {x: 0, y: 0}
m_AnchorMax: {x: 1, y: 1}
m_AnchoredPosition: {x: 0, y: 0}
m_SizeDelta: {x: 0, y: 0}
m_Pivot: {x: 0.5, y: 0.5}
--- !u!114 &1676708954
MonoBehaviour:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_GameObject: {fileID: 1676708952}
m_Enabled: 1
m_EditorHideFlags: 0
m_Script: {fileID: 11500000, guid: f4688fdb7df04437aeb418b961361dc5, type: 3}
m_Name:
m_EditorClassIdentifier:
m_Material: {fileID: 0}
m_Color: {r: 1, g: 1, b: 1, a: 1}
m_RaycastTarget: 1
m_RaycastPadding: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0, w: 0}
m_Maskable: 1
m_OnCullStateChanged:
m_PersistentCalls:
m_Calls: []
m_text: "\u200B"
m_isRightToLeft: 0
m_fontAsset: {fileID: 11400000, guid: 8f586378b4e144a9851e7b34d9b748ee, type: 2}
m_sharedMaterial: {fileID: 2180264, guid: 8f586378b4e144a9851e7b34d9b748ee, type: 2}
m_fontSharedMaterials: []
m_fontMaterial: {fileID: 0}
m_fontMaterials: []
m_fontColor32:
serializedVersion: 2
rgba: 4281479730
m_fontColor: {r: 0.19607843, g: 0.19607843, b: 0.19607843, a: 1}
m_enableVertexGradient: 0
m_colorMode: 3
m_fontColorGradient:
topLeft: {r: 1, g: 1, b: 1, a: 1}
topRight: {r: 1, g: 1, b: 1, a: 1}
bottomLeft: {r: 1, g: 1, b: 1, a: 1}
bottomRight: {r: 1, g: 1, b: 1, a: 1}
m_fontColorGradientPreset: {fileID: 0}
m_spriteAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_tintAllSprites: 0
m_StyleSheet: {fileID: 0}
m_TextStyleHashCode: -1183493901
m_overrideHtmlColors: 0
m_faceColor:
serializedVersion: 2
rgba: 4294967295
m_fontSize: 14
m_fontSizeBase: 14
m_fontWeight: 400
m_enableAutoSizing: 0
m_fontSizeMin: 18
m_fontSizeMax: 72
m_fontStyle: 0
m_HorizontalAlignment: 1
m_VerticalAlignment: 256
m_textAlignment: 65535
m_characterSpacing: 0
m_wordSpacing: 0
m_lineSpacing: 0
m_lineSpacingMax: 0
m_paragraphSpacing: 0
m_charWidthMaxAdj: 0
m_enableWordWrapping: 0
m_wordWrappingRatios: 0.4
m_overflowMode: 0
m_linkedTextComponent: {fileID: 0}
parentLinkedComponent: {fileID: 0}
m_enableKerning: 1
m_enableExtraPadding: 1
checkPaddingRequired: 0
m_isRichText: 1
m_parseCtrlCharacters: 1
m_isOrthographic: 1
m_isCullingEnabled: 0
m_horizontalMapping: 0
m_verticalMapping: 0
m_uvLineOffset: 0
m_geometrySortingOrder: 0
m_IsTextObjectScaleStatic: 0
m_VertexBufferAutoSizeReduction: 0
m_useMaxVisibleDescender: 1
m_pageToDisplay: 1
m_margin: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0, w: 0}
m_isUsingLegacyAnimationComponent: 0
m_isVolumetricText: 0
m_hasFontAssetChanged: 0
m_baseMaterial: {fileID: 0}
m_maskOffset: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0, w: 0}
--- !u!222 &1676708955
CanvasRenderer:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_GameObject: {fileID: 1676708952}
m_CullTransparentMesh: 1
--- !u!1 &1732033233
GameObject:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
serializedVersion: 6
m_Component:
- component: {fileID: 1732033234}
- component: {fileID: 1732033237}
- component: {fileID: 1732033236}
- component: {fileID: 1732033235}
m_Layer: 5
m_Name: Start Call Button
m_TagString: Untagged
m_Icon: {fileID: 0}
m_NavMeshLayer: 0
m_StaticEditorFlags: 0
m_IsActive: 1
--- !u!224 &1732033234
