Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Data security becomes a top priority as organizations shift data to cloud storage solutions like Azure Storage. This document outlines common security threats and risks linked to misconfigured settings. It also explains the security alerts that Microsoft Defender for Storage provides to detect and respond to potential security threats.
Security threats in cloud-based storage services
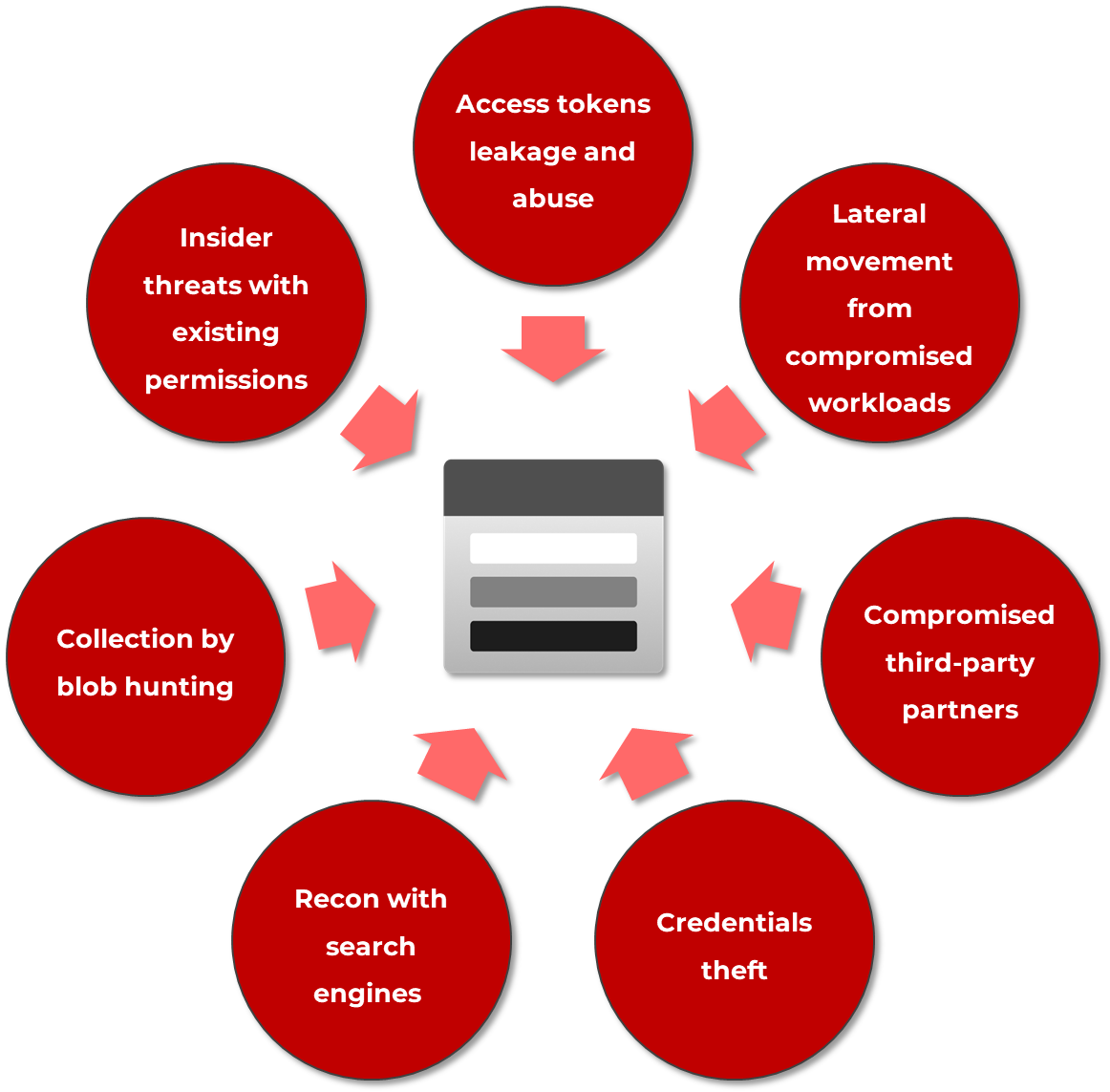
Azure Storage is a widely used cloud storage solution, and like any cloud-based service, it's susceptible to various security threats. Common security threats in Azure Storage include:
- Access token abuse and leakage
- Lateral movement from compromised workloads
- Compromised third-party partners with privileged permissions
- Credentials theft
- Reconnaissance with search engines
- Data collection by blob hunting
- Insider threats with existing permissions
These threats can result in malware uploads, data corruption, and sensitive data exfiltration, posing significant risks.
