Automated recommendations for Azure Cosmos DB
APPLIES TO:
NoSQL
MongoDB
Cassandra
Gremlin
Table
All the cloud services including Azure Cosmos DB get frequent updates with new features, capabilities, and improvements. It’s important for your application to keep up with the latest performance and security updates. The Azure portal offers customized recommendations that enable you to maximize the performance of your application. The Azure Cosmos DB's advisory engine continuously analyzes the usage history of your Azure Cosmos DB resources and provides recommendations based on your workload patterns. These recommendations correspond to areas like partitioning, indexing, network, security etc. These customized recommendations help you to improve the performance of your application.
View recommendations
You can view recommendations for Azure Cosmos DB in the following ways:
One way to view the recommendations is within the notifications tab. If there are new recommendations, you will see a message bar. Sign into your Azure portal and navigate to your Azure Cosmos DB account. Within your Azure Cosmos DB account, open the Notifications pane and then select the Recommendations tab. You can select the message and view recommendations.
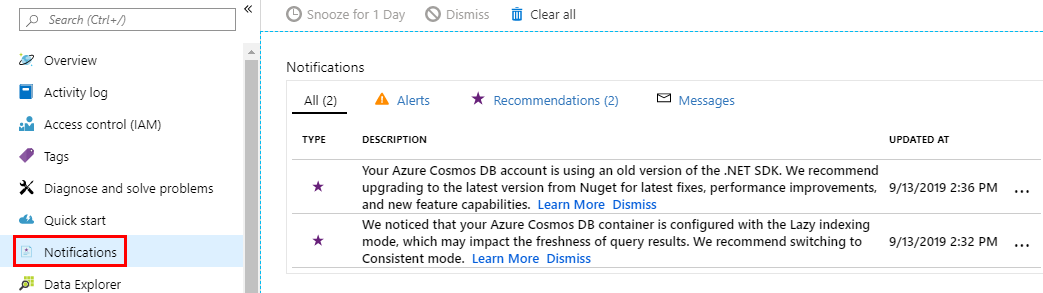
You can also find the recommendations through Azure Advisor in categorized by different buckets such as cost, security, reliability, performance, and operational excellence. You can select specific subscriptions and filter by the resource type, which is Azure Cosmos DB accounts. When you select a specific recommendation, it displays the actions you can take to benefit your workloads.
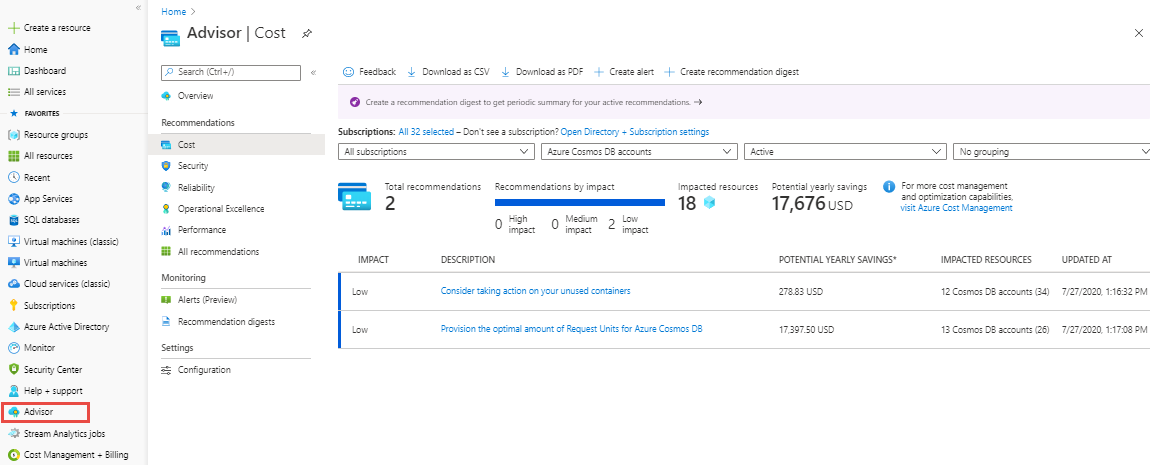
Not all recommendations shown in the Azure Cosmos DB pane are available in the Azure Advisor and vice versa. That’s because based on the type of recommendation they fit in either the Azure Advisor pane, Azure Cosmos DB pane or both.
