Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
If you host a private Git server (such as GitHub Enterprise Server, Bitbucket Server, or GitLab self-managed) or your Git server is behind a firewall, you can use the Git server proxy to connect Databricks Git folders to your private repositories. The proxy routes Git commands from your Azure Databricks workspace through a compute resource to your private Git server.
About Git server proxy
Databricks Git server proxy for Git folders lets you proxy Git commands from your Azure Databricks workspace to a private Git server that isn't accessible on the internet.
Databricks Git folders represent your connected Git repositories as folders. The contents of these folders are version-controlled by syncing to the connected Git repository. By default, Git folders can only synchronize with repositories accessible on the internet. If you host a private Git server or your Git server is behind a firewall, you must use Git server proxy with Git folders. Your Git server must be accessible from your Azure Databricks compute plane.
When to use Git server proxy
Use the following guidance to determine whether you need to set up Git server proxy:
- You need Git server proxy if your Git server is private, on-premises, or behind a firewall, such as GitHub Enterprise Server, Bitbucket Server, GitLab self-managed, or Azure DevOps Server.
- You don't need Git server proxy if your repositories are on cloud-hosted services accessible from the public internet, such as GitHub.com, GitLab.com, Bitbucket Cloud, or Azure DevOps Services.
Once enabled, all Git folders traffic in your workspace routes through the proxy cluster, including public repositories.
How Git server proxy works
Git server proxy for Databricks Git folders proxies Git commands from the Databricks control plane to a proxy cluster running in your workspace's compute plane. The proxy cluster is configured to run a proxy service that receives Git commands from the Databricks control plane and forwards them to your Git server. Proxying doesn't affect the security architecture of your Databricks control plane.
The following illustrates the overall system architecture:
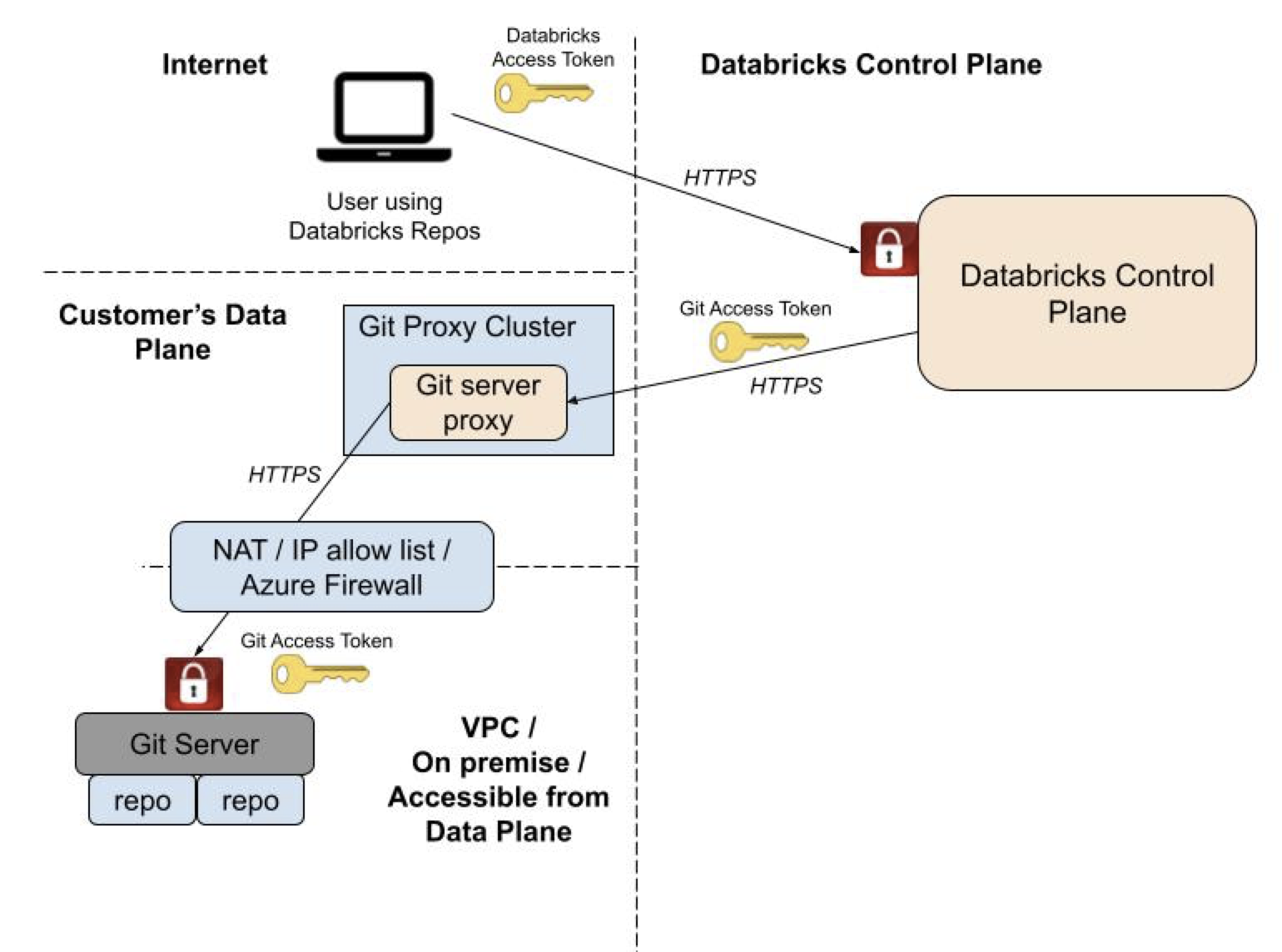
Important
Databricks provides an enablement notebook to configure your Git server instance to proxy commands for Databricks Git folders. Get the enablement notebook on GitHub. The Databricks Git server proxy is designed to work with the Databricks Runtime version included in the configuration notebook. Don't update the Databricks Runtime version of the proxy cluster.
