Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This article helps you troubleshoot Cloud Solution Provider (CSP) billing issues using pivot tables in your Partner Center reconciliation (usage) files. Azure usage files contain all your Azure usage and consumption information. The information in the file can help you understand:
- Understand how Azure reservations are getting used and applied
- Reconcile information in Cost Management with your billed invoice
- Troubleshoot a cost spike
- Calculate a refund amount for a service level agreement
By using the information from your usage files, you can get a better understanding of usage issues and diagnose them. Usage files are generated in comma delimited (CSV) format. Because the usage files might be large CSV files, they're easier to manipulate and view as pivot tables in a spreadsheet application like Excel. Examples in this article use Excel, but you can use any spreadsheet application that you want.
Only billing admins and admin agents have access to download reconciliation files. For more information, see Learn how to read the line items in your Partner Center reconciliation files.
Get the data and format it
Because Azure usage files are in CSV format, you need to prepare the data for use in Excel. Use the following steps to format the data as table.
- Download the usage file using the instructions at Find your bill.
- Open the file in Excel.
- The unformatted data resembles the following example.

- Select the first field in the table, PartnerID.
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Down arrow and then Ctrl + Shift + Right Arrow to select all the information in the table.
- In the top menu, select Insert > Table. In the Create table box, select My table has headers and then select OK.

- In top menu, select Insert > Pivot Table and then select OK. The action creates a new sheet in the file and takes you to the pivot table area on the right side of the sheet.

The PivotTable Fields area is a drag-and-drop area. Continue to the next section to create the pivot table.
Create pivot table to view Azure costs by resources
In this section, you create a pivot table where you can troubleshoot overall general Azure usage. The example table can help you investigate which service consumes the most resources. Or you can view the resources that incur the most cost and see how a service is getting charged.
- In the PivotTable Fields area, drag Service Name and Resource to the Rows area. Put Resource below Service Name.

- Next, put Post-Tax Total in the Values area. You can also use the Consumed Quantity column instead to get information about consumption units and transactions. For example, GB and Hours. Or, transactions instead of cost in different currencies like USD, EUR, and INR.
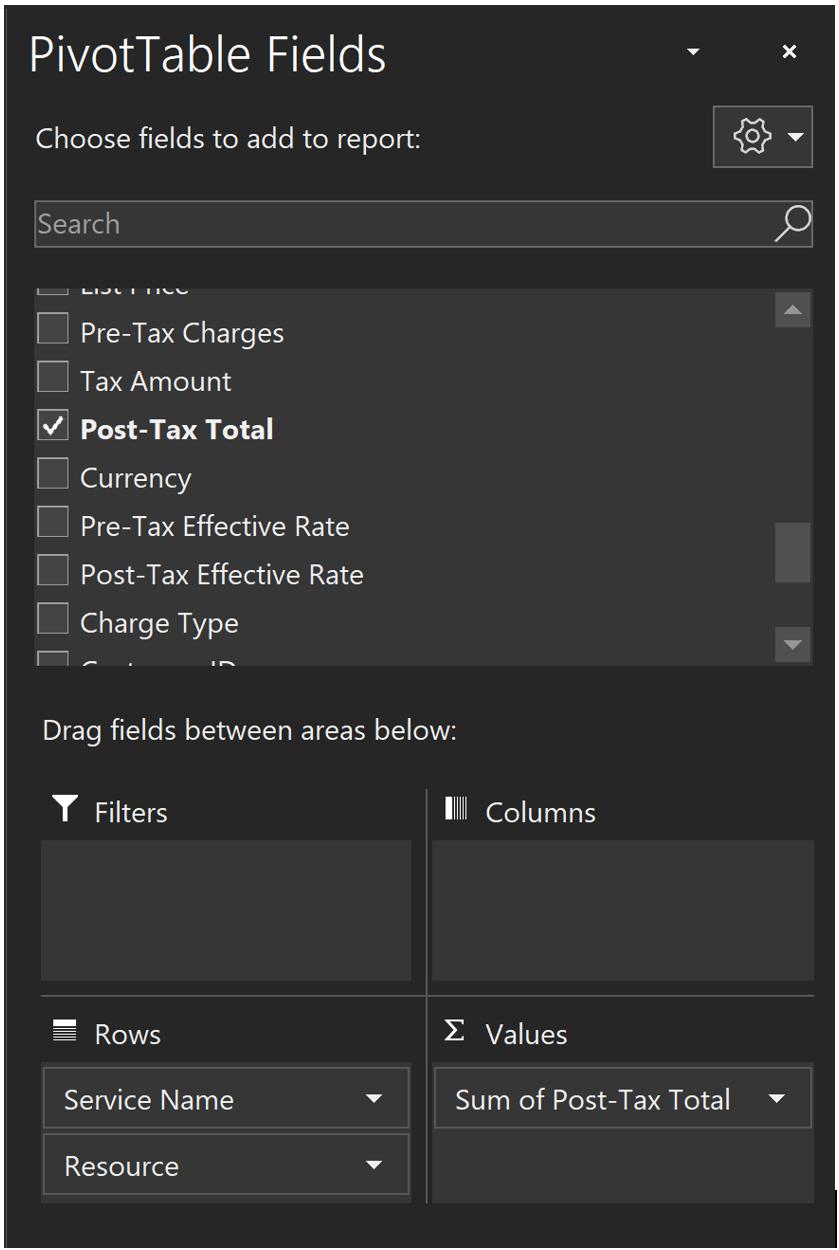
- Now you have a dashboard for generalized consumption investigation. You can filter for a specific service using the filtering options in the pivot table.
 To filter a second level in a pivot table, for example a resource, select a second-level item in the table.
To filter a second level in a pivot table, for example a resource, select a second-level item in the table.