In addition to security threats, configuration errors might inadvertently expose sensitive resources. Some common misconfiguration issues include:
- Inadequate access controls and networking rules, leading to unintended data exposure on the internet
- Insufficient authentication mechanisms
- Lack of data encryption protocols for both data in transit and at rest
To minimize the risk of security breaches and configuration errors, security teams employ a combination of posture management tools and workload protection tools. These tools ensure Azure Storage stays secure by providing visibility into early signs of breaches. They help prevent attacks and maintain secure configurations.
Microsoft security researchers analyzed the attack surface of storage services. The potential security risks are described in the threat matrix for cloud-based storage services, which are based on the MITRE ATT&CK® framework, a knowledge base for the tactics and techniques employed in cyber-attacks.
For a comparison between malware scanning and hash reputation analysis, see Understanding the differences between these methods.
What kind of security alerts does Microsoft Defender for Storage provide?
Tip
For a comprehensive list of all Defender for Storage alerts, see the alerts reference guide page. This is useful for workload owners who want to know what threats can be detected and help SOC teams gain familiarity with detections before investigating them. Learn more about Defender for Cloud security alerts and how to respond to them.
Security alerts are triggered in the following scenarios:
| Scenario | Description |
|---|---|
| Malicious content upload | Malware scanning scans every blob uploaded to your storage accounts. It detects ransomware, viruses, spyware, and other malware uploaded to the storage account, helping you prevent it from entering the organization and spreading. The classic malware hash analysis alert operates differently from malware scanning. It compares the uploaded blob/file hash with a list of known malicious hash signatures rather than analyzing the file contents for malware. |
| Sensitive data exposure event | Detection of access level change allowing unauthenticated public access to blob containers with sensitive data from the internet |
| Suspicious activities on resources with sensitive data | Detection of suspicious activities occurring on blob containers containing sensitive data |
| Compromised, misconfigured, and unusual authentication tokens | Detection of compromised SAS tokens used for data plane authentication and operations, and detection of unusual SAS tokens that can be generated by a malicious actor |
| Data and permissions inspection | Detection of unusual exploration of the data and inspection of access permissions |
| Data exfiltration | Detection of unusual extraction of data from storage accounts |
| Data deletion | Detection of unusual deletions in storage accounts |
| Blob-hunting attempts | Detection of collection attempts by scanning and enumerating resources for publicly exposed storage resources. Read more on how to detect, investigate, and prevent blob-hunting. |
| Unusual access patterns | Detection of unusual access to storage accounts from unusual locations, applications, and with unusual authentication |
| Suspicious access signatures | Detection of known suspicious IP addresses by Microsoft Threat Intelligence, known Tor exit nodes, and known suspicious applications |
| Phishing campaigns | Detection of phishing content hosted on storage accounts and identified as part of a phishing attack impacting Microsoft 365 users |
Security alerts include details of the suspicious activity, relevant investigation steps, remediation actions, and security recommendations. Alerts can be exported to Microsoft Sentinel or any other third-party SIEM/XDR tool. Learn more about how to stream alerts to a SIEM, SOAR, or IT Service Management solution.