Burst capacity in Azure Cosmos DB
APPLIES TO:
NoSQL
MongoDB
Cassandra
Gremlin
Table
Azure Cosmos DB burst capacity allows you to take advantage of your database or container's idle throughput capacity to handle spikes of traffic. With burst capacity, each physical partition can accumulate up to 5 minutes of idle capacity, which can be consumed at a rate up to 3000 RU/s. With burst capacity, requests that would have otherwise been rate limited can now be served with burst capacity while it's available.
Burst capacity applies only to Azure Cosmos DB accounts using provisioned throughput (manual and autoscale) and doesn't apply to serverless containers. The feature is configured at the Azure Cosmos DB account level and automatically applies to all databases and containers in the account that have physical partitions with less than 3000 RU/s of provisioned throughput. Resources that have greater than or equal to 3000 RU/s per physical partition can't benefit from or use burst capacity.
How burst capacity works
Note
The current implementation of burst capacity is subject to change in the future. Usage of burst capacity is subject to system resource availability and is not guaranteed. Azure Cosmos DB may also use burst capacity for background maintenance tasks. If your workload requires consistent throughput beyond what you have provisioned, it's recommended to provision your RU/s accordingly without relying on burst capacity. Before enabling burst capacity, it is also recommended to evaluate if your partition layout can be merged to permanently give more RU/s per physical partition without relying on burst capacity.
Let's take an example of a physical partition that has 100 RU/s of provisioned throughput and is idle for 5 minutes. With burst capacity, it can accumulate a maximum of 100 RU/s * 300 seconds = 30,000 RU of burst capacity. The capacity can be consumed at a maximum rate of 3000 RU/s, so if there's a sudden spike in request volume, the partition can burst up to 3000 RU/s for up 30,000 RU / 3000 RU/s = 10 seconds. Without burst capacity, any requests that are consumed beyond the provisioned 100 RU/s would have been rate limited (429).
After the 10 seconds is over, the burst capacity has been used up. If the workload continues to exceed the provisioned 100 RU/s, any requests that are consumed beyond the provisioned 100 RU/s would now be rate limited (429). The maximum amount of burst capacity a physical partition can accumulate at any point in time is equal to 300 seconds * the provisioned RU/s of the physical partition.
Getting started
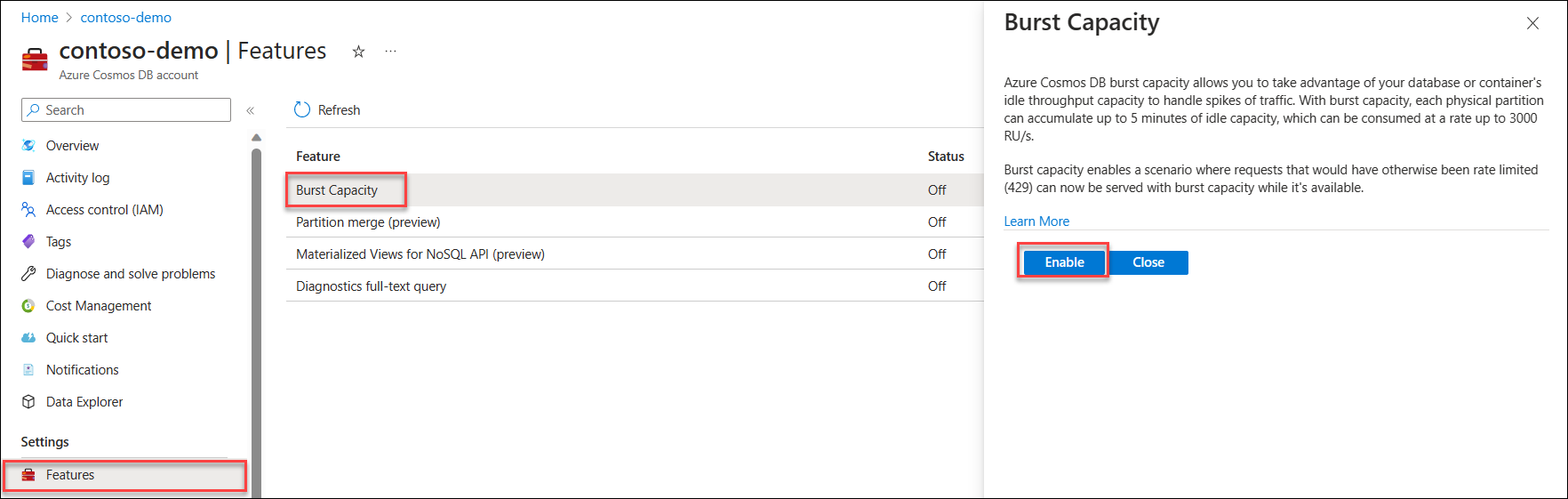
To get started using burst capacity, navigate to the Features page in your Azure Cosmos DB account. Select and enable the Burst Capacity feature.
Once you've enabled the feature, it takes 15-20 minutes to take effect.
Requirements
To enable burst capacity, your Azure Cosmos DB account must meet all the following criteria:
- Your Azure Cosmos DB account is using provisioned throughput (manual or autoscale). Burst capacity doesn't apply to serverless accounts.
- Your Azure Cosmos DB account is using API for NoSQL, Cassandra, Gremlin, MongoDB, or Table.
Next steps
- See the FAQ on burst capacity.
- Learn more about provisioned throughput.
- Learn more about request units.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for