Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Security recommendations in Microsoft Defender for Cloud contain actionable guidance that helps you secure your resources and improve your security posture. Each recommendation provides detailed steps to address specific security issues identified in your cloud environments.
Security recommendations are generated based on continuous assessment of your resources against security policies and compliance standards. They provide clear remediation steps, prioritization based on risk, and guidance to help you strengthen your defenses against potential threats.
What are risk factors?
Defender for Cloud uses the context of an environment, including the resource's configuration, network connections, and security posture, to assess the risk of potential security problems. By using this context, it identifies the most significant security risks and distinguishes them from less risky problems. The recommendations are sorted based on their risk level.
This risk assessment engine considers important risk factors, such as:
- Internet exposure: Whether resources are accessible from the internet
- Data sensitivity: The presence of sensitive or confidential data
- Lateral movement: Potential for bad actors to move between resources
- Attack paths: Whether the security problem is part of potential attack scenarios
Understanding risk prioritization
Microsoft Defender for Cloud proactively utilizes a dynamic engine that assesses the risks in your environment. It takes into account the potential for exploitation and the potential business impact to your organization. The engine prioritizes security recommendations based on the risk factors of each resource. The context of the environment, including the resource's configuration, network connections, and security posture, determines these risk factors.
When Defender for Cloud performs a risk assessment of your security problems, the engine identifies the most significant security risks and distinguishes them from less risky problems. The engine sorts the recommendations based on their risk level. You can address the security problems that pose immediate threats with the greatest potential of being exploited in your environment.
Learn more about risk prioritization.
Risk levels and calculation
Defender for Cloud uses a context-aware risk-prioritization engine to calculate the risk level of each security recommendation. The risk level comes from the risk factors of each resource, such as its configuration, network connections, and security posture. The risk level is calculated based on the potential impact of the security problem, the categories of risk, and the attack path that the security problem is part of.
Recommendations are classified into five categories based on their risk level:
- Critical: Recommendations that require immediate action due to their significant potential impact on your organization's security posture.
- High: Recommendations that indicate a potential security risk that should be addressed in a timely manner, but might not require immediate attention.
- Medium: Recommendations that indicate a relatively minor security problem that you can address at your convenience.
- Low: Recommendations that indicate a relatively minor security problem that you can address at your convenience.
- Not evaluated: Recommendations that aren't evaluated yet. This status could be due to the resource not being covered by the Defender CSPM plan, which is a prerequisite for risk level.
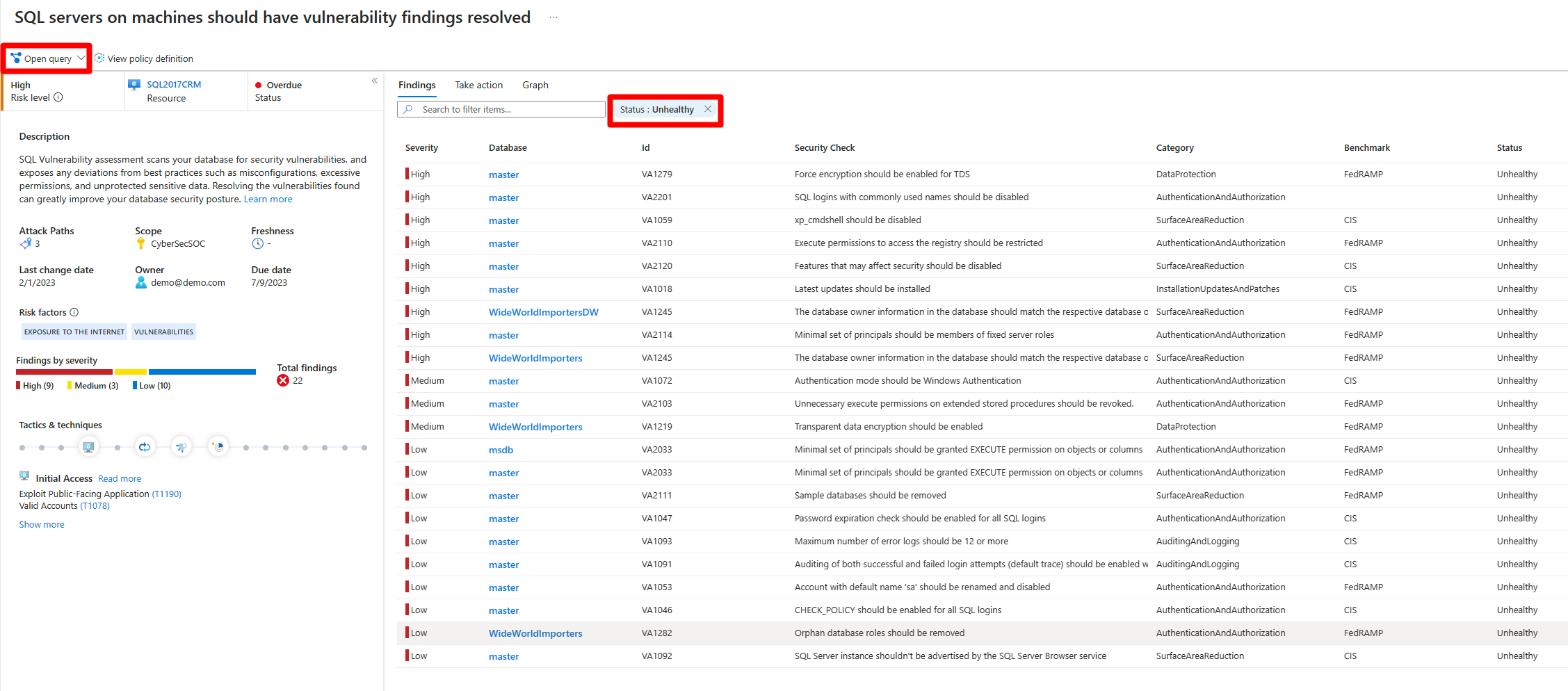
Recommendation dashboard details
On the recommendations page, you can review the following risk-prioritized details:
- Title: The title of the recommendation.
- Affected resource: The resource that the recommendation applies to.
- Risk level: The exploitability and the business impact of the underlying security issue, taking into account environmental resource context such as Internet exposure, sensitive data, lateral movement, and more.