RectTransform:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_GameObject: {fileID: 1732033233}
m_LocalRotation: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0, w: 1}
m_LocalPosition: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0}
m_LocalScale: {x: 1, y: 1, z: 1}
m_ConstrainProportionsScale: 0
m_Children:
- {fileID: 438770861}
m_Father: {fileID: 1843906927}
m_RootOrder: 1
m_LocalEulerAnglesHint: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0}
m_AnchorMin: {x: 0.5, y: 0.5}
m_AnchorMax: {x: 0.5, y: 0.5}
m_AnchoredPosition: {x: -525.52, y: -329}
m_SizeDelta: {x: 212.1357, y: 53.698}
m_Pivot: {x: 0.5, y: 0.5}
--- !u!114 &1732033235
MonoBehaviour:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_GameObject: {fileID: 1732033233}
m_Enabled: 1
m_EditorHideFlags: 0
m_Script: {fileID: 11500000, guid: 4e29b1a8efbd4b44bb3f3716e73f07ff, type: 3}
m_Name:
m_EditorClassIdentifier:
m_Navigation:
m_Mode: 3
m_WrapAround: 0
m_SelectOnUp: {fileID: 0}
m_SelectOnDown: {fileID: 0}
m_SelectOnLeft: {fileID: 0}
m_SelectOnRight: {fileID: 0}
m_Transition: 1
m_Colors:
m_NormalColor: {r: 1, g: 1, b: 1, a: 1}
m_HighlightedColor: {r: 0.9607843, g: 0.9607843, b: 0.9607843, a: 1}
m_PressedColor: {r: 0.78431374, g: 0.78431374, b: 0.78431374, a: 1}
m_SelectedColor: {r: 0.9607843, g: 0.9607843, b: 0.9607843, a: 1}
m_DisabledColor: {r: 0.78431374, g: 0.78431374, b: 0.78431374, a: 0.5019608}
m_ColorMultiplier: 1
m_FadeDuration: 0.1
m_SpriteState:
m_HighlightedSprite: {fileID: 0}
m_PressedSprite: {fileID: 0}
m_SelectedSprite: {fileID: 0}
m_DisabledSprite: {fileID: 0}
m_AnimationTriggers:
m_NormalTrigger: Normal
m_HighlightedTrigger: Highlighted
m_PressedTrigger: Pressed
m_SelectedTrigger: Selected
m_DisabledTrigger: Disabled
m_Interactable: 1
m_TargetGraphic: {fileID: 1732033236}
m_OnClick:
m_PersistentCalls:
m_Calls:
- m_Target: {fileID: 293984670}
m_TargetAssemblyTypeName: CallClientHost, Assembly-CSharp
m_MethodName: CallButton_Click
m_Mode: 1
m_Arguments:
m_ObjectArgument: {fileID: 0}
m_ObjectArgumentAssemblyTypeName: UnityEngine.Object, UnityEngine
m_IntArgument: 0
m_FloatArgument: 0
m_StringArgument:
m_BoolArgument: 0
m_CallState: 2
--- !u!114 &1732033236
MonoBehaviour:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_GameObject: {fileID: 1732033233}
m_Enabled: 1
m_EditorHideFlags: 0
m_Script: {fileID: 11500000, guid: fe87c0e1cc204ed48ad3b37840f39efc, type: 3}
m_Name:
m_EditorClassIdentifier:
m_Material: {fileID: 0}
m_Color: {r: 1, g: 1, b: 1, a: 1}
m_RaycastTarget: 1
m_RaycastPadding: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0, w: 0}
m_Maskable: 1
m_OnCullStateChanged:
m_PersistentCalls:
m_Calls: []
m_Sprite: {fileID: 10905, guid: 0000000000000000f000000000000000, type: 0}
m_Type: 1
m_PreserveAspect: 0
m_FillCenter: 1
m_FillMethod: 4
m_FillAmount: 1
m_FillClockwise: 1
m_FillOrigin: 0
m_UseSpriteMesh: 0
m_PixelsPerUnitMultiplier: 1
--- !u!222 &1732033237
CanvasRenderer:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_GameObject: {fileID: 1732033233}
m_CullTransparentMesh: 1
--- !u!1 &1787936406
GameObject:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
