Secure pipeline resources
Azure DevOps Services | Azure DevOps Server 2022 | Azure DevOps Server 2020
Azure Pipelines provides robust security features to protect your pipelines and resources. When YAML pipelines run, access to resources goes through a system called checks. Checks can suspend or even fail a pipeline run to keep resources safe. A pipeline can access two types of resources, protected and open.
Protected resources
Protected resources allow you to apply approvals and checks to limit access. Examples include agent pools, secret variables in variable groups, secure files, service connections, environments, and repositories.
"Protected" means only specific users and pipelines within the project have access. You can define checks that must be satisfied before a stage consuming a protected resource can start. For example, manual approval before using a protected resource.
Azure Pipelines requires the Administrator role when opening up access to a resource to all pipelines for all protected resources except for Environments. For Environments, you need the Creator role.
For more information, see About pipeline resources and Add resource protection.
Repository resources
- Repositories can optionally be protected.
- By limiting the scope of the Azure Pipelines access token to specific repositories, you add extra protections.
- The access token given to agents only has access to explicitly mentioned repositories in the pipeline’s
resourcessection. - Repositories added to the pipeline need authorization from a user with Contribute access to the repository.
Permissions
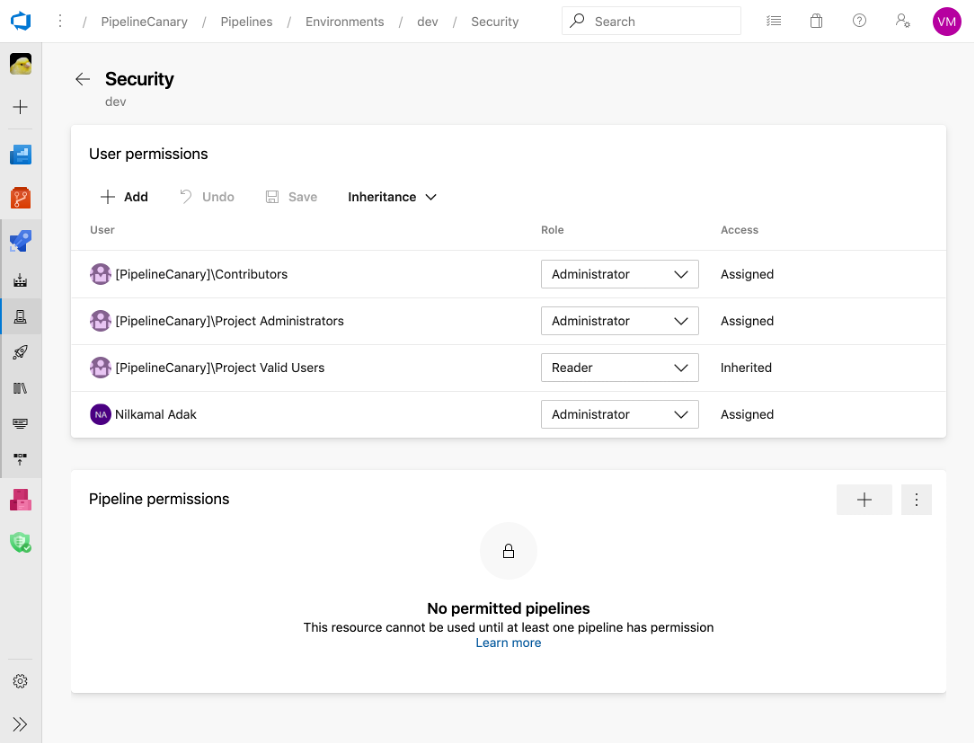
User permissions:
User permissions are the frontline of defense for protected resources.
Only grant permissions to users who require them.
Members of the user role for a resource can manage approvers and checks.
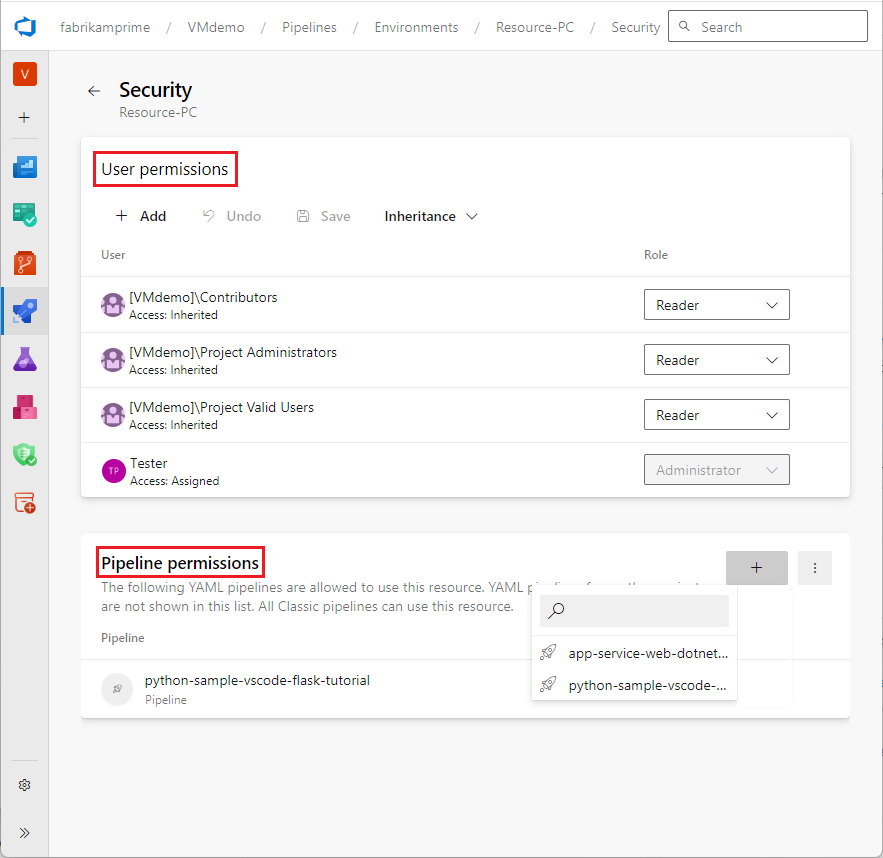
Pipeline permissions:
Pipeline permissions protect against copying protected resource names to other pipelines.
Disable the option to grant access to "all pipelines" for each protected resource.
Explicitly grant access to specific pipelines you trust.
Open resources
- Artifacts, pipelines, test plans, and work items are considered "open" resources.
- They don't have the same restrictions as protected resources.
- You can fully automate workflows by subscribing to trigger events on open resources.
For more information about which pipelines can access what resources in the section on projects.
Checks
When you're securing your protected resources in YAML pipelines, relying solely on user and pipeline permissions isn’t sufficient, which is where checks come into play. Let’s explore them in more detail:
- Manual approval check:
- Whenever a YAML pipeline uses a protected resource, it can be blocked until you manually approve it.
- This gives you the chance to review the code and ensure it’s coming from the correct branch or source.
- Manual approval provides an extra layer of security before proceeding with the pipeline run.
- Protected branch check:
- If you have manual code review processes for specific branches, you can extend this protection to pipelines.
- Configure a protected branch check for each of your resources.
- This automatically prevents your pipeline from running on top of any user branches.
- It ensures that only authorized branches can access protected resources.
- Protected resource check:
- You can add checks to various resources, including environments, service connections, repositories, variable groups, agent pools, and secure files.
- These checks specify conditions that must be satisfied before a stage in any pipeline can consume a resource.
- For example, you might require specific approvals or other criteria before using a protected resource.
For more information, see Checks and approvals.
Next steps
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for