Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Important
Lakebase Autoscaling is in Beta in the following regions: eastus2, westeurope, westus.
Lakebase Autoscaling is the latest version of Lakebase with autoscaling compute, scale-to-zero, branching, and instant restore. For feature comparison with Lakebase Provisioned, see choosing between versions.
When you create a project, Lakebase creates several Postgres roles in the project:
- A Postgres role for the project owner's Azure Databricks identity (for example,
user@databricks.com), which owns the defaultdatabricks_postgresdatabase - A
databricks_superuseradministrative role
The databricks_postgres database is created so you can connect and try out Lakebase immediately after project creation.
Several system-managed roles are also created. These are internal roles used by Azure Databricks services for management, monitoring, and data operations.
Note
Postgres roles control database access (who can query data). For project permissions (who can manage infrastructure), see Project permissions. For a tutorial on setting up both, see Tutorial: Grant project and database access to a new user.
See Pre-created roles and System roles.
Create Postgres roles
Lakebase supports two types of Postgres roles for database access:
- OAuth roles for Azure Databricks identities: Create these using the
databricks_authextension and SQL. Enables Azure Databricks identities (users, service principals, and groups) to connect using OAuth tokens. - Native Postgres password roles: Create these using the Lakebase UI or SQL. Use any valid role name with password authentication.
For guidance on choosing the type of role to use, see Authentication overview. Each is designed for different use cases.
Create an OAuth role for a Azure Databricks identity using SQL
To allow Azure Databricks identities (users, service principals, or groups) to connect using OAuth tokens, you must create their Postgres roles using the databricks_auth extension. Creating a role for a group enables all group members to authenticate using the group role, simplifying permission management.
For detailed instructions on obtaining OAuth tokens in user-to-machine and machine-to-machine flows, see Obtain an OAuth token in a user-to-machine flow and Obtain an OAuth token in a machine-to-machine flow in the authentication documentation.
Prerequisites:
- You must have
CREATEandCREATE ROLEpermissions on the database - You must be authenticated as a Azure Databricks identity with a valid OAuth token
- Native Postgres authenticated sessions cannot create OAuth roles
To create an OAuth role:
Create the
databricks_authextension. Each Postgres database must have its own extension.CREATE EXTENSION IF NOT EXISTS databricks_auth;Use the
databricks_create_rolefunction to create a Postgres role for the Azure Databricks identity:SELECT databricks_create_role('identity_name', 'identity_type');For a Azure Databricks user:
SELECT databricks_create_role('myuser@databricks.com', 'USER');For a Azure Databricks service principal:
SELECT databricks_create_role('8c01cfb1-62c9-4a09-88a8-e195f4b01b08', 'SERVICE_PRINCIPAL');For a Azure Databricks group:
SELECT databricks_create_role('My Group Name', 'GROUP');The group name is case-sensitive and must match exactly as it appears in your Azure Databricks workspace. When you create a Postgres role for a group, any direct or indirect member (user or service principal) of that Databricks group can authenticate to Postgres as the group role using their individual OAuth token. This allows you to manage permissions at the group level in Postgres instead of maintaining permissions for individual users.
Grant database permissions to the newly created role.
The databricks_create_role() function creates a Postgres role with LOGIN permission only. After creating the role, you must grant the appropriate database privileges and permissions on the specific databases, schemas, or tables the user needs to access. Learn how: Manage permissions
Group-based authentication
When you create a Postgres role for a Azure Databricks group, you enable group-based authentication. This allows any member of the Azure Databricks group to authenticate to Postgres using the group's role, simplifying permission management.
How it works:
- Create a Postgres role for a Databricks group using
databricks_create_role('Group Name', 'GROUP'). - Grant database permissions to the group role in Postgres. See Manage permissions.
- Any direct or indirect member (user or service principal) of the Databricks group can connect to Postgres using their individual OAuth token.
- When connecting, the member authenticates as the group role and inherits all permissions granted to that role.
Authentication flow:
When a group member connects, they specify the group's Postgres role name as the username and their own OAuth token as the password:
export PGPASSWORD='<OAuth token of a group member>'
export GROUP_ROLE_NAME='<pg-case-sensitive-group-role-name>'
psql -h $HOSTNAME -p 5432 -d databricks_postgres -U $GROUP_ROLE_NAME
Important considerations:
- Group membership validation: Group membership is validated only at authentication time. If a member is removed from the Azure Databricks group after establishing a connection, the connection remains active. New connection attempts from removed members are rejected.
- Workspace scoping: Only groups assigned to the same Azure Databricks workspace as the project are supported for group-based authentication. To learn how to assign groups to a workspace, see Manage groups.
- Case sensitivity: The group name used in
databricks_create_role()must match the group name exactly as it appears in your Azure Databricks workspace, including case. - Permission management: Managing permissions at the group level in Postgres is more efficient than managing individual user permissions. When you grant permissions to the group role, all current and future group members inherit those permissions automatically.