serializedVersion: 6
m_Component:
- component: {fileID: 1787936407}
- component: {fileID: 1787936408}
m_Layer: 5
m_Name: Text Area
m_TagString: Untagged
m_Icon: {fileID: 0}
m_NavMeshLayer: 0
m_StaticEditorFlags: 0
m_IsActive: 1
--- !u!224 &1787936407
RectTransform:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_GameObject: {fileID: 1787936406}
m_LocalRotation: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0, w: 1}
m_LocalPosition: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0}
m_LocalScale: {x: 1, y: 1, z: 1}
m_ConstrainProportionsScale: 0
m_Children:
- {fileID: 857336306}
- {fileID: 1676708953}
m_Father: {fileID: 963546687}
m_RootOrder: 0
m_LocalEulerAnglesHint: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0}
m_AnchorMin: {x: 0, y: 0}
m_AnchorMax: {x: 1, y: 1}
m_AnchoredPosition: {x: 0, y: -0.4999962}
m_SizeDelta: {x: -20, y: -13}
m_Pivot: {x: 0.5, y: 0.5}
--- !u!114 &1787936408
MonoBehaviour:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_GameObject: {fileID: 1787936406}
m_Enabled: 1
m_EditorHideFlags: 0
m_Script: {fileID: 11500000, guid: 3312d7739989d2b4e91e6319e9a96d76, type: 3}
m_Name:
m_EditorClassIdentifier:
m_Padding: {x: -8, y: -5, z: -8, w: -5}
m_Softness: {x: 0, y: 0}
--- !u!1 &1843906923
GameObject:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
serializedVersion: 6
m_Component:
- component: {fileID: 1843906927}
- component: {fileID: 1843906926}
- component: {fileID: 1843906925}
- component: {fileID: 1843906924}
m_Layer: 5
m_Name: Canvas
m_TagString: Untagged
m_Icon: {fileID: 0}
m_NavMeshLayer: 0
m_StaticEditorFlags: 0
m_IsActive: 1
--- !u!114 &1843906924
MonoBehaviour:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_GameObject: {fileID: 1843906923}
m_Enabled: 1
m_EditorHideFlags: 0
m_Script: {fileID: 11500000, guid: dc42784cf147c0c48a680349fa168899, type: 3}
m_Name:
m_EditorClassIdentifier:
m_IgnoreReversedGraphics: 1
m_BlockingObjects: 0
m_BlockingMask:
serializedVersion: 2
m_Bits: 4294967295
--- !u!114 &1843906925
MonoBehaviour:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_GameObject: {fileID: 1843906923}
m_Enabled: 1
m_EditorHideFlags: 0
m_Script: {fileID: 11500000, guid: 0cd44c1031e13a943bb63640046fad76, type: 3}
m_Name:
m_EditorClassIdentifier:
m_UiScaleMode: 0
m_ReferencePixelsPerUnit: 100
m_ScaleFactor: 1
m_ReferenceResolution: {x: 800, y: 600}
m_ScreenMatchMode: 0
m_MatchWidthOrHeight: 0
m_PhysicalUnit: 3
m_FallbackScreenDPI: 96
m_DefaultSpriteDPI: 96
m_DynamicPixelsPerUnit: 1
m_PresetInfoIsWorld: 0
--- !u!223 &1843906926
Canvas:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_GameObject: {fileID: 1843906923}
m_Enabled: 1
serializedVersion: 3
m_RenderMode: 0
m_Camera: {fileID: 0}
m_PlaneDistance: 100
m_PixelPerfect: 0
m_ReceivesEvents: 1
m_OverrideSorting: 0
m_OverridePixelPerfect: 0
m_SortingBucketNormalizedSize: 0
m_AdditionalShaderChannelsFlag: 25
m_SortingLayerID: 0
m_SortingOrder: 0
m_TargetDisplay: 0
--- !u!224 &1843906927
RectTransform:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_GameObject: {fileID: 1843906923}
