Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Use vector search in Azure Cosmos DB with the Node.js client library. Store and query vector data efficiently in your applications.
This quickstart uses a sample hotel dataset in a JSON file with vectors from the text-embedding-3-small model. The dataset includes hotel names, locations, descriptions, and vector embeddings.
Find the sample code with resource provisioning on GitHub.
Prerequisites
An Azure subscription
- If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a free account
An existing Azure Cosmos DB resource data plane access
- If you don't have a resource, create a new resource
- Firewall configured to allow access to your client IP address
- Role-based access control (RBAC) roles assigned:
- Cosmos DB Built-in Data Contributor (data plane)
- Role ID:
00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000002
-
- Custom domain configured
- Role-based access control (RBAC) role assigned:
- Cognitive Services OpenAI User
- Role ID:
5e0bd9bd-7b93-4f28-af87-19fc36ad61bd
text-embedding-3-smallmodel deployed
TypeScript: Install TypeScript globally:
npm install -g typescript
Create data file with vectors
Create a new data directory for the hotels data file:
mkdir dataCopy the raw data file with vectors to your
datadirectory.
Create a Node.js project
Create a new sibling directory for your project, at the same level as the data directory, and open it in Visual Studio Code:
mkdir vector-search-quickstart code vector-search-quickstartIn the terminal, initialize a Node.js project:
npm init -y npm pkg set type="module"Install the required packages:
npm install @azure/identity @azure/cosmos openai npm install @types/node cross-env --save-dev- @azure/identity - Azure authentication library for passwordless (managed identity) connections
- @azure/cosmos - Azure Cosmos DB client library for database operations
- openai - OpenAI SDK for generating embeddings with Azure OpenAI
- @types/node (dev) - TypeScript type definitions for Node.js APIs
- cross-env (dev) - Cross-platform environment variable setting for npm scripts
Create a
.envfile in your project root for environment variables:# Identity for local developer authentication with Azure CLI AZURE_TOKEN_CREDENTIALS=AzureCliCredential # Azure OpenAI Embedding Settings AZURE_OPENAI_EMBEDDING_MODEL=text-embedding-3-small AZURE_OPENAI_EMBEDDING_API_VERSION=2023-05-15 AZURE_OPENAI_EMBEDDING_ENDPOINT= # Cosmos DB configuration AZURE_COSMOSDB_ENDPOINT= # Data file DATA_FILE_WITH_VECTORS=../data/HotelsData_toCosmosDB_Vector.json FIELD_TO_EMBED=Description EMBEDDED_FIELD=DescriptionVector EMBEDDING_DIMENSIONS=1536Replace the placeholder values in the
.envfile with your own information:AZURE_OPENAI_EMBEDDING_ENDPOINT: Your Azure OpenAI resource endpoint URLAZURE_COSMOSDB_ENDPOINT: Your Azure Cosmos DB endpoint URL
Add a
tsconfig.jsonfile to configure TypeScript:{ "compilerOptions": { "target": "ES2020", "module": "NodeNext", "moduleResolution": "nodenext", "declaration": true, "outDir": "./dist", "strict": true, "esModuleInterop": true, "skipLibCheck": true, "noImplicitAny": false, "forceConsistentCasingInFileNames": true, "sourceMap": true, "resolveJsonModule": true, }, "include": [ "src/**/*" ], "exclude": [ "node_modules", "dist" ] }
Understand the document schema
Before building the application, understand how vectors are stored in Azure Cosmos DB documents. Each hotel document contains:
- Standard fields:
HotelId,HotelName,Description,Category, etc. - Vector field:
DescriptionVector- an array of 1536 floating-point numbers representing the semantic meaning of the hotel description
Here's a simplified example of a hotel document structure:
{
"HotelId": "1",
"HotelName": "Stay-Kay City Hotel",
"Description": "This classic hotel is fully-refurbished...",
"Rating": 3.6,
"DescriptionVector": [
-0.04886505,
-0.02030743,
0.01763356,
...
// 1536 dimensions total
]
}
Key points about storing embeddings:
- Vector arrays are stored as standard JSON arrays in your documents
- Vector policy defines the path (
/DescriptionVector), data type (float32), dimensions (1536), and distance function (cosine) - Indexing policy creates a vector index on the vector field for efficient similarity search
- The vector field should be excluded from standard indexing to optimize insertion performance
These policies are defined in the Bicep templates for the distance metrics for this sample project. For more information on vector policies and indexing, see Vector search in Azure Cosmos DB.