Note
Role names cannot exceed 63 characters, and some names are not permitted. Learn more: Manage roles
Create a native Postgres password role
You can create native Postgres password roles using either the Lakebase UI or standard SQL commands.
Using the UI:
- In the Lakebase App, navigate to your branch overview page and then the branch's Roles & Databases tab.
- Click Add role and specify a role name (any valid Postgres role name).
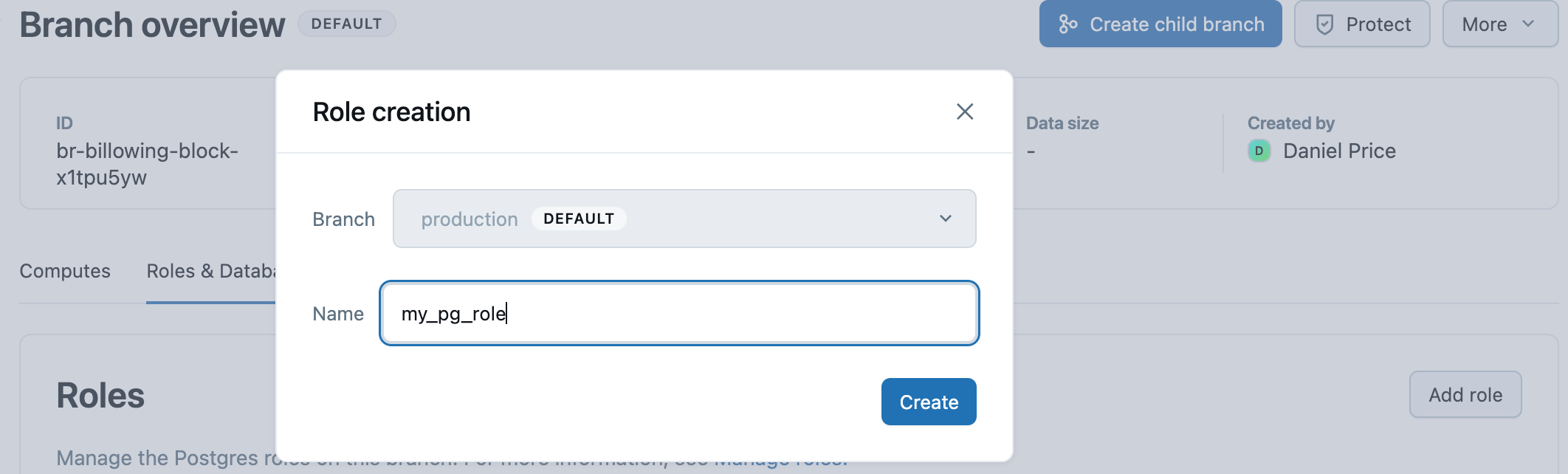
- Click Create.
- Copy the generated password and provide it securely to the user who will use this role.
The Lakebase UI generates a secure password automatically with 60-bit entropy. Roles created through the UI are automatically granted membership in the databricks_superuser role, which provides broad database privileges.
Using SQL:
You can also create native Postgres password roles using standard Postgres SQL commands:
CREATE ROLE role_name WITH LOGIN PASSWORD 'your_secure_password';
When creating roles with SQL, the password should have at least 12 characters with a mix of lowercase, uppercase, number, and symbol characters. User-defined passwords are validated at creation time to ensure 60-bit entropy.
