Identify and remediate attack paths
Defender for Cloud's contextual security capabilities assists security teams in the reduction of the risk of impactful breaches. Defender for Cloud uses environment context to perform a risk assessment of your security issues. Defender for Cloud identifies the biggest security risk issues, while distinguishing them from less risky issues.
Attack path analysis helps you to address the security issues that pose immediate threats with the greatest potential of being exploited in your environment. Defender for Cloud analyzes which security issues are part of potential attack paths that attackers could use to breach your environment. It also highlights the security recommendations that need to be resolved in order to mitigate it.
By default attack paths are organized by their risk level. The risk level is determined by a context-aware risk-prioritization engine that considers the risk factors of each resource. Learn more about how Defender for Cloud prioritizes security recommendations.
Prerequisites
You must enable Defender Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) and have agentless scanning enabled.
Required roles and permissions: Security Reader, Security Admin, Reader, Contributor or Owner.
To view attack paths that are related to containers:
You must enable agentless container posture extension in Defender CSPM or
You can enable Defender for Containers, and install the relevant agents in order to view attack paths that are related to containers. This also gives you the ability to query containers data plane workloads in security explorer.
Required roles and permissions: Security Reader, Security Admin, Reader, Contributor or Owner.
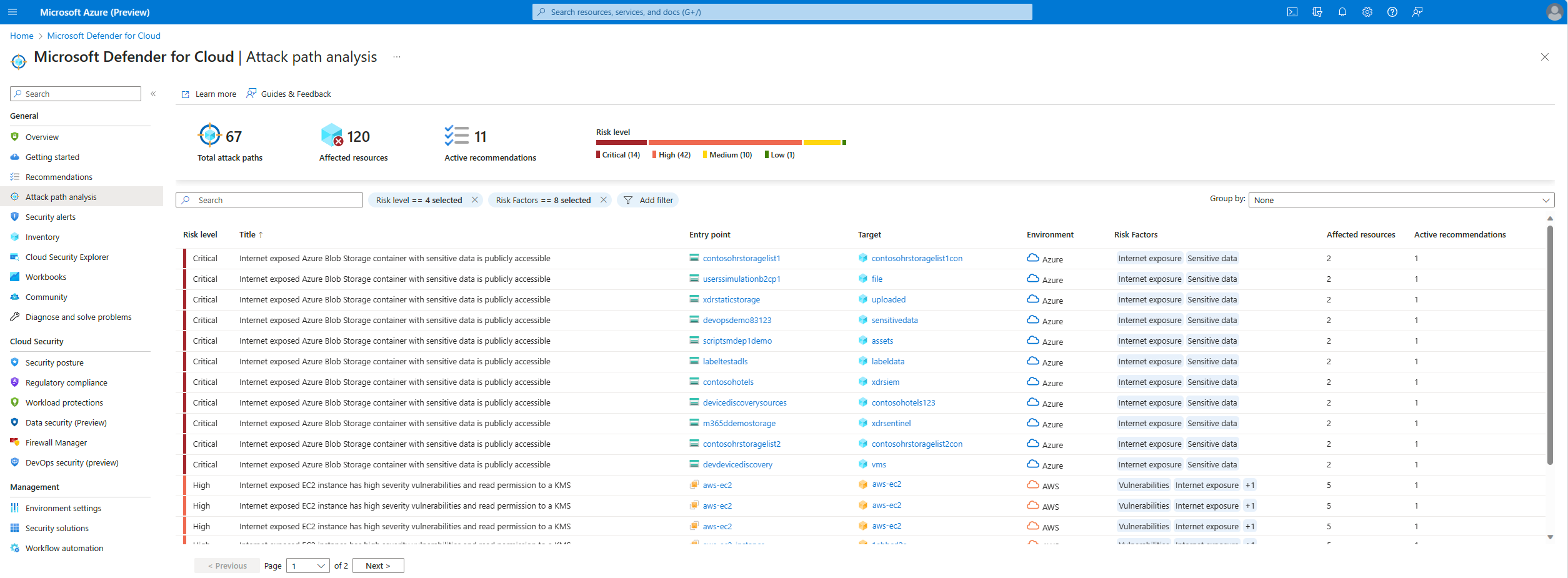
Identify attack paths
The attack path page shows you an overview of all of your attack paths. You can also see your affected resources and a list of active attack paths.
You can use Attack path analysis to locate the biggest risks to your environment and to remediate them.
To identify attack paths:
Sign in to the Azure portal.