- Risk factors: Environmental factors of the resource affected by the recommendation, which influences the exploitability and the business impact of the underlying security issue.
- Attack paths: The number of attack paths that the recommendation is part of based on the security engine's search for all potential attack paths.
- Owner: The person the recommendation is assigned to.
- Status: The current status of the recommendation (unassigned, on time, overdue).
- Insights: Information related to the recommendation such as if it's in preview, if it can be denied, if there's a fix option available.
Recommendation classification
Every security recommendation from Defender for Cloud has a severity rating.
Critical severity
Address these recommendations immediately. Critical severity recommendations indicate an urgent and highly exploitable security vulnerability that poses an immediate threat to your environment.
Critical severity recommendations require immediate remediation. They highlight severe, easily exploitable vulnerabilities that could allow bad actors to gain privileged access, compromise sensitive data, or move laterally across your environment.
Examples of critical severity recommendations include:
- Exposure of highly sensitive or privileged secrets that, if compromised, could grant full administrative access across systems.
- Internet-exposed resources that allow unauthenticated access to critical workloads, management interfaces, or sensitive data stores.
- Critical CVSS 9.0+ vulnerabilities discovered on machines or containers that allow remote code execution, privilege escalation, or full system takeover.
- Misconfigurations enabling direct lateral movement to high-value assets, such as domain controllers or production databases.
High severity
We recommend that you address these recommendations immediately. They indicate that there's a critical security vulnerability that an attacker could exploit to gain unauthorized access to your systems or data.
Examples of high severity recommendations include:
- Unprotected secrets on a machine.
- Overly permissive inbound network security group rules.
- Clusters that allow images to be deployed from untrusted registries.
- Unrestricted public access to storage accounts or databases.
Medium severity
These recommendations indicate a potential security risk. Address these recommendations in a timely manner, but they might not require immediate attention.
Examples of medium severity recommendations include:
- Containers that share sensitive host namespaces.
- Web apps that don't use managed identities.
- Linux machines that don't require SSH keys during authentication.
- Unused credentials left in the system after 90 days of inactivity.
Low severity
These recommendations indicate a relatively minor security issue that you can address at your convenience.
Examples of low severity recommendations include:
- The use of local authentication instead of Microsoft Entra ID.
- Health issues with your endpoint protection solution.
- Users not following best practices with network security groups.
- Misconfigured logging settings, which might make it harder to detect and respond to security incidents.
An organization's internal policies might differ from Microsoft's classification of a specific recommendation. Always carefully review each recommendation and consider its potential effect on your security posture before you decide how to address it.
Note
Defender CSPM customers have access to a richer classification system where recommendations feature a Risk level determination that utilizes the context of the resource and all related resources. For more information, see risk prioritization and detailed guidance in the risk prioritization sections above.
Example
In this example, the Recommendation details page shows 15 affected resources:
When you open and run the underlying query, Azure Resource Graph Explorer returns the same affected resources for this recommendation.