Currently Azure Cosmos DB supports recommendations on the following areas. Each of these recommendations includes a link to the relevant section of the documentation, so it’s easy for you to take the next steps.
SDK usage recommendations
In this category, the advisor detects the usage of an old version of SDKs and recommends that you upgrade to a newer version to leverage the latest bug fixes and performance improvements. Currently the following SDK-specific recommendations are available:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Old Spark connector | Detects the usage of old versions of the Spark connector and recommends upgrading. |
| Old .NET SDK | Detects the usage of old versions of the .NET SDK and recommends upgrading. |
| Old Java SDK | Detects the usage of old versions of the Java connector and recommends upgrading. |
Indexing recommendations
In this category, the advisor detects the indexing mode, indexing policy, indexed paths and recommends changing if the current configuration impacts the query performance. Currently the following indexing-specific recommendations are available:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Lazy indexing | Detects usage of lazy indexing mode and recommends using consistent indexing mode instead. The purpose of Azure Cosmos DB’s lazy indexing mode is limited and can impact the freshness of query results in some situations so consistent indexing mode is recommended. |
| Default indexing policy with many indexed paths | Detects containers running on default indexing with many indexed paths and recommends customizing the indexing policy. |
| ORDER BY queries with high RU/s charge | Detects containers issuing ORDER BY queries with high RU/s charge and recommends exploring composite indexes for one container per account that issues the highest number of these queries in a 24 hour period. |
| MongoDB 3.6 accounts with no index and high RU/s consumption | Detects Azure Cosmos DB’s API for MongoDB with 3.6 version of containers issuing queries with high RU/s charge and recommends adding indexes. |
Cost optimization recommendations
In this category, the advisor detects the RU/s usage and determines that you can optimize the price by making some changes to your resources or by leveraging a different pricing model. Currently the following cost optimization-specific recommendations are available:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Reserved capacity | Detects your RU/s utilization and recommends reserved instances to users who can benefit from it. |
| Inactive containers | Detects the containers that haven't been used for more than 30 days and recommends reducing the throughput for such containers or deleting them. |
| New subscriptions with high throughput | Detects new subscriptions with accounts spending unusually high RU/s per day and provides them a notification. This notification is specifically to bring awareness to new customers that Azure Cosmos DB operates on provisioned throughput-based model and not consumption-based model. |
| Enable autoscale | Detects if your databases and containers currently using manual throughput would see cost savings by enabling autoscale. |
| Use manual throughput instead of autoscale | Detects if your databases and containers currently using autoscale throughput would see cost savings by switching to manual throughput. |
Migration recommendations
In this category, the advisor detects that you are using legacy features recommends migrating so that you can leverage Azure Cosmos DB’s massive scalability and other benefits. Currently the following migration-specific recommendations are available:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Non-partitioned containers | Detects fixed-size containers that are approaching their max storage limit and recommends migrating them to partitioned containers. |
Query usage recommendations
In this category, the advisor detects the query execution and identifies that the query performance can be tuned with some changes. Currently the following query usage recommendations are available:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Queries with fixed page size | Detects queries issued with a fixed page size and recommends using -1 (no limit on the page size) instead of defining a specific value. This option reduces the number of network round trips required to retrieve all results. |
Next steps
- Tuning query performance in Azure Cosmos DB
- Troubleshoot query issues when using Azure Cosmos DB
- Trying to do capacity planning for a migration to Azure Cosmos DB? You can use information about your existing database cluster for capacity planning.
- If all you know is the number of vcores and servers in your existing database cluster, read about estimating request units using vCores or vCPUs
- If you know typical request rates for your current database workload, read about estimating request units using Azure Cosmos DB capacity planner
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for