Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Important
Azure Cosmos DB for PostgreSQL is no longer supported for new projects. Don't use this service for new projects. Instead, use one of these two services:
Use Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL for a distributed database solution designed for high-scale scenarios with a 99.999% availability service level agreement (SLA), instant autoscale, and automatic failover across multiple regions.
Use the Elastic Clusters feature of Azure Database For PostgreSQL for sharded PostgreSQL using the open-source Citus extension.
Common filter as shard key
To pick the shard key for a high-throughput transactional application, follow these guidelines:
- Choose a column that is used for point lookups and is present in most create, read, update, and delete operations.
- Choose a column that is a natural dimension in the data, or a central piece
of the application. For example:
- In an IOT workload,
device_idis a good distribution column.
- In an IOT workload,
The choice of a good shard key helps optimize network hops, while taking advantage of memory and compute to achieve millisecond latency.
Optimal data model for high-throughput apps
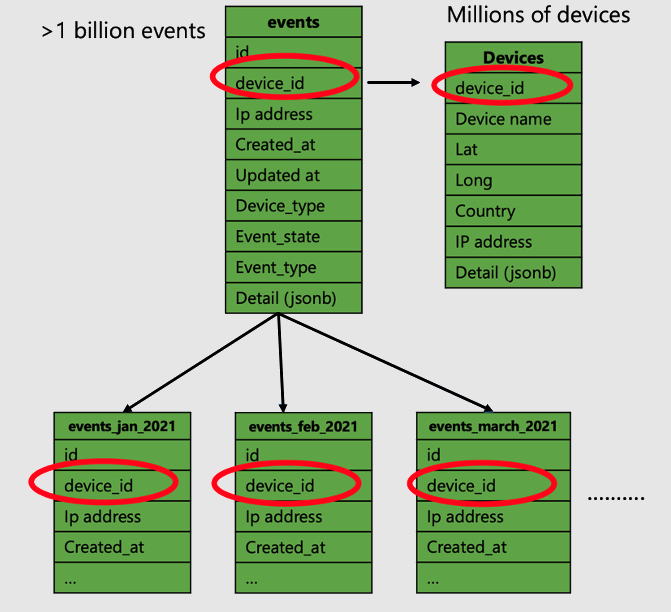
Below is an example of a sample data-model for an IoT app that captures
telemetry (time series data) from devices. There are two tables for capturing
telemetry: devices and events. There could be other tables, but they're not
covered in this example.
When building a high-throughput app, keep some optimization in mind.
- Distribute large tables on a common column that is central piece of the app,
and the column that your app mostly queries. In the above example of an IOT
app,
device_idis that column, and it co-locates the events and devices tables. - The rest of the small tables can be reference tables.
- As IOT apps have a time dimension, partition your distributed tables based on
time. You can use native Azure Cosmos DB for PostgreSQL time series capabilities to
create and maintain partitions.
- Partitioning helps efficiently filter data for queries with time filters.
- Expiring old data is also fast, using the DROP vs DELETE command.
- The events table in our example is partitioned by month.
- Use the JSONB datatype to store semi-structured data. Device telemetry
data is typically not structured, every device has its own metrics.
- In our example, the events table has a
detailcolumn, which is JSONB.
- In our example, the events table has a
- If your IoT app requires geospatial features, you can use the PostGIS extension, which Azure Cosmos DB for PostgreSQL supports natively.
Next steps
Now we've finished exploring data modeling for scalable apps. The next step is connecting and querying the database with your programming language of choice.