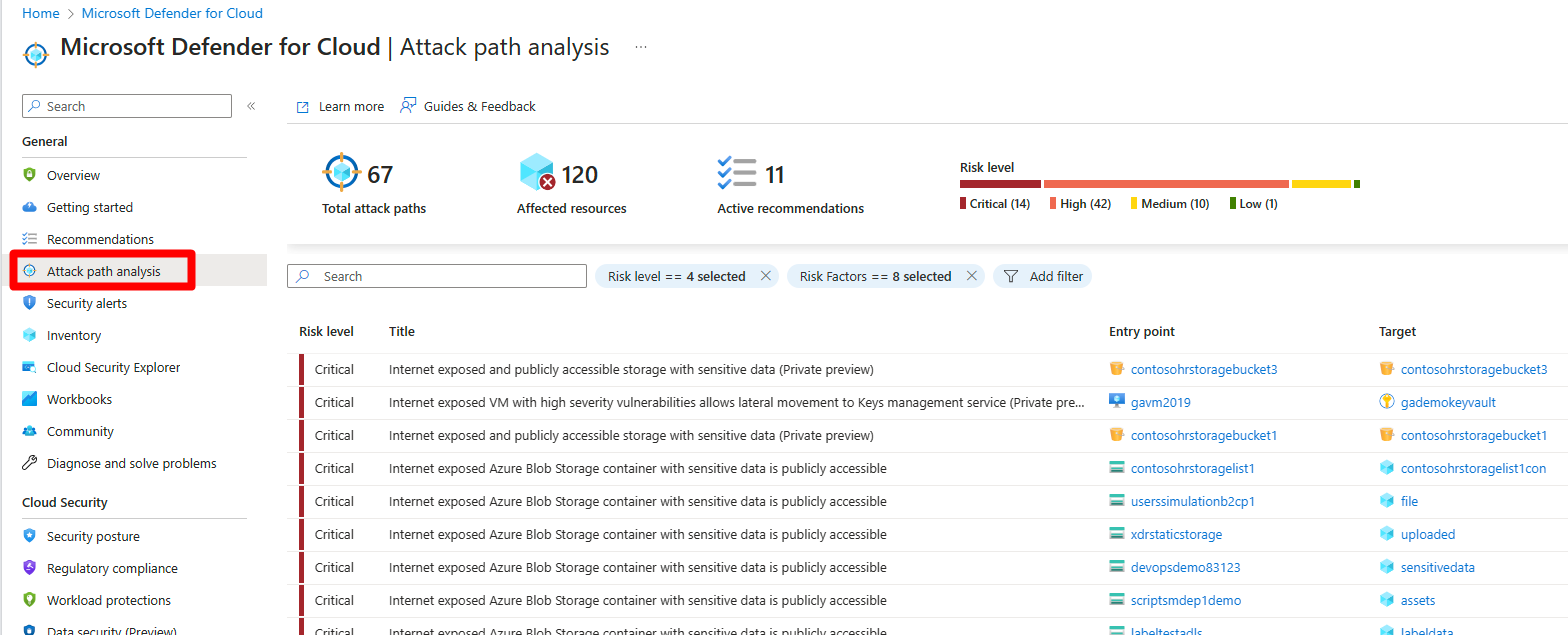
Navigate to Microsoft Defender for Cloud > Attack path analysis.
Select an attack path.
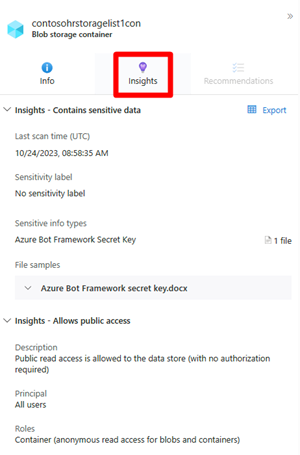
Select a node.
Select Insight to view the associated insights for that node.
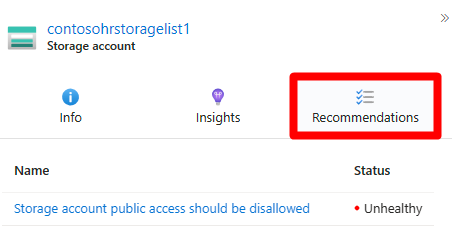
Select Recommendations.
Select a recommendation.
