How to secure access to data catalog and data assets
Important
Azure Data Catalog was retired on May 15, 2024.
For data catalog features, use the Microsoft Purview service, which offers unified data governance for your entire data estate.
Important
This feature is available only in the standard edition of Azure Data Catalog.
Azure Data Catalog allows you to specify who can access the data catalog and what operations (register, annotate, take ownership) they can perform on metadata in the catalog.
Catalog users and permissions
To give a user or a group the access to a data catalog and set permissions:
On the home page of your data catalog, select Settings on the toolbar.

In the settings page, expand the Catalog Users section.

Select Add.
Enter the fully qualified user name or name of the security group in the Microsoft Entra ID associated with the catalog. Use comma (`,’) as a separator if you're adding more than one user or group.
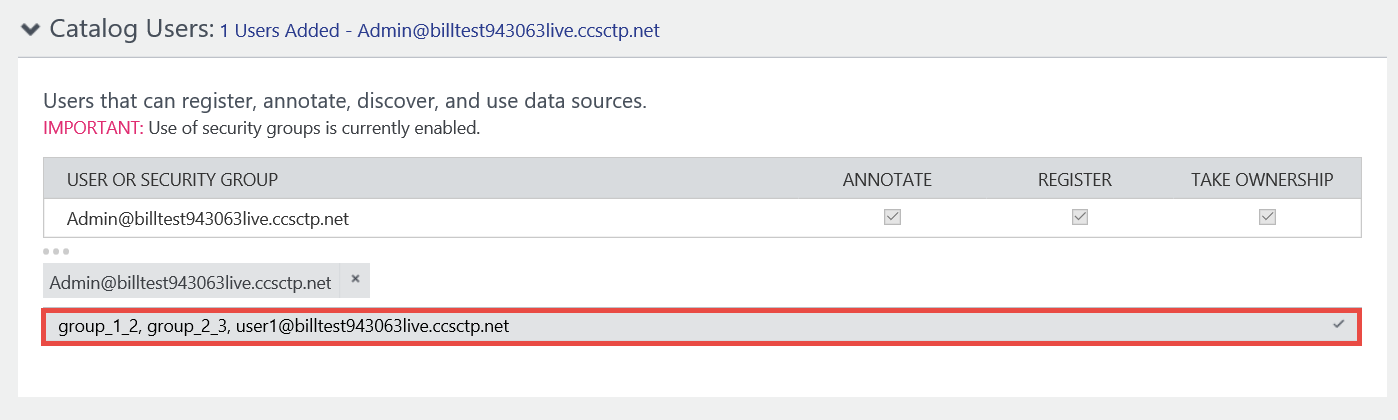
Press ENTER or TAB out of the text box.
Confirm that all permissions (Annotate, Register, and Take Ownership) are assigned to these users or groups by default. That is, the user or group can register data assets, annotate data assets, and take ownership of data assets.
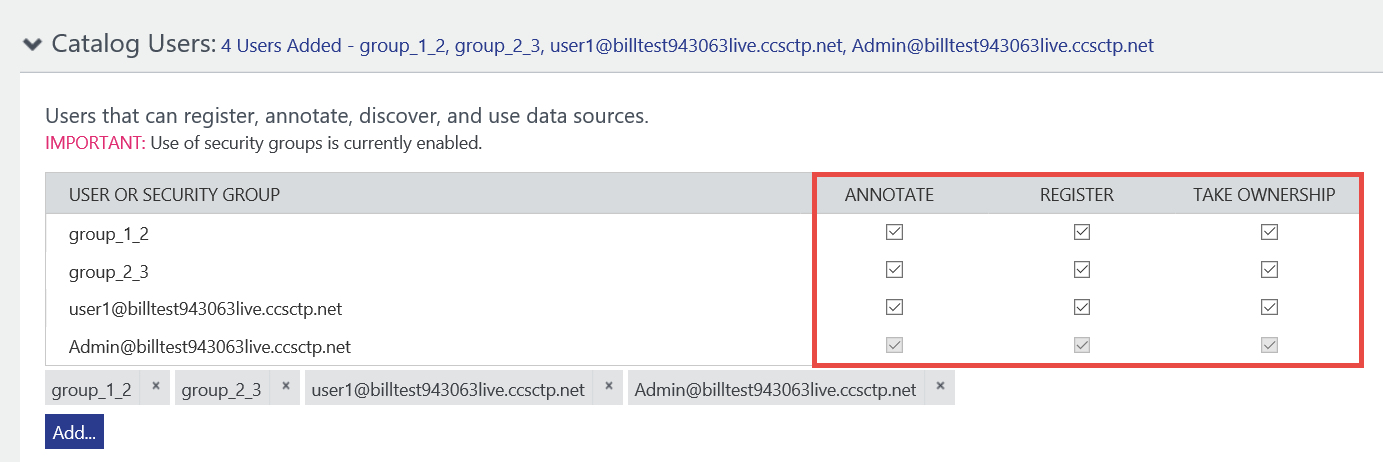
To give a user or group only the read access to the catalog, clear the annotate option for that user or group. Now the user or group can’t annotate data assets in the catalog, but they can view them.
To deny a user or group from registering data assets, clear the register option for that user or group.
To deny a user from taking ownership of a data asset, clear the take ownership option for that user or group.
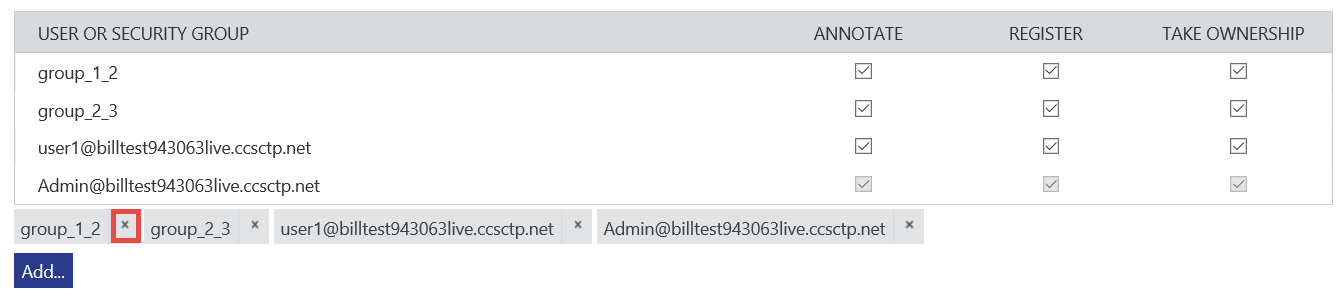
To delete a user/group from catalog users, select x for the user/group at the bottom of the list.
Important
We recommend that you add security groups to catalog users rather than adding users directly and assign permissions. Then, add users to the security groups that match their roles and their required access to the catalog.
Special considerations
- The permissions assigned to security groups are additive. For example: a user is in two groups. One group has annotate permissions and other group doesn't have annotate permissions. Then, the user has annotate permissions.
- The permissions assigned explicitly to a user override the permissions assigned to groups to which the user belongs. For example: A user is in a group that has annotate permissions. If you explicitly add the user to catalog users and don't assign annotate permissions, then the user can’t annotate data assets. The explicit permission on the user overrides the group permissions.