Set up Git Server Proxy
To enable private Git connectivity for Databricks Git folders, prepare your Git server instance, run the enablement notebook to create the proxy, and validate your configuration.
To set up the Git server proxy:
- Prepare your Git server instance with static IP addresses and HTTPS transport.
- Run the enablement notebook to create the proxy cluster.
- Validate your configuration by cloning a repository.
- Configure Git credentials for users.
Prerequisites
Before you enable the proxy, verify the following:
- Your workspace has the Databricks Git folders feature enabled. See Enable or disable Databricks Git folders.
- Your Git server instance is accessible from your Azure Databricks workspace's compute plane Azure virtual network (VNet), and has both HTTPS and personal access tokens (PATs) enabled.
Note
Git server proxy for Databricks works in all regions supported by your VNet.
Step 1: Prepare your Git server instance
Important
To create a compute resource and complete this task, you must be a workspace admin with access rights.
Configure your Git server to accept connections from the proxy cluster and enable HTTPS transport.
Your enterprise Git server typically has an allowlist of IP addresses from which access is permitted. To allow the proxy cluster driver node to access your Git server, associate a static outbound IP address for traffic originating from your proxy cluster and add it to your Git server's allowlist.
- Associate a static outbound IP address for traffic originating from your proxy cluster by using Azure Firewall or an egress appliance.
- Add the IP address from the previous step to your Git server's allowlist.
Then, configure your Git server instance to allow HTTPS transport:
- GitHub Enterprise: See Which remote URL should I use in the GitHub Enterprise help.
- Bitbucket Server: On the Bitbucket server administration page, click Server settings and select HTTP(S) enabled.
Step 2: Run the enablement notebook
To enable the proxy:
Log into your Azure Databricks workspace as a workspace admin with access rights to create a cluster.
Import this notebook, which chooses the smallest instance type available from your cloud provider to run the Git proxy:
Click Run all to run the notebook, which performs the following tasks:
- Creates a single node compute resource named "Databricks Git Proxy" that doesn't auto-terminate. This proxy service processes and forwards Git commands from your Azure Databricks workspace to your private Git server.
- Enables a feature flag that controls whether Git requests in Databricks Git folders are proxied through the compute instance.
As a best practice, create a job to run the Git proxy compute resource on a regular schedule. This keeps the Git proxy service available for your users.
Note
Running an additional long-running compute resource incurs extra Databricks Units (DBUs). To minimize costs, the notebook configures the proxy to use a single-node compute resource with an inexpensive node type. Modify the compute options to suit your needs. For pricing information, see the Databricks pricing calculator.
Step 3: Validate your Git server configuration
To validate your Git server configuration, clone a repository hosted on your private Git server through the proxy cluster. A successful clone confirms that the Git server proxy is working for your workspace.
Step 4: Create proxy-enabled Git repositories
After users configure their Git credentials, no further steps are required to create or synchronize repositories. To configure credentials and access repositories programmatically, see Connect your Git provider to Databricks.
Remove global CAN ATTACH TO permissions
The Git server proxy doesn't require CAN ATTACH TO permission for any user. To prevent users from running arbitrary workloads on the proxy cluster, restrict cluster access control list (ACL) permissions on the proxy server:
Click Compute from the sidebar, and then choose the compute entry for the Git Server Proxy you're running.