m_LocalRotation: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0, w: 1}
m_LocalPosition: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0}
m_LocalScale: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0}
m_ConstrainProportionsScale: 0
m_Children:
- {fileID: 963546687}
- {fileID: 1732033234}
- {fileID: 1332239154}
- {fileID: 1184525249}
- {fileID: 1529611527}
m_Father: {fileID: 0}
m_RootOrder: 3
m_LocalEulerAnglesHint: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0}
m_AnchorMin: {x: 0, y: 0}
m_AnchorMax: {x: 0, y: 0}
m_AnchoredPosition: {x: 0, y: 0}
m_SizeDelta: {x: 0, y: 0}
m_Pivot: {x: 0, y: 0}
--- !u!1 &1917486033
GameObject:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
serializedVersion: 6
m_Component:
- component: {fileID: 1917486034}
- component: {fileID: 1917486036}
- component: {fileID: 1917486035}
m_Layer: 5
m_Name: Text (TMP)
m_TagString: Untagged
m_Icon: {fileID: 0}
m_NavMeshLayer: 0
m_StaticEditorFlags: 0
m_IsActive: 1
--- !u!224 &1917486034
RectTransform:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_GameObject: {fileID: 1917486033}
m_LocalRotation: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0, w: 1}
m_LocalPosition: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0}
m_LocalScale: {x: 1, y: 1, z: 1}
m_ConstrainProportionsScale: 0
m_Children: []
m_Father: {fileID: 1332239154}
m_RootOrder: 0
m_LocalEulerAnglesHint: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0}
m_AnchorMin: {x: 0, y: 0}
m_AnchorMax: {x: 1, y: 1}
m_AnchoredPosition: {x: 0, y: 0}
m_SizeDelta: {x: 0, y: 0}
m_Pivot: {x: 0.5, y: 0.5}
--- !u!114 &1917486035
MonoBehaviour:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_GameObject: {fileID: 1917486033}
m_Enabled: 1
m_EditorHideFlags: 0
m_Script: {fileID: 11500000, guid: f4688fdb7df04437aeb418b961361dc5, type: 3}
m_Name:
m_EditorClassIdentifier:
m_Material: {fileID: 0}
m_Color: {r: 1, g: 1, b: 1, a: 1}
m_RaycastTarget: 1
m_RaycastPadding: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0, w: 0}
m_Maskable: 1
m_OnCullStateChanged:
m_PersistentCalls:
m_Calls: []
m_text: Hang Up
m_isRightToLeft: 0
m_fontAsset: {fileID: 11400000, guid: 8f586378b4e144a9851e7b34d9b748ee, type: 2}
m_sharedMaterial: {fileID: 2180264, guid: 8f586378b4e144a9851e7b34d9b748ee, type: 2}
m_fontSharedMaterials: []
m_fontMaterial: {fileID: 0}
m_fontMaterials: []
m_fontColor32:
serializedVersion: 2
rgba: 4281479730
m_fontColor: {r: 0.19607843, g: 0.19607843, b: 0.19607843, a: 1}
m_enableVertexGradient: 0
m_colorMode: 3
m_fontColorGradient:
topLeft: {r: 1, g: 1, b: 1, a: 1}
topRight: {r: 1, g: 1, b: 1, a: 1}
bottomLeft: {r: 1, g: 1, b: 1, a: 1}
bottomRight: {r: 1, g: 1, b: 1, a: 1}
m_fontColorGradientPreset: {fileID: 0}
m_spriteAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_tintAllSprites: 0
m_StyleSheet: {fileID: 0}
m_TextStyleHashCode: -1183493901
m_overrideHtmlColors: 0
m_faceColor:
serializedVersion: 2
rgba: 4294967295
m_fontSize: 24
m_fontSizeBase: 24
m_fontWeight: 400
m_enableAutoSizing: 0
m_fontSizeMin: 18
m_fontSizeMax: 72
m_fontStyle: 0
m_HorizontalAlignment: 2
m_VerticalAlignment: 512
m_textAlignment: 65535
