Virtual TPMs in Azure confidential VMs
A Trust Platform Module (TPM) is designed to provide hardware based security functions. These functions include secret storage for cryptographic keys, storage for measurements of the boot process and an external hardware root-of-trust.
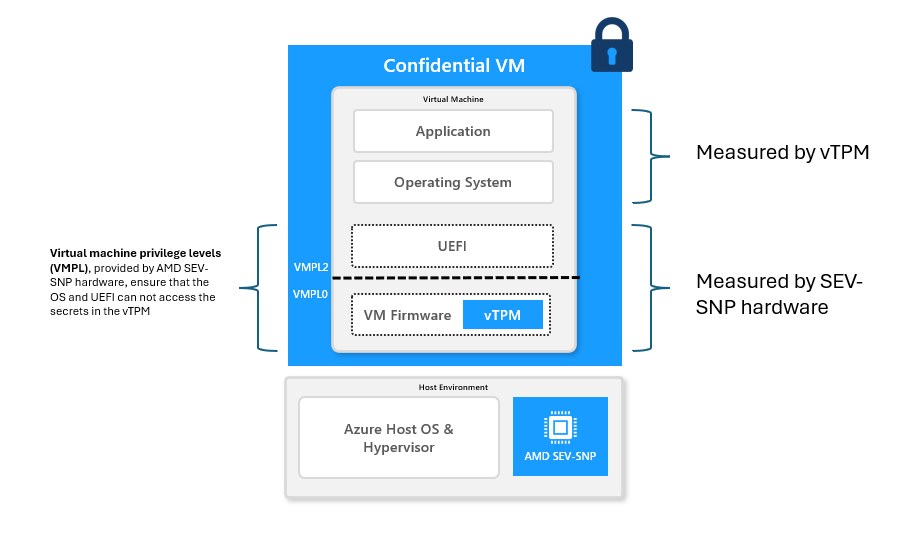
Azure confidential VMs each have their own dedicated virtual TPM (vTPM). The vTPM is a virtualized version of a hardware TPM, and complies with the TPM2.0 spec. In a confidential VM, the vTPM runs inside the VM in a hardware-based protected memory region. With this architecture, each confidential VM has its own unique vTPM instance that is isolated and encrypted by AMD SEV-SNP. Thus, an Azure confidential VM's vTPM instance is isolated from the hosting environment and all other VMs on the system.
For more information on the technology, see our blog on confidential VMs.
Since the vTPM runs within the Confidential VM, it's measured by the AMD SEV-SNP hardware. Customers can retrieve the hardware report generated by the Platform Security Processor (PSP) to attest the identity and integrity of the vTPM that guarantees that the TPM is authentic.
The hardware report can be used to verify that the Confidential VM is running as an isolated, secure machine with an isolated, integrity protected and measured vTPM. The vTPM can in-turn be used to measure and securely the boot the OS components in the confidential VM. By using usual TPM based primitives such as Measured Boot and Secured Boot, you can ensure and prove that your confidential VM is launched as intended.
TPMs have platform configuration registers (PCRs) that can be used to cryptographically measure the software state to ensure that nothing has been tampered with or misused. The PCR values are one-way hashes to ensure that the measurements can't be removed or altered. PCRs are used to store the measurements of various boot artifacts to help with the measured boot process. PCRs can also be used to measure applications, disk integrity measurements and other components. Additionally, PCRs can be used to enforce security policies such as application and code integrity (CI) policies to ensure the system remains compliant with the desired policies.
To utilize vTPMs in confidential VMs further, see How to leverage vTPMs in confidential VMs.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for