Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
You can move DevTest Labs and their associated schedules to another region or resource group. You can move resource groups through the Azure Portal. To move a lab, create a copy of an existing lab in another region. When you've moved your lab, and you have a virtual machine (VM) in the target region, you can move your lab schedules..
In this article, you learn how to:
- Move resources to different resource groups.
- Export an Azure Resource Manager (ARM) template of your lab.
- Modify the template by adding or updating the target region and other parameters.
- Deploy the template to create the new lab in the target region.
- Configure the new lab.
- Move data to the new lab.
- Move schedules to the new lab.
- Delete the resources in the source region.
Prerequisites
Ensure that the services and features that your account uses are supported in the target region.
For preview features, ensure that your subscription is allowlisted for the target region.
DevTest Labs doesn't store or expose passwords from the exported ARM template. You need to know the passwords/secrets for:
- the VMs
- the Stored Secrets
- PAT tokens of the private Artifact Repos to move the private repos together with the lab.
When moving a lab schedule, ensure a Compute VM exists in the target region.
Move a lab
The following section describes how to move resources to a different resource group and create and customize an ARM template to move a lab from one region to another.
You can move a schedule without moving a lab, if you have a VM in the target region. If you want to move a schedule without moving a lab, see Move a schedule.
Move Resource Groups using Azure Portal
Moving resources between resource groups in different locations is now seamlessly enabled in DevTest Labs. You can effortlessly transfer any resource from one group to another within the same subscription.
To begin, select the resource you wish to move. On the resource's Overview page, you'll find the current Resource Group displayed at the top. Next to the resource group name, you'll see the word (move) in parentheses.
Click the hyperlinked move text, which will direct you to a new page where you can relocate the resource to any other resource group within the same subscription. Please note that moving the resource will not change its location, even if the destination resource group is in a different location. If you're not moving resources through the Azure Portal or if you're transferring to a resource group in a different subscription, alternative methods using ARM are outlined below.
Move Labs to a Different Region
When you move a lab, there are some steps you must take to prepare for the move. You need to:
- Prepare the virtual network
- Export an ARM template of the lab
- Modify the template
- Deploy the template to move the lab
- Configure the new lab
- Swap the OS disks of the Compute VMs under the new VMs
- Clean up the original lab
Prepare the Virtual Network
To get started, export and modify a Resource Manager template.
Sign in to the Azure portal.
If you don't have Resource Group under the target region, create one now.
Move the current Virtual Network to the new region and resource group using the steps included in the article, "Move an Azure virtual network to another region".
Alternately, you can create a new virtual network, if you don't have to keep the original one.
Export an ARM template of the lab
Next, you export a JSON template contains settings that describe the lab.
To export a template by using Azure portal:
Select All resources, and then select the resource group for the lab.
Select Export template.
Choose Download in Export template.
Locate the .zip file that you downloaded from the portal, and unzip that file to a folder of your choice.
This zip file contains the .json files that comprise the template and scripts to deploy the template. It contains all the resources under your lab listed in ARM template format, except for the Shared Image Gallery resources.
Modify the template
In order for the ARM template to deploy correctly in the new region, you must change a few parts of the template.
To update the template by using Azure portal:
In the Azure portal, select Create a resource.
In Search the Marketplace, type template deployment, and then press ENTER.
Select Template deployment.
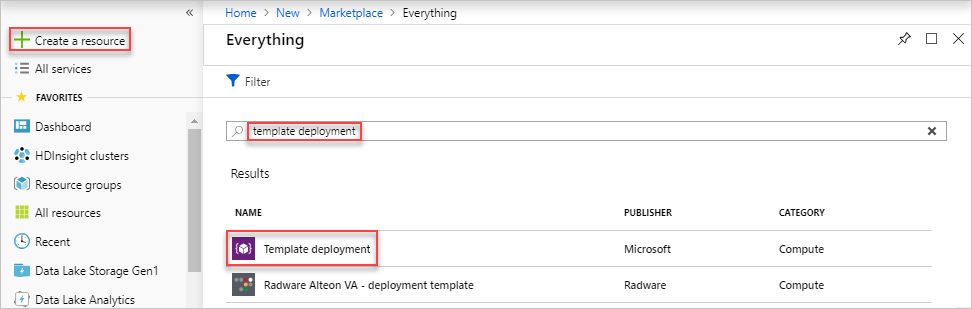
Select Create.
Select Build your own template in the editor.
Select Load file, and then follow the instructions to load the template.json file that you downloaded in the last section.
In the editor, make the following changes to the template.json file:
Replace the original
locationwith the new region in which you want to deploy, such aswestus2,southeastasia, etc. To obtain region location codes, see Azure Locations. The code for a region is the region name with no spaces, Central US =centralus."variables": {}, "resources": [ { "type": "microsoft.devtestlab/labs", "location": "centralus",If you have "All virtual machines in one resource group" set in the "Lab settings", also update the following values in the ARM template:
- Update the
apiVersionof themicrosoft.devtestlab/labsresource to2018-10-15-preview. - Add
vmCreationResourceGroupIdto thepropertiessection.