Create npm scripts
Edit the package.json file and add these scripts:
Use these scripts to compile TypeScript files and run the DiskANN index implementation.
"scripts": {
"build": "tsc",
"start:diskann": "cross-env VECTOR_ALGORITHM=diskann node --env-file .env dist/vector-search.js"
}
Create code files for vector search
Create a src directory for your TypeScript files. Add two files: vector-search.ts and utils.ts for your vector search implementation:
mkdir src
touch src/vector-search.ts
touch src/utils.ts
Create code for vector search
Paste the following code into the vector-search.ts file.
import path from 'path';
import { readFileReturnJson, getClientsPasswordless, validateFieldName, insertData, printSearchResults, getQueryActivityId } from './utils.js';
// ESM specific features - create __dirname equivalent
import { fileURLToPath } from "node:url";
import { dirname } from "node:path";
const __filename = fileURLToPath(import.meta.url);
const __dirname = dirname(__filename);
type VectorAlgorithm = 'diskann' | 'quantizedflat';
interface AlgorithmConfig {
containerName: string;
algorithmName: string;
}
const algorithmConfigs: Record<VectorAlgorithm, AlgorithmConfig> = {
diskann: {
containerName: 'hotels_diskann',
algorithmName: 'DiskANN'
},
quantizedflat: {
containerName: 'hotels_quantizedflat',
algorithmName: 'QuantizedFlat'
}
};
const config = {
query: "quintessential lodging near running trails, eateries, retail",
dbName: "Hotels",
algorithm: (process.env.VECTOR_ALGORITHM || 'diskann').trim().toLowerCase() as VectorAlgorithm,
dataFile: process.env.DATA_FILE_WITH_VECTORS!,
embeddedField: process.env.EMBEDDED_FIELD!,
embeddingDimensions: parseInt(process.env.EMBEDDING_DIMENSIONS! || process.env.VECTOR_EMBEDDING_DIMENSIONS || '1536', 10),
deployment: process.env.AZURE_OPENAI_EMBEDDING_MODEL!,
distanceFunction: process.env.VECTOR_DISTANCE_FUNCTION || 'cosine',
};
async function main() {
const { aiClient, dbClient } = getClientsPasswordless();
try {
// Validate algorithm selection
if (!Object.keys(algorithmConfigs).includes(config.algorithm)) {
throw new Error(`Invalid algorithm '${config.algorithm}'. Must be one of: ${Object.keys(algorithmConfigs).join(', ')}`);
}
if (!aiClient) {
throw new Error('Azure OpenAI client is not configured. Please check your environment variables.');
}
if (!dbClient) {
throw new Error('Database client is not configured. Please check your environment variables.');
}
const algorithmConfig = algorithmConfigs[config.algorithm];
const collectionName = algorithmConfig.containerName;
try {
const database = dbClient.database(config.dbName);
console.log(`Connected to database: ${config.dbName}`);
const container = database.container(collectionName);
console.log(`Connected to container: ${collectionName}`);
console.log(`\n📊 Vector Search Algorithm: ${algorithmConfig.algorithmName}`);
console.log(`📏 Distance Function: ${config.distanceFunction}`);
// Verify container exists by attempting a read
await container.read();
const data = await readFileReturnJson(path.join(__dirname, "..", config.dataFile));
await insertData(container, data);
const createEmbeddedForQueryResponse = await aiClient.embeddings.create({
model: config.deployment,
input: [config.query]
});
const safeEmbeddedField = validateFieldName(config.embeddedField);
const queryText = `SELECT TOP 5 c.HotelName, c.Description, c.Rating, VectorDistance(c.${safeEmbeddedField}, @embedding) AS SimilarityScore FROM c ORDER BY VectorDistance(c.${safeEmbeddedField}, @embedding)`;
console.log('\n--- Executing Vector Search Query ---');
console.log('Query:', queryText);
console.log('Parameters: @embedding (vector with', createEmbeddedForQueryResponse.data[0].embedding.length, 'dimensions)');
console.log('--------------------------------------\n');
const queryResponse = await container.items
.query({
query: queryText,
parameters: [
{ name: "@embedding", value: createEmbeddedForQueryResponse.data[0].embedding }
]
})
.fetchAll();
const activityId = getQueryActivityId(queryResponse);
if (activityId) {
console.log('Query activity ID:', activityId);
}
const { resources, requestCharge } = queryResponse;
printSearchResults(resources, requestCharge);
} catch (error) {
if ((error as any).code === 404) {
throw new Error(`Container or database not found. Ensure database '${config.dbName}' and container '${collectionName}' exist before running this script.`);
}
throw error;
}
} catch (error) {
console.error('App failed:', error);
process.exitCode = 1;
}
}
// Execute the main function
main().catch(error => {
console.error('Unhandled error:', error);
process.exitCode = 1;
});
This code:
- Configures either a
DiskANNorquantizedFlatvector algorithm from environment variables. - Connects to Azure OpenAI and Azure Cosmos DB using passwordless authentication.