- For additional filters, you can add SubscriptionID and Customer Company Name to the Filters area and select the desired scope.
Create a pivot table to view Azure usage by date
In this section, you create a pivot table where you can troubleshoot overall general Azure usage by Consumed Quantity and date. It's useful to identify billing spikes by date and service. Or you can view the resources that incur the most cost and see how a service is getting charged.
Your reconciliation file has two tables. One is at the top (the main table) and there's another table at the bottom of the document. This second table has much of the same information, however it doesn't include pricing or cost details. It does have usage date and consumed quantity.
- Use the same steps from the Get the data and format it section to create an Excel table with the information at the bottom of the reconciliation file.
- When the table is ready and you have a pivot table sheet, use the same steps from the create-pivot-table-to-view-azure-costs-by-resources section to prepare the dashboard. Instead of using the Post-Tax total, put Consumed quantity in the Values area.
- Add Usage Date to the columns section. The pivot table should look like the following example.

- You now have a dashboard that shows the usage per date. You can extend each month by selecting the + symbol.
The dashboard shows the consumed quantity in units such as GB, Hours, and Transfers.
To view the price per day, you can add Resource GUID to the Rows area. In the upper table, add the unit price ( ListPrice ) for the resource. Multiply ListPrice by the Consumed quantity to calculate your pre-tax charges. The amounts should match.
Some resources (services) have scaled pricing by consumed quantity. For example, some resources have a higher price for the first 100 GB consumed and a lower price for the GB used afterward. Keep scaled pricing in mind when you calculate costs manually.
Create pivot table to view cost for a specific resource
A single resource can incur several charges for different services. For example, a virtual machine can incur Compute charges, OS licensing, Bandwidth (Data transfers), RI usage, and storage for snapshots. Whenever you want to review the overall usage for specific resources, the following steps guide you through creating a dashboard to view overall usage with your usage files.
Reconciliation files don't contain resource-specific details. So, you use the aggregated usage file. Contact Azure Billing support to have them provide you with the aggregated usage file for your subscription. Aggregated files are generated at the subscription level. The unformatted data resembles the following example.
The file contains the following columns.
- UsageStart and UsageEnd - Date for each line item (each unit of usage). For example, each day.
- MeteredResourceID – In Azure, it corresponds to the meter ID.
- Properties - Contains the Instance ID (resource name) with other details such as location.
- Quantity - Consumed quantity in the reconciliation file.
- Select the first field in the table, PartnerID.
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Down arrow and then Ctrl + Shift + Right Arrow to select all the information in the table.
- In the top menu, select Insert > Table. In the Create table box, select My table has headers and then select OK.