m_characterSpacing: 0
m_wordSpacing: 0
m_lineSpacing: 0
m_lineSpacingMax: 0
m_paragraphSpacing: 0
m_charWidthMaxAdj: 0
m_enableWordWrapping: 1
m_wordWrappingRatios: 0.4
m_overflowMode: 0
m_linkedTextComponent: {fileID: 0}
parentLinkedComponent: {fileID: 0}
m_enableKerning: 1
m_enableExtraPadding: 0
checkPaddingRequired: 0
m_isRichText: 1
m_parseCtrlCharacters: 1
m_isOrthographic: 1
m_isCullingEnabled: 0
m_horizontalMapping: 0
m_verticalMapping: 0
m_uvLineOffset: 0
m_geometrySortingOrder: 0
m_IsTextObjectScaleStatic: 0
m_VertexBufferAutoSizeReduction: 0
m_useMaxVisibleDescender: 1
m_pageToDisplay: 1
m_margin: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0, w: 0}
m_isUsingLegacyAnimationComponent: 0
m_isVolumetricText: 0
m_hasFontAssetChanged: 0
m_baseMaterial: {fileID: 0}
m_maskOffset: {x: 0, y: 0, z: 0, w: 0}
--- !u!222 &1917486036
CanvasRenderer:
m_ObjectHideFlags: 0
m_CorrespondingSourceObject: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabInstance: {fileID: 0}
m_PrefabAsset: {fileID: 0}
m_GameObject: {fileID: 1917486033}
m_CullTransparentMesh: 1
Create a script called AppManager.cs and link it to the AppManager object in Unity Editor. Replace the content with the following implementation:
using Azure.Communication.Calling.UnityClient;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices.ComTypes;
using System;
using UnityEngine;
using System.Linq;
using UnityEngine.UI;
using UnityEngine.Video;
using TMPro;
/// <summary>
/// A singleton which hosts an Azure Communication calling client. This calling client
/// is then shared across the application.
/// </summary>
public class AppManager : MonoBehaviour
{
private CallClient callClient;
private CallAgent callAgent;
private DeviceManager deviceManager;
private CommunicationCall call;
private LocalOutgoingAudioStream micStream;
public string CalleeIdentity { get; set; }
public TMP_Text callStatus;
public static AppManager Instance;
private void Awake()
{
// start of new code
if (Instance != null)
{
Destroy(gameObject);
return;
}
// end of new code
callClient = new CallClient();
Instance = this;
DontDestroyOnLoad(gameObject);
InitCallAgentAndDeviceManagerAsync();
}
public async void CallButton_Click()
{
// Start a call
}
public async void HangupButton_Click()
{
// Hang up a call
}
private async void OnIncomingCallAsync(object sender, IncomingCallReceivedEventArgs args)
{
// Handle incoming call event
}
private void OnStateChangedAsync(object sender, Azure.Communication.Calling.UnityClient.PropertyChangedEventArgs args)
{
// Handle connected and disconnected state change of a call
}
//Used For Updating the UI
private void Update()
{
if (call != null)
{
switch (call.State)
{
case CallState.Connected:
if (callStatus.text != "Connected")
callStatus.text = "Connected";
break;
case CallState.Disconnected:
if (callStatus.text != "Disconnected")
callStatus.text = "Disconnected";
break;
}
}
}
}
In the GameObject called AppManager, drag the newly created script into its script component. Also, drag the Status text object into the Call Status text field to enable UI updates of the Call state.