- Loads pre-vectorized hotel data from a JSON file.
- Inserts data into the appropriate container.
- Generates an embedding for a natural-language query (
quintessential lodging near running trails, eateries, retail). - Executes a
VectorDistanceSQL query to retrieve the top 5 most semantically similar hotels ranked by similarity score. - Handles errors for missing clients, invalid algorithm selection, and non-existent containers/databases.
Understand the code: Generate embeddings with Azure OpenAI
The code creates embeddings for query text:
const createEmbeddedForQueryResponse = await aiClient.embeddings.create({
model, // OpenAI embedding model, e.g. "text-embedding-3-small"
input // Array of description strings to embed, e.g. ["quintessential lodging near running trails"]
});
This OpenAI API call for client.embeddings.create converts text like "quintessential lodging near running trails" into a 1536-dimension vector that captures its semantic meaning. For more details on generating embeddings, see Azure OpenAI embeddings documentation.
Understand the code: Store vectors in Azure Cosmos DB
All documents with vector arrays are inserted at scale using the executeBulkOperations function:
const response = await container.items.executeBulkOperations(operations);
This inserts hotel documents including their pre-generated DescriptionVector arrays into the container. You can safely pass in all the document data, and the client library handles the batch processing and retries for you.
Understand the code: Run vector similarity search
The code performs a vector search using the VectorDistance function:
const queryText = `SELECT TOP 5 c.HotelName, c.Description, c.Rating, VectorDistance(c.${safeEmbeddedField}, @embedding) AS SimilarityScore FROM c ORDER BY VectorDistance(c.${safeEmbeddedField}, @embedding)`;
const queryResponse = await container.items
.query({
query: queryText,
parameters: [
{ name: "@embedding", value: createEmbeddedForQueryResponse.data[0].embedding }
]
})
.fetchAll();
This code builds a parameterized SQL query that uses the VectorDistance function to compare the query's embedding vector (@embedding) against each document's stored vector field (DescriptionVector), returning the top 5 hotels with their name and similarity score, ordered from most similar to least similar. The query embedding is passed as a parameter to avoid injection and comes from a prior Azure OpenAI embeddings.create call.
What this query returns:
- Top 5 most similar hotels based on vector distance
- Hotel properties:
HotelName,Description,Rating SimilarityScore: A numeric value indicating how similar each hotel is to your query- Results ordered from most similar to least similar
For more information on the VectorDistance function, see VectorDistance documentation.