Click the
kebab menu and click Permissions.
From the dialog, remove the Can Attach To entry for All workspace users.
Troubleshooting
This section covers common issues and how to diagnose them.
Checklist for common problems
Before you start diagnosing an error, confirm the following:
- Your proxy cluster is running with this Git proxy server debug notebook.
- You're a workspace administrator.
Run the rest of the debug notebook and capture the results. If you can't resolve the issue or don't see any failures reported, Databricks support can review the results. Export and send the debug notebook as a DBC archive if requested.
Change your Git proxy configuration
If your Git proxy service isn't working with the default configuration, set environment variables to support your network infrastructure.
Use the following environment variables to update the configuration for your Git proxy service:
| Environment variable | Format | Description |
|---|---|---|
GIT_PROXY_ENABLE_SSL_VERIFICATION |
true/false |
Set this to false if you are using a self-signed certificate for your private Git server. |
GIT_PROXY_CA_CERT_PATH |
File path (string) | Set this to the path to a CA certificate file used for SSL verification. Example: /FileStore/myCA.pem |
GIT_PROXY_HTTP_PROXY |
https://<hostname>:<port #> |
Set this to the HTTPS URL for your network's firewall proxy for HTTP traffic. |
GIT_PROXY_CUSTOM_HTTP_PORT |
Port number (integer) | Set this to the port number assigned to your Git server's HTTP port. |
To set these environment variables:
- Go to the Compute tab in your Azure Databricks workspace.
- Select the compute configuration for your Git proxy service.
- At the bottom of the Configuration pane, expand Advanced and select the Spark tab.
- Add environment variables to the Environment variables field.
Inspect logs on the proxy cluster
The file at /databricks/git-proxy/git-proxy.log on the proxy cluster contains logs that are useful for debugging purposes.
The log file should start with Data-plane proxy server binding to ('', 8000)…. If it doesn't, the proxy server didn't start properly. Restart the cluster, or delete the cluster and run the enablement notebook again.
If the log file starts with this line, review the log statements that follow for each Git request initiated by Git operations in Databricks Git folders.
For example:
do_GET: https://server-address/path/to/repo/info/refs?service=git-upload-pack 10.139.0.25 - - [09/Jun/2021 06:53:02] /
"GET /server-address/path/to/repo/info/refs?service=git-upload-pack HTTP/1.1" 200`
Error logs written to this file can be useful to help you or Databricks Support debug issues.
SSL certificate errors
You might see the following error:
https://git.consult-prodigy.com/Prodigy/databricks_test: Secure connection to https://git.consult-prodigy.com/Prodigy/databricks_test could not be established because of SSL problems
This often means you're using a repository that requires special SSL certificates. Check the /databricks/git-proxy/git-proxy.log file on the proxy cluster. If certificate validation failed, add the certificate authority to the system certificate chain:
- Extract the root certificate using your browser or another method, and upload it to Databricks File System.
- Edit the Git folders Git Proxy cluster to set the
GIT_PROXY_CA_CERT_PATHenvironment variable to point to the root certificate file. See Environment variables.
After you complete these steps, restart the cluster.
Frequently asked questions
The following are common questions about Git server proxy configuration and usage.
How do I check if the Git proxy is running?
Import and run the Git proxy debug notebook. The results show if there are issues with the Git proxy service.
Can workspaces share proxy clusters?
Each Azure Databricks workspace requires its own proxy cluster. You can't share a proxy cluster across multiple workspaces, and each workspace can have only one Git proxy server cluster.
Can I route only some Git traffic through the proxy?
All Databricks Git folders-related traffic routes through the proxy cluster, even for public Git repositories. Your Azure Databricks workspace doesn't differentiate between proxied and non-proxied repositories.
Which Git providers are supported?
Databricks Git folders support GitHub Enterprise, Bitbucket Server, Azure DevOps Server, and GitLab self-managed. Other enterprise Git server providers should also work if they conform to common Git specifications.
Is GNU Privacy Guard (GPG) commit signing supported?
No.
Is SSH transport supported?
No. Only HTTPS is supported.
Can I use a non-default HTTPS port?
The enablement notebook assumes your Git server uses the default HTTPS port 443. Set the environment variable GIT_PROXY_CUSTOM_HTTP_PORT to use a different port.
Do users need to change Git URLs for the proxy?
No. Users enter the normal Git repository URL, such as https://git.company.com/org/repo-name.git. All Git traffic for Databricks Git folders routes through the proxy transparently.
How does authentication work with the proxy?
The proxy uses the user's Git credential to authenticate to the Git server. Access is restricted by the permissions specified in that credential.