Object model
The next table listed the classes and interfaces handle some of the major features of the Azure Communication Services Calling SDK:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
CallClient |
The CallClient is the main entry point to the Calling SDK. |
CallAgent |
The CallAgent is used to start and manage calls. |
Call |
The CommunicationCall is used to manage an ongoing call. |
CallTokenCredential |
The CallTokenCredential is used as the token credential to instantiate the CallAgent. |
CallIdentifier |
The CallIdentifier is used to represent the identity of the user, which can be one of the following options: UserCallIdentifier, PhoneNumberCallIdentifier etc. |
Authenticate the client
Initialize a CallAgent instance with a User Access Token that enables us to make and receive calls, and optionally obtain a DeviceManager instance to query for client device configurations.
In the code, replace <AUTHENTICATION_TOKEN> with a User Access Token. Refer to the user access token documentation if you don't already have a token available.
Add InitCallAgentAndDeviceManagerAsync function, which bootstraps the SDK. This helper can be customized to meet the requirements of your application.
private async void InitCallAgentAndDeviceManagerAsync()
{
deviceManager = await callClient.GetDeviceManager();
var tokenCredential = new CallTokenCredential(<AUTHENTICATION_TOKEN>);
var callAgentOptions = new CallAgentOptions()
{
DisplayName = $"{Environment.MachineName}/{Environment.UserName}",
};
callAgent = await callClient.CreateCallAgent(tokenCredential, callAgentOptions);
callAgent.IncomingCallReceived += OnIncomingCallAsync;
}
Start the call
Once a StartCallOptions object is obtained, CallAgent can be used to initiate the Azure Communication Services call:
public async void CallButton_Click()
{
var startCallOptions = new StartCallOptions();
startCallOptions = new StartCallOptions();
var callee = new UserCallIdentifier(CalleeIdentity);
call = await callAgent.StartCallAsync(new CallIdentifier[] { callee }, startCallOptions);
// Set up handler for call StateChanged event
call.StateChanged += OnStateChangedAsync;
}
End a call
End the current call when the Hang up button is clicked. Add the implementation to the HangupButton_Click to end a call, and stop the preview and video streams.
public async void HangupButton_Click()
{
if (call != null)
{
try
{
await call.HangUpAsync(new HangUpOptions() { ForEveryone = false });
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
}
}
}
Accept an incoming call
IncomingCallReceived event sink is set up in the SDK bootstrap helper InitCallAgentAndDeviceManagerAsync.
callAgent.IncomingCallReceived += OnIncomingCallAsync;
Application has an opportunity to configure how the incoming call should be accepted, such as video and audio stream kinds.
private async void OnIncomingCallAsync(object sender, IncomingCallReceivedEventArgs args)
{
var incomingCall = args.IncomingCall;
var acceptCallOptions = new AcceptCallOptions()
{
IncomingVideoOptions = new IncomingVideoOptions()
{
StreamKind = VideoStreamKind.RemoteIncoming
}
};
call = await incomingCall.AcceptAsync(acceptCallOptions);
// Set up handler for incoming call StateChanged event
call.StateChanged += OnStateChangedAsync;
}
Monitor and response to call state change event
StateChanged event on Call object is fired when an in progress call transactions from one state to another. Application is offered the opportunities to reflect the state changes on UI or insert business logics.
private async void OnStateChangedAsync(object sender, PropertyChangedEventArgs args)
{
var call = sender as CommunicationCall;
if (call != null)
{
var state = call.State;
switch (state)
{
case CallState.Connected:
{
await call.StartAudioAsync(micStream);
break;
}
case CallState.Disconnected:
{
call.StateChanged -= OnStateChangedAsync;
call.Dispose();
break;
}
default: break;
}
}
}
Run the code
You can build and run the code on Unity Editor or devices that uses Unity.
You can make an outbound call by providing a user ID in the text field and clicking the Start Call/Join button. Calling 8:echo123 connects you with an echo bot, this feature is great for getting started and verifying your audio devices are working.
Clean up resources
If you want to clean up and remove a Communication Services subscription, you can delete the resource or resource group. Deleting the resource group also deletes any other resources associated with it. Learn more about cleaning up resources.
Next steps
For more information, see the following articles:
- Check out our calling hero sample
- Get started with the UI Library
- Learn about Calling SDK capabilities
- Learn more about how calling works