Create utility functions
Paste the following code into utils.ts:
import { CosmosClient, BulkOperationType } from '@azure/cosmos';
import { AzureOpenAI } from "openai";
import { promises as fs } from "fs";
import { DefaultAzureCredential, getBearerTokenProvider } from "@azure/identity";
// Define a type for JSON data
export type JsonData = Record<string, any>;
export function getClients(): { aiClient: AzureOpenAI | null; dbClient: CosmosClient | null } {
let aiClient: AzureOpenAI | null = null;
let dbClient: CosmosClient | null = null;
const apiKey = process.env.AZURE_OPENAI_EMBEDDING_KEY!;
const apiVersion = process.env.AZURE_OPENAI_EMBEDDING_API_VERSION!;
const endpoint = process.env.AZURE_OPENAI_EMBEDDING_ENDPOINT!;
const deployment = process.env.AZURE_OPENAI_EMBEDDING_MODEL!;
if (apiKey && apiVersion && endpoint && deployment) {
aiClient = new AzureOpenAI({
apiKey,
apiVersion,
endpoint,
deployment
});
}
// Cosmos DB connection string or endpoint/key
// You may need to use endpoint and key separately for CosmosClient
const cosmosEndpoint = process.env.AZURE_COSMOSDB_ENDPOINT!;
const cosmosKey = process.env.AZURE_COSMOSDB_KEY!;
if (cosmosEndpoint && cosmosKey) {
dbClient = new CosmosClient({ endpoint: cosmosEndpoint, key: cosmosKey });
}
return { aiClient, dbClient };
}
/**
* Get Azure OpenAI and Cosmos DB clients using passwordless authentication (managed identity)
* This function uses DefaultAzureCredential for authentication instead of API keys
*
* @returns Object containing AzureOpenAI and CosmosClient instances or null if configuration is missing
*/
export function getClientsPasswordless(): { aiClient: AzureOpenAI | null; dbClient: CosmosClient | null } {
let aiClient: AzureOpenAI | null = null;
let dbClient: CosmosClient | null = null;
// For Azure OpenAI with DefaultAzureCredential
const apiVersion = process.env.AZURE_OPENAI_EMBEDDING_API_VERSION!;
const endpoint = process.env.AZURE_OPENAI_EMBEDDING_ENDPOINT!;
const deployment = process.env.AZURE_OPENAI_EMBEDDING_MODEL!;
if (apiVersion && endpoint && deployment) {
const credential = new DefaultAzureCredential();
const scope = "https://cognitiveservices.azure.com/.default";
const azureADTokenProvider = getBearerTokenProvider(credential, scope);
aiClient = new AzureOpenAI({
apiVersion,
endpoint,
deployment,
azureADTokenProvider
});
}
// For Cosmos DB with DefaultAzureCredential
const cosmosEndpoint = process.env.AZURE_COSMOSDB_ENDPOINT!;
if (cosmosEndpoint) {
const credential = new DefaultAzureCredential();
dbClient = new CosmosClient({
endpoint: cosmosEndpoint,
aadCredentials: credential // Use DefaultAzureCredential instead of key
});
}
return { aiClient, dbClient };
}
export async function readFileReturnJson(filePath: string): Promise<JsonData[]> {
console.log(`Reading JSON file from ${filePath}`);
const fileAsString = await fs.readFile(filePath, "utf-8");
return JSON.parse(fileAsString);
}
export async function writeFileJson(filePath: string, jsonData: JsonData): Promise<void> {
const jsonString = JSON.stringify(jsonData, null, 2);
await fs.writeFile(filePath, jsonString, "utf-8");
console.log(`Wrote JSON file to ${filePath}`);
}
/**
* Check if a container has any documents
* @param container - Cosmos DB container reference
* @returns Number of documents in the container
*/
async function getDocumentCount(container: any): Promise<number> {
const countResult = await container.items
.query('SELECT VALUE COUNT(1) FROM c')
.fetchAll();
return countResult.resources[0];
}
export async function insertData(container, data): Promise<{ total: number; inserted: number; failed: number; skipped: number; requestCharge: number }> {
// Check if container already has documents
const existingCount = await getDocumentCount(container);
if (existingCount > 0) {
console.log(`Container already has ${existingCount} documents. Skipping insert.`);
return { total: 0, inserted: 0, failed: 0, skipped: existingCount, requestCharge: 0 };
}
// Cosmos DB uses containers instead of collections
// Use SDK bulk operations; let SDK handle batching, dispatch, and throttling
console.log(`Inserting ${data.length} items using executeBulkOperations...`);
// Prepare bulk operations for all items
const operations = data.map((item: any) => ({
operationType: BulkOperationType.Create,
resourceBody: {
id: item.HotelId, // Map HotelId to id (required by Cosmos DB)
...item,
},
// Partition key must be passed as array: [value] for /HotelId partition
partitionKey: [item.HotelId],
}));
let inserted = 0;
let failed = 0;
let skipped = 0;
let totalRequestCharge = 0;
try {
const startTime = Date.now();
console.log(`Starting bulk insert (${operations.length} items)...`);
const response = await container.items.executeBulkOperations(operations);
const endTime = Date.now();
const duration = ((endTime - startTime) / 1000).toFixed(2);
console.log(`Bulk insert completed in ${duration}s`);
totalRequestCharge += getBulkOperationRUs(response);
// Count inserted, skipped, and failed
if (response) {
response.forEach((result: any) => {
if (result.statusCode >= 200 && result.statusCode < 300) {
inserted++;
} else if (result.statusCode === 409) {
skipped++;
} else {
failed++;
}
});
}
} catch (error) {
console.error(`Bulk insert failed:`, error);
failed = operations.length;
}
console.log(`\nInsert Request Charge: ${totalRequestCharge.toFixed(2)} RUs\n`);
return { total: data.length, inserted, failed, skipped, requestCharge: totalRequestCharge };
}
/**
* Validates a field name to ensure it's a safe identifier for use in queries.