View Postgres roles
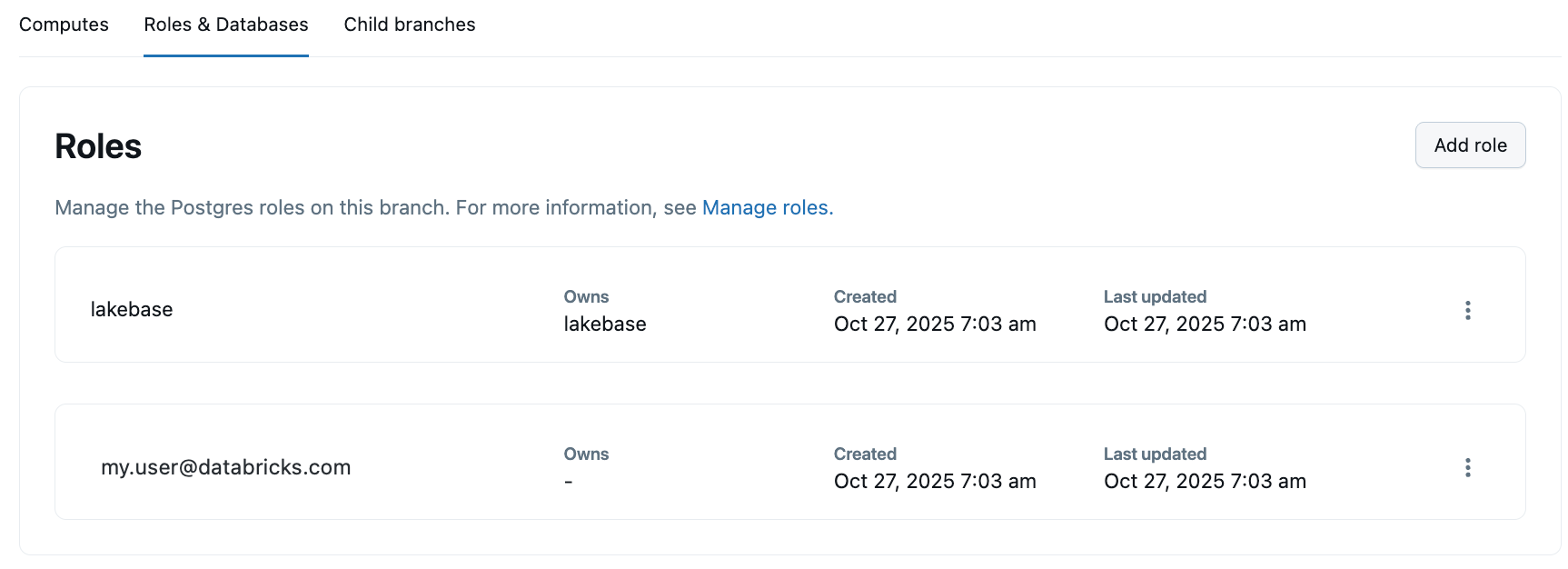
UI
To view all Postgres roles in your project, navigate to your branch's Roles & Databases tab in the Lakebase App. All roles created in the branch, with the exception of System roles, are listed, including native Postgres roles with password authentication.
PostgreSQL
View all roles with \du command:
You can view all Postgres roles, including system roles, using the \du meta-command from any Postgres client (such as psql) or the Lakebase SQL editor:
\du
List of roles
Role name | Attributes
-----------------------------+------------------------------------------------------------
cloud_admin | Superuser, Create role, Create DB, Replication, Bypass RLS
my.user@databricks.com | Create role, Create DB, Bypass RLS
databricks_control_plane | Superuser
databricks_gateway |
databricks_monitor |
databricks_reader_12345 | Create role, Create DB, Replication, Bypass RLS
databricks_replicator | Replication
databricks_superuser | Create role, Create DB, Cannot login, Bypass RLS
databricks_writer_12345 | Create role, Create DB, Replication, Bypass RLS
This displays all roles and their attributes (Superuser, Create role, Create DB, etc.).
Drop a Postgres role
You can drop both Databricks identity-based roles and native Postgres password roles.
UI
Deleting a role is a permanent action that cannot be undone. You cannot delete a role that owns a database. The database must be deleted before deleting the role that owns the database.
To delete any Postgres role using the UI:
- Navigate to your branch's Roles & Databases tab in the Lakebase App.
- Select Delete role from the role menu and confirm the deletion.
PostgreSQL
You can drop any Postgres role using standard Postgres commands. For details, see the PostgreSQL documentation on dropping roles.
Drop a role:
DROP ROLE role_name;
After a Azure Databricks identity-based role is dropped, that identity can no longer authenticate to Postgres using OAuth tokens until a new role is created.
Pre-created roles
After a project is created, Azure Databricks automatically creates Postgres roles for project administration and getting started.
| Role | Description | Inherited privileges |
|---|---|---|
<project_owner_role> |
The Azure Databricks identity of the project creator (for example, my.user@databricks.com). This role owns the default databricks_postgres database and can log in and administer the project. |
Member of databricks_superuser |
databricks_superuser |
An internal administrative role. Used to configure and manage access across the project. This role is granted broad privileges. | Inherits from pg_read_all_data, pg_write_all_data, and pg_monitor. |
Learn more about these roles' specific capabilities and privileges: Pre-created role capabilities
System roles created by Azure Databricks
Azure Databricks creates the following system roles required for internal services. You can view these roles by issuing a \du command from psql or the Lakebase SQL Editor.
| Role | Purpose |
|---|---|
cloud_admin |
Superuser role used for cloud infrastructure management |
databricks_control_plane |
Superuser role used by internal Databricks components for management operations |
databricks_monitor |
Used by internal metrics collection services |
databricks_replicator |
Used for database replication operations |
databricks_writer_<dbid> |
Per-database role used to create and manage synced tables |
databricks_reader_<dbid> |
Per-database role used to read tables registered in Unity Catalog |
databricks_gateway |
Used for internal connections for managed data serving services |
To learn how roles, privileges, and role memberships work in Postgres, use the following resources in the Postgres documentation: