Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This article provides a high-level overview of Azure Databricks architecture, including its enterprise architecture, in combination with Azure.
Databricks objects
A Azure Databricks account is the top-level construct that you use to manage Azure Databricks across your organization. At the account level, you manage:
- Identity and access: Users, groups, service principals, and user provisioning.
Workspace management: Create, update, and delete workspaces across multiple regions.
Unity Catalog metastore management: Create and attach metastore to workspaces.
Usage management: Billing, compliance, and policies.
An account can contain multiple workspaces and Unity Catalog metastores.
Workspaces are the collaboration environment where users run compute workloads such as ingestion, interactive exploration, scheduled jobs, and ML training.
Unity Catalog metastores are the central governance system for data assets such as tables and ML models. You organize data in a metastore under a three-level namespace:
<catalog-name>.<schema-name>.<object-name>
Metastores are attached to workspaces. You can link a single metastore to multiple Azure Databricks workspaces in the same region, giving each workspace the same data view. Data access controls can be managed across all linked workspaces.

Workspace architecture
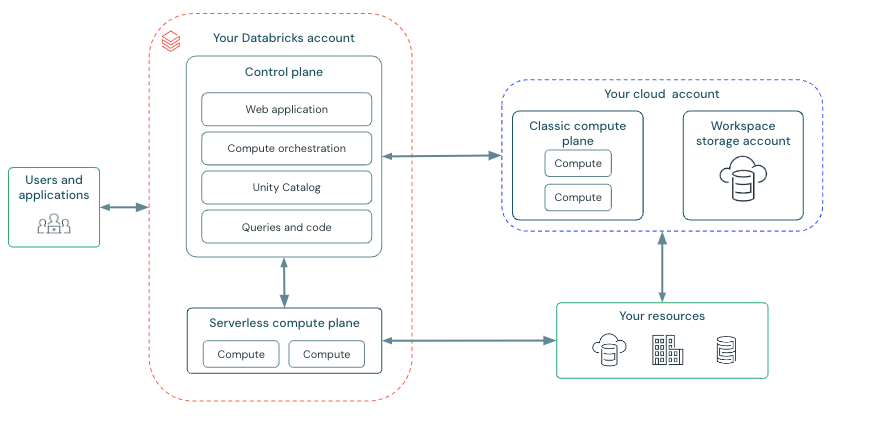
Azure Databricks operates out of a control plane and a compute plane.
The control plane includes the backend services that Azure Databricks manages in your Azure Databricks account. The control plane is located in the Azure Databricks account, not your cloud account. The web application is in the control plane.
The compute plane is where your data is processed. There are two types of compute planes depending on the compute that you are using.
- For serverless compute, the serverless compute resources run in a serverless compute plane in your Azure Databricks account.
- For classic Azure Databricks compute, the compute resources are in your Azure subscription in what is called the classic compute plane. This refers to the network in your Azure subscription and its resources.
To learn more about classic compute and serverless compute, see Compute.
Classic workspace architecture
Classic Azure Databricks workspaces have an associated storage account known as the workspace storage account. The workspace storage account is in your Azure subscription.
The following diagram describes the general Azure Databricks architecture for classic workspaces.
Serverless workspace architecture
Workspace storage in serverless workspaces is stored in the workspace's default storage. You can also connect to your cloud storage account to access your data. The following diagram describes the general architecture for serverless workspaces.

Serverless compute plane
In the serverless compute plane, Azure Databricks compute resources run in a compute layer within your Azure Databricks account. Azure Databricks creates a serverless compute plane in the same Azure region as your workspace's classic compute plane. You select this region when creating a workspace.
To protect customer data within the serverless compute plane, serverless compute runs within a network boundary for the workspace, with various layers of security to isolate different Azure Databricks customer workspaces and additional network controls between clusters of the same customer.
To learn more about networking in the serverless compute plane, Serverless compute plane networking.
Classic compute plane
In the classic compute plane, Azure Databricks compute resources run in your Azure subscription. New compute resources are created within each workspace's virtual network in the customer's Azure subscription.
A classic compute plane has natural isolation because it runs in each customer's own Azure subscription. To learn more about networking in the classic compute plane, see Classic compute plane networking.
For regional support, see Azure Databricks regions.
Workspace storage
Workspace storage is handled differently depending on your workspace type. For more information about the workspace types, see Create a workspace.
Serverless workspaces
Serverless workspaces use default storage, which is a fully managed storage location for internal workspace system data and Unity Catalog data assets. Serverless workspaces also support the ability to connect to your cloud storage locations for your own catalogs, tables, and other data assets. See Default storage in Databricks.
Classic workspaces
The workspace storage account contains:
- Workspace system data: Workspace system data is generated as you use various Azure Databricks features such as creating notebooks. This bucket includes notebook revisions, job run details, command results, and Spark logs
- Unity Catalog workspace catalog: If your workspace was enabled for Unity Catalog automatically, the workspace storage account contains the default workspace catalog. All users in your workspace can create assets in the default schema in this catalog. See Get started with Unity Catalog.
- DBFS (legacy): DBFS root and DBFS mounts are legacy and might be disabled in your workspace. DBFS (Databricks File System) is a distributed file system in Azure Databricks environments accessible under the
dbfs:/namespace. DBFS root and DBFS mounts are both in thedbfs:/namespace. Storing and accessing data using DBFS root or DBFS mounts is a deprecated pattern and not recommended by Databricks. For more information, see What is DBFS?.
To limit access to your workspace storage account from only authorized resources and networks, see Enable firewall support for your workspace storage account.