* This prevents NoSQL injection when using string interpolation in query construction.
*
* @param fieldName - The field name to validate
* @returns The validated field name
* @throws Error if the field name contains invalid characters
*
* @example
* ```typescript
* const safeField = validateFieldName(config.embeddedField);
* const query = `SELECT * FROM c WHERE c.${safeField} = @value`;
* ```
*/
export function validateFieldName(fieldName: string): string {
// Allow only alphanumeric characters and underscores, must start with letter or underscore
const validIdentifierPattern = /^[A-Za-z_][A-Za-z0-9_]*$/;
if (!validIdentifierPattern.test(fieldName)) {
throw new Error(
`Invalid field name: "${fieldName}". ` +
`Field names must start with a letter or underscore and contain only letters, numbers, and underscores.`
);
}
return fieldName;
}
/**
* Print search results in a consistent format
*/
export function printSearchResults(searchResults: any[], requestCharge?: number): void {
console.log('\n--- Search Results ---');
if (!searchResults || searchResults.length === 0) {
console.log('No results found.');
return;
}
searchResults.forEach((result, index) => {
console.log(`${index + 1}. ${result.HotelName}, Score: ${result.SimilarityScore.toFixed(4)}`);
});
if (requestCharge !== undefined) {
console.log(`\nVector Search Request Charge: ${requestCharge.toFixed(2)} RUs`);
}
console.log('');
}
export function getQueryActivityId(queryResponse: any): string | undefined {
if (!queryResponse) {
return undefined;
}
const diagnostics = queryResponse.diagnostics as any;
const gatewayStats = Array.isArray(diagnostics?.clientSideRequestStatistics?.gatewayStatistics)
? diagnostics.clientSideRequestStatistics.gatewayStatistics
: [];
const gatewayActivityId = gatewayStats.find((entry: any) => entry?.activityId)?.activityId;
return queryResponse.activityId ?? gatewayActivityId;
}
export function getBulkOperationRUs(response: any): number {
// Response shape can vary depending on SDK/version:
// - An array of operation results
// - An object with `resources` or `results` array
// - A single operation result object
if (!response) {
console.warn('Empty response. Cannot calculate RUs from bulk operation.');
return 0;
}
// Normalize into an array of result items
let items: any[] = [];
if (Array.isArray(response)) {
items = response;
} else if (Array.isArray(response.resources)) {
items = response.resources;
} else if (Array.isArray(response.results)) {
items = response.results;
} else if (Array.isArray(response.result)) {
items = response.result;
} else if (typeof response === 'object') {
// If it's a single operation result, wrap it so downstream logic is uniform
items = [response];
} else {
console.warn('Response does not contain bulk operation results.');
return 0;
}
let totalRequestCharge = 0;
items.forEach((result: any) => {
let requestCharge = 0;
// 1) Direct numeric property
if (typeof result.requestCharge === 'number') {
requestCharge = result.requestCharge;
}
// 1b) Some SDKs nest the operation response under `response` and expose requestCharge there
if (!requestCharge && result.response && typeof result.response.requestCharge === 'number') {
requestCharge = result.response.requestCharge;
}
if (!requestCharge && result.response && typeof result.response.requestCharge === 'string') {
const parsed = parseFloat(result.response.requestCharge);
requestCharge = isNaN(parsed) ? 0 : parsed;
}
// 2) String numeric value
if (!requestCharge && typeof result.requestCharge === 'string') {
const parsed = parseFloat(result.requestCharge);
requestCharge = isNaN(parsed) ? 0 : parsed;
}
// 3) operationResponse may contain headers in different shapes
if (!requestCharge && result.operationResponse) {
const op = result.operationResponse;
const headerVal = op.headers?.['x-ms-request-charge']
?? (typeof op.headers?.get === 'function' ? op.headers.get('x-ms-request-charge') : undefined)
?? op._response?.headers?.['x-ms-request-charge'];