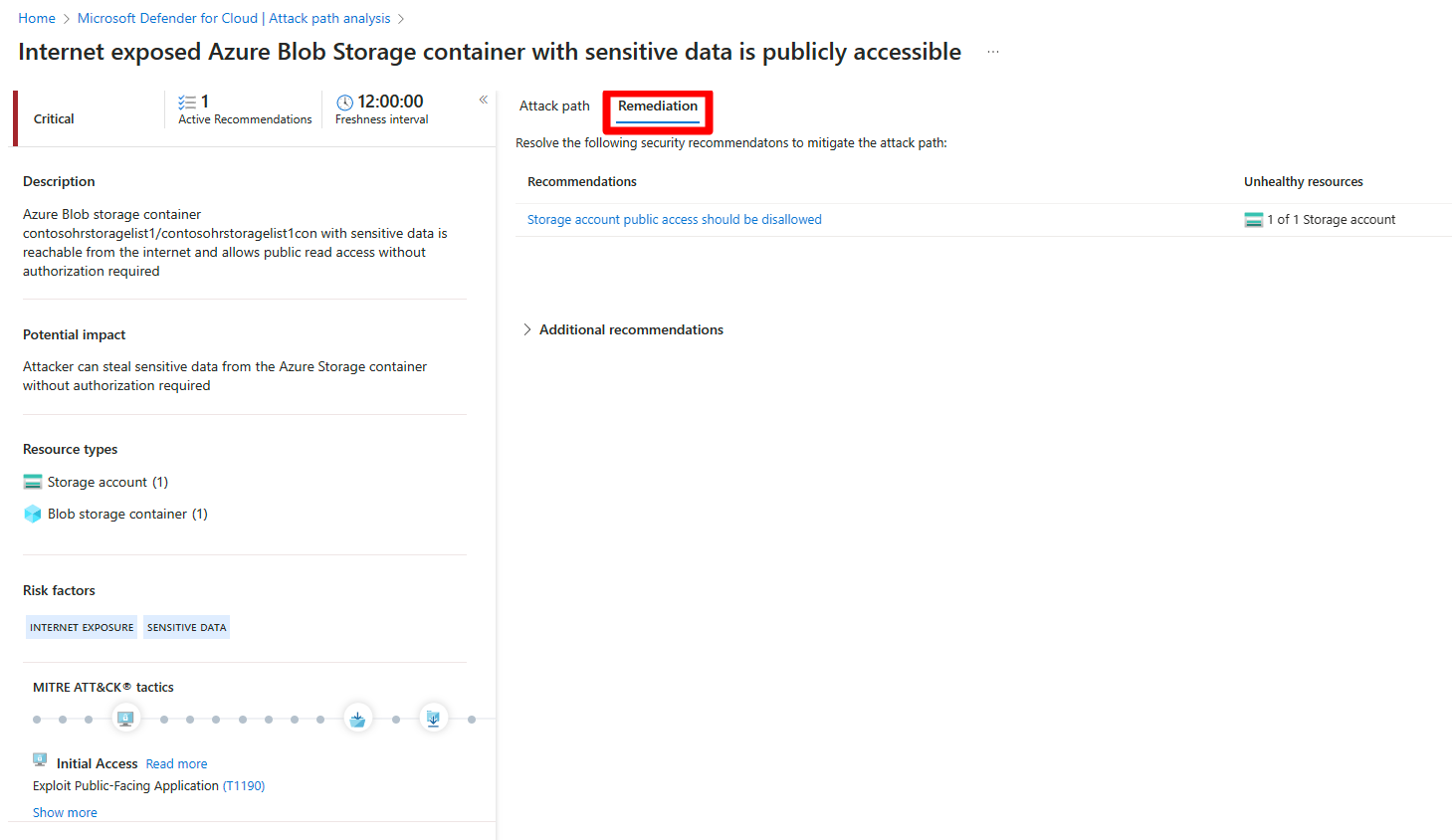
Remediate attack paths
Once you have investigated an attack path and reviewed all of the associated findings and recommendations, you can start to remediate the attack path.
To remediate an attack path:
Navigate to Microsoft Defender for Cloud > Attack path analysis.
Select an attack path.
Select Remediation.
Select a recommendation.
Once an attack path is resolved, it can take up to 24 hours for an attack path to be removed from the list.
Remediate all recommendations within an attack path
Attack path analysis grants you the ability to see all recommendations by attack path without having to check each node individually. You can resolve all recommendations without having to view each node individually.
The remediation path contains two types of recommendation:
- Recommendations - Recommendations that mitigate the attack path.
- Additional recommendations - Recommendations that reduce the exploitation risks, but don’t mitigate the attack path.
To resolve all recommendations:
Sign in to the Azure portal.
Navigate to Microsoft Defender for Cloud > Attack path analysis.
Select an attack path.
Select Remediation.
Expand Additional recommendations.
Select a recommendation.
Once an attack path is resolved, it can take up to 24 hours for an attack path to be removed from the list.
Next Step
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for