- In top menu, select Insert > Pivot Table and then select OK. The action creates a new sheet in the file and takes you to the pivot table area on the right side of the sheet.

- Next, add MeteredResourceID to the Rows area and Quantity to Values. Results show the overall usage information. For additional details, put UsageEndDateTime in the Columns area.

- To view an overall report, add Properties to Rows under MeteredResourceID. It shows a complete dashboard for your usage.
- To filter by a specific resource, add Properties to the Filters area and select the desired usage. You can use Search to find a resource name. To view the cost for the resource, find the total consumed quantity and multiply the value by the list price. The list price is specific for each Resource GUID (MeteredResourceID). If a resource is consuming several MeteredResourceIDs, you have to note the total value for each ID.
Transform data before using large usage files
Sometimes your usage or reconciliation file is too large to open. Or, you might need just a portion of the information to troubleshoot an issue. For example, you might want only information only a particular resource or just the consumption for few services or resource groups. You can transform the data to summarize it before you create pivot tables.
Open a blank workbook in Excel.
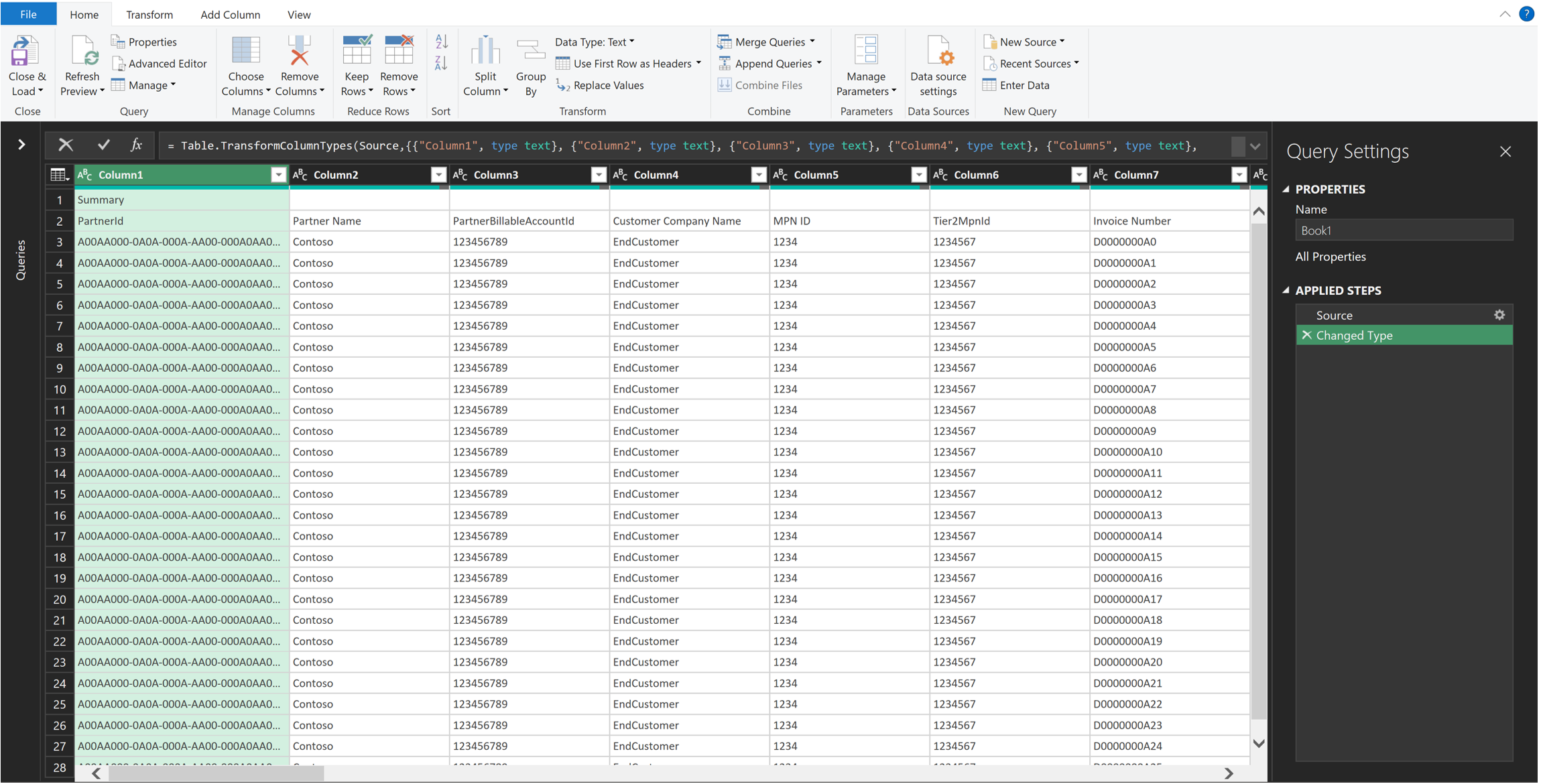
In the upper menu, select Data > From Text/CSV, select your usage file, and then select Import.
At the bottom of the window, select Transform Data. A new window shows a summary of the data.
If you have a Microsoft Customer Agreement, skip this step and continue to the next because MCA usage files usually have the column titles in the first rows. Prepare the data by creating the table. Remove the top rows, leaving only the titles. Select Remove Rows > Remove Top Rows.
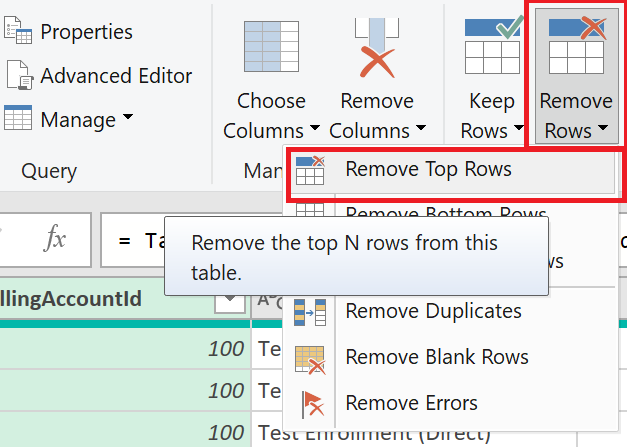
In the Remove Top Rows window, enter the number of rows to remove at the top. For EA usually 2, for CSP usually 1. Select OK.
Select Use First Row as Headers.
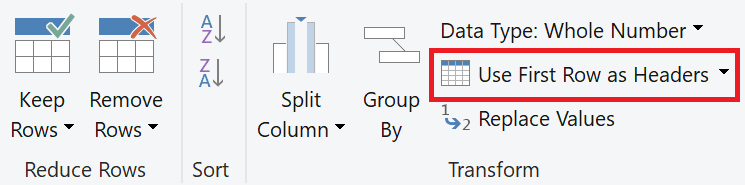
The table view shows column titles at the top.
Next, add a filter. Use the selector arrows at the right of each column title to filter. Suggested filters are Subscription ID, Service Name (Meter category), Instance ID, resource group. You can use multiple filters in the same document. We recommend that you apply all possible filters to reduce the document size and help later work.
After you've applied your filters, select Close & Load.
The file loads and shows a table with filtered usage data. Now you can create a new pivot table to troubleshoot usage issues.