if (headerVal !== undefined) {
const parsed = parseFloat(headerVal as any);
requestCharge = isNaN(parsed) ? 0 : parsed;
}
}
// 4) Some responses include headers at top-level or in `headers`
if (!requestCharge && result.headers) {
const hv = result.headers['x-ms-request-charge'] ?? (typeof result.headers.get === 'function' ? result.headers.get('x-ms-request-charge') : undefined);
if (hv !== undefined) {
const parsed = parseFloat(hv as any);
requestCharge = isNaN(parsed) ? 0 : parsed;
}
}
// 5) Fallback: some SDKs expose RU on resourceOperation or nested fields
if (!requestCharge) {
// Try several nested locations where headers may be present
const candidateHeaders =
result.operationResponse?._response?.headers
?? result.operationResponse?.headers
?? result._response?.headers
?? result.headers;
const fallback = candidateHeaders ? (candidateHeaders['x-ms-request-charge'] ?? (typeof candidateHeaders.get === 'function' ? candidateHeaders.get('x-ms-request-charge') : undefined)) : undefined;
if (fallback !== undefined) {
const parsed = parseFloat(fallback as any);
requestCharge = isNaN(parsed) ? 0 : parsed;
}
}
totalRequestCharge += requestCharge;
});
// If we didn't find any RUs, print a small sample to help debugging
if (totalRequestCharge === 0) {
try {
const sample = items[0];
const sampleKeys = sample ? Object.keys(sample) : [];
console.warn('getBulkOperationRUs: no RUs found. Sample result keys:', sampleKeys);
if (sample && sample.response) {
try {
const respKeys = Object.keys(sample.response);
console.warn(' sample.response keys:', respKeys);
const hdrs = sample.response.headers ?? sample.response._response?.headers ?? sample.response?.operationResponse?.headers;
console.warn(' sample.response headers sample:', hdrs ? Object.keys(hdrs) : hdrs);
} catch (e) {
console.warn(' Could not inspect sample.response for headers:', e);
}
}
} catch (e) {
console.warn('Could not inspect sample result for debugging:', e);
}
}
return totalRequestCharge;
}
This utility module provides these key functions:
getClientsPasswordless: Creates and returns clients for Azure OpenAI and Azure Cosmos DB using passwordless authentication. Enable RBAC on both resources and sign in to Azure CLIinsertData: Inserts data in batches into an Azure Cosmos DB container and creates standard indexes on specified fieldsprintSearchResults: Prints the results of a vector search, including the score and hotel namevalidateFieldName: Validates that a field name exists in the datagetBulkOperationRUs: Estimates the Request Units (RUs) for bulk operations based on the number of documents and vector dimensions
Authenticate with Azure CLI
Sign in to Azure CLI before you run the application so the app can access Azure resources securely.
az login
The code uses your local developer authentication to access Azure Cosmos DB and Azure OpenAI with the getClientsPasswordless function from utils.ts. When you set AZURE_TOKEN_CREDENTIALS=AzureCliCredential, you deterministically select which credential DefaultAzureCredential uses from its credential chain. The function relies on DefaultAzureCredential from @azure/identity, which walks an ordered chain of credential providers but honors the environment variable to resolve to Azure CLI credentials first. Learn more about how to Authenticate JavaScript apps to Azure services using the Azure Identity library.
Build and run the application
Build the TypeScript files, then run the application:
npm run build
npm run start:diskann
The app logging and output show:
- Data insertion status
- Vector index creation
- Search results with hotel names and similarity scores
Connected to database: Hotels
Connected to container: hotels_diskann
📊 Vector Search Algorithm: DiskANN
📏 Distance Function: cosine
Reading JSON file from C:\azure-samples\cosmos-db-vector-samples\data\HotelsData_toCosmosDB_Vector.json
Inserting 50 items using executeBulkOperations...
Starting bulk insert (50 items)...
Bulk insert completed in 3.19s
Insert Request Charge: 6805.25 RUs
--- Executing Vector Search Query ---
Query: SELECT TOP 5 c.HotelName, c.Description, c.Rating, VectorDistance(c.DescriptionVector, @embedding) AS SimilarityScore FROM c ORDER BY VectorDistance(c.DescriptionVector, @embedding)
Parameters: @embedding (vector with 1536 dimensions)
--------------------------------------
Query activity ID: <ACTIVITY_ID>
--- Search Results ---
1. Royal Cottage Resort, Score: 0.4991
2. Country Comfort Inn, Score: 0.4786
3. Nordick's Valley Motel, Score: 0.4635
4. Economy Universe Motel, Score: 0.4461
5. Roach Motel, Score: 0.4388
Vector Search Request Charge: 5.32 RUs
Distance metrics
Azure Cosmos DB supports three distance functions for vector similarity:
| Distance Function | Score Range | Interpretation | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cosine (default) | 0.0 to 1.0 | Higher scores (closer to 1.0) indicate greater similarity | General text similarity, Azure OpenAI embeddings (used in this quickstart) |
| Euclidean (L2) | 0.0 to ∞ | Lower = more similar | Spatial data, when magnitude matters |
| Dot Product | -∞ to +∞ | Higher = more similar | When vector magnitudes are normalized |
The distance function is set in the vector embedding policy when creating the container. This is provided in the infrastructure in the sample repository. It is defined as part of the container definition.
{
name: 'hotels_diskann'
partitionKeyPaths: [
'/HotelId'
]
indexingPolicy: {
indexingMode: 'consistent'
automatic: true
includedPaths: [
{
path: '/*'
}
]
excludedPaths: [
{
path: '/_etag/?'
}
{
path: '/DescriptionVector/*'
}
]
vectorIndexes: [
{
path: '/DescriptionVector'
type: 'diskANN'
}
]
}
vectorEmbeddingPolicy: {
vectorEmbeddings: [
{
path: '/DescriptionVector'
dataType: 'float32'
dimensions: 1536
distanceFunction: 'cosine'
}
]
}
}
This Bicep code defines an Azure Cosmos DB container configuration for storing hotel documents with vector search capabilities.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
partitionKeyPaths |
Partitions documents by HotelId for distributed storage. |
indexingPolicy |
Configures automatic indexing on all document properties (/*) except the system _etag field and the DescriptionVector array to optimize write performance. Vector fields don't need standard indexing because they use a specialized vectorIndexes configuration instead. |
vectorIndexes |
Creates either a DiskANN or quantizedFlat index on the /DescriptionVector path for efficient similarity searches. |
vectorEmbeddingPolicy |
Defines the vector field's characteristics: float32 data type with 1536 dimensions (matching the text-embedding-3-small model output) and cosine as the distance function to measure similarity between vectors during queries. |
Interpret similarity scores
In the example output using cosine similarity:
- 0.4991 (Royal Cottage Resort) - Highest similarity, best match for "lodging near running trails, eateries, retail"
- 0.4388 (Roach Motel) - Lower similarity, still relevant but less matching
- Scores closer to 1.0 indicate stronger semantic similarity
- Scores near 0 indicate little similarity
Important notes:
- Absolute score values depend on your embedding model and data
- Focus on relative ranking rather than absolute thresholds
- Azure OpenAI embeddings work best with cosine similarity
For detailed information on distance functions, see What are distance functions?
View and manage data in Visual Studio Code
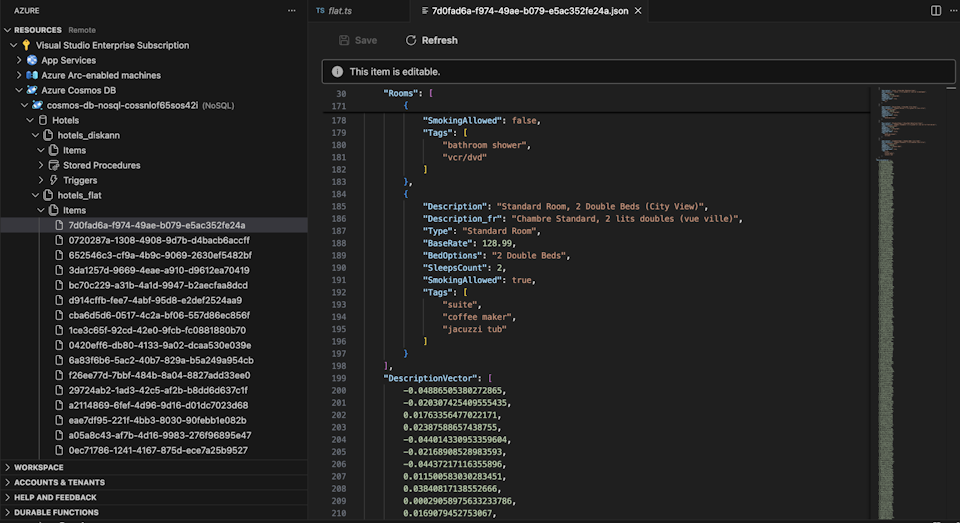
Select the Cosmos DB extension in Visual Studio Code to connect to your Azure Cosmos DB account.
View the data and indexes in the Hotels database.
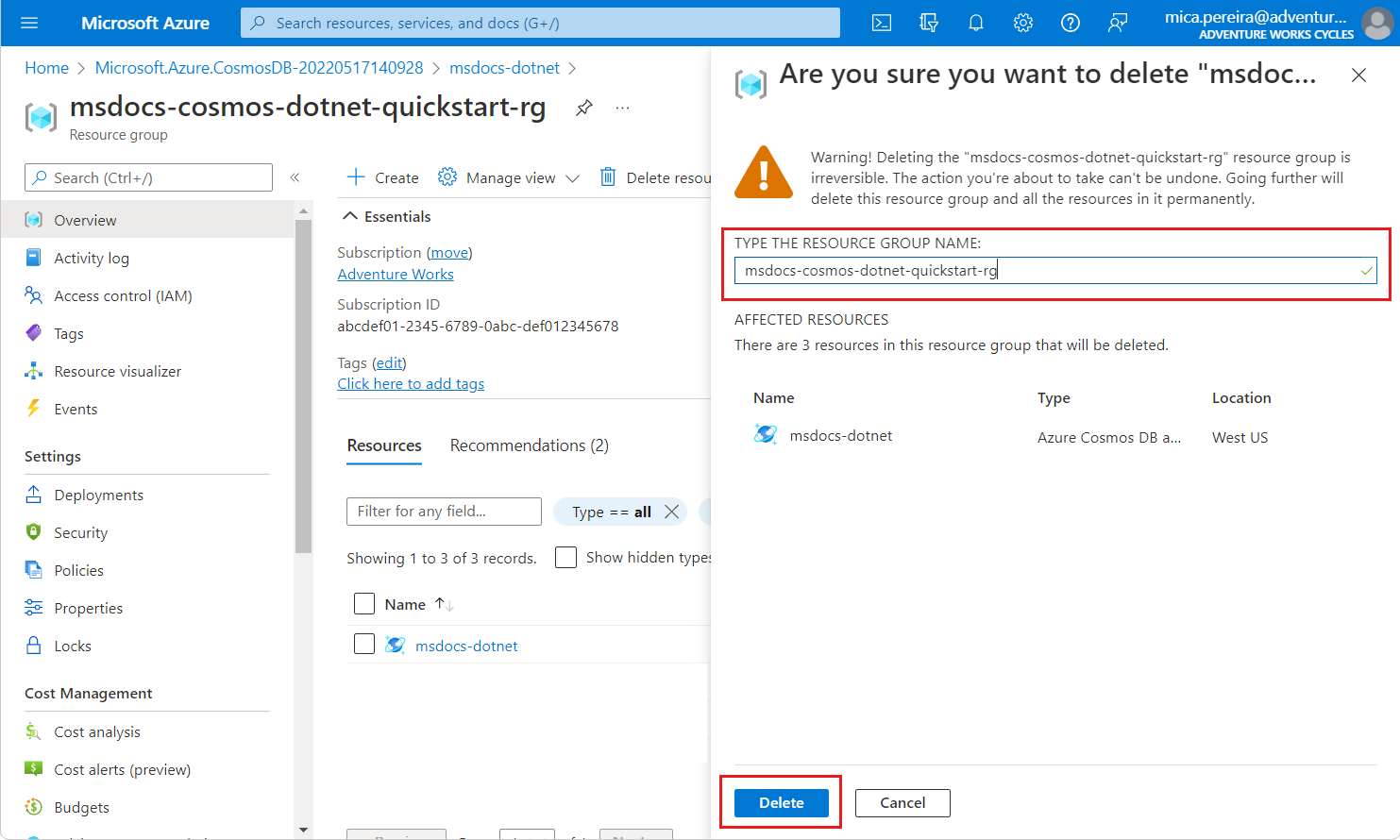
Clean up resources
When you no longer need the API for NoSQL account, you can delete the corresponding resource group.