"variables": {}, "resources": [ { "type": "microsoft.devtestlab/labs", "apiVersion": "2018-10-15-preview", "name": "[parameters('labs_lj_dtl_rgsettings_name')]", "location": "<regionName>", "properties": { "vmCreationResourceGroupId": "/subscriptions/<subscriptionID>/resourceGroups/<myResourceGroup>", "labStorageType": "Premium",- Update the
Find the
"type": "microsoft.devtestlab/labs/users"resource. There, remove the entiresecretStoresection, including thekeyVaultldand thekeyVaultUriparameters.secretStore": { "keyVaultUri": "<vaultvalue>" "keyVaultld": "<id>" }Find the
"type": "microsoft.devtestlab/labs/virtualnetworks"resource. If you created a new virtual network earlier in these steps, you must add the actual subnet name in/subnets/[SUBNET_NAME]. If you chose to move the virtual network to a new region, you should skip this step.Find the
"type": "microsoft.devtestlab/labs/virtualmachines"resource.Under the "properties", add
"password": "RANDOM_PASSWORD"Note
A "password" property is required to create a new VM. We input a random password because we will later be swapping the OS disk with the original VM.
For Shared IP virtual machines, add this snippet under the "properties.networkInterface",
Windows VM with RDP:
"networkInterface": { "sharedPublicIpAddressConfiguration": { "inboundNatRules": [ { "transportProtocol": "tcp", "backendPort": 3389 } ] } }Linux VM with SSH:
"networkInterface": { "sharedPublicIpAddressConfiguration": { "inboundNatRules": [ { "transportProtocol": "tcp", "backendPort": 22 } ] } }
Under the
microsoft.devtestlab/labs/users/secretsresources, the following parameter the "properties". ReplaceYOUR_STORED_PASSWORDwith your password.Important
Use secureString for password values.
"value": "YOUR_STORED_PASSWORD"Under the
microsoft.devtestlab/labs/artifactsourcesresources, the following parameter the "properties". ReplaceYOUR_STORED_PASSWORDwith your password. Again, use secureString for password values."securityToken": "YOUR_PAT_TOKEN_VALUE"In the editor, save the template.
Deploy the template to move the lab
Deploy the template to create a new lab in the target region.
In the Custom deployment page, update all the parameters with the corresponding values defined in the template.
Enter the following values:
Name Value Subscription Select an Azure subscription. Resource group Select the resource group name you created in the last section. Location Select a location for the lab. For example, Central US. Lab Name Must be a different name. Vnet ID Must be the moved one, or the new one you created. Select Review + create.
Select Create.
Select the bell icon (notifications) from the top of the screen to see the deployment status. You shall see Deployment in progress. Wait until the deployment is completed.
Configure the new lab
While most Lab resources have been replicated under the new region using the ARM template, a few edits still need to be moved manually.
- Add the Compute Gallery back to the lab if there are any in the original one.
- Add the policies "Virtual machines per user", "Virtual machines per lab" and "Allowed Virtual machine sizes" back to the moved lab
Swap the OS disks of the Compute VMs under the new VMs
Note the VMs under the new Lab have the same specs as the ones under the old Lab. The only difference is their OS Disks.
Create an empty disk under the new region.
Get the target Compute VM OS disk name under the new Lab. You can find the Compute VM and its disk under the Resource group on the lab's Virtual Machine page.
Use AzCopy to copy the old disk content into the new/empty disks in the new region. You can run the PowerShell commands from your Dev Box or from the Azure Cloud Shell.
AzCopy is the preferred tool to move your data over. It's optimized for performance. One way that it's faster, is that data is copied directly, so AzCopy doesn't use the network bandwidth of your computer. Use AzCopy at the command line or as part of a custom script. See Get started with AzCopy.
# Fill in the source/target disk names and their resource group names $sourceDiskName = "SOURCE_DISK" $sourceRG = "SOURCE_RG" $targetDiskName = "TARGET_DISK" $targetRG = "TARGET_RG" $targetRegion = "TARGET_LOCATION" # Create an empty target disk from the source disk $sourceDisk = Get-AzDisk -ResourceGroupName $sourceRG -DiskName $sourceDiskName $targetDiskconfig = New-AzDiskConfig -SkuName $sourceDisk.Sku.Name -UploadSizeInBytes $($sourceDisk.DiskSizeBytes+512) -Location $targetRegion -OsType $sourceDisk.OsType -CreateOption 'Upload' $targetDisk = New-AzDisk -ResourceGroupName $targetRG -DiskName $targetDiskName -Disk $targetDiskconfig # Copy the disk content from source to target $sourceDiskSas = Grant-AzDiskAccess -ResourceGroupName $sourceRG -DiskName $sourceDiskName -DurationInSecond 1800 -Access 'Read' $targetDiskSas = Grant-AzDiskAccess -ResourceGroupName $targetRG -DiskName $targetDiskName -DurationInSecond 1800 -Access 'Write' azcopy copy $sourceDiskSas.AccessSAS $targetDiskSas.AccessSAS --blob-type PageBlob Revoke-AzDiskAccess -ResourceGroupName $sourceRG -DiskName $sourceDiskName Revoke-AzDiskAccess -ResourceGroupName $targetRG -DiskName $targetDiskNameAfter that, you'll have a new disk under the new region.
- Swap the OS disk of the Compute VM under the new lab with the new disk. To learn how, see the article, "Change the OS disk used by an Azure VM using PowerShell".
Move a schedule
There are two ways to move a schedule:
- Manually recreate the schedules on the moved VMs. This process can be time consuming and error prone. This approach is most useful when you have a few schedules and VMs.
- Export and redeploy the schedules by using ARM templates.
Use the following steps to export and redeploy your schedule in another Azure region by using an ARM template:
Sign in to the Azure portal.
Go to the source resource group that held your VMs.
On the Resource Group Overview page, under Resources, select Show hidden types.
Select all resources with the type microsoft.devtestlab/schedules.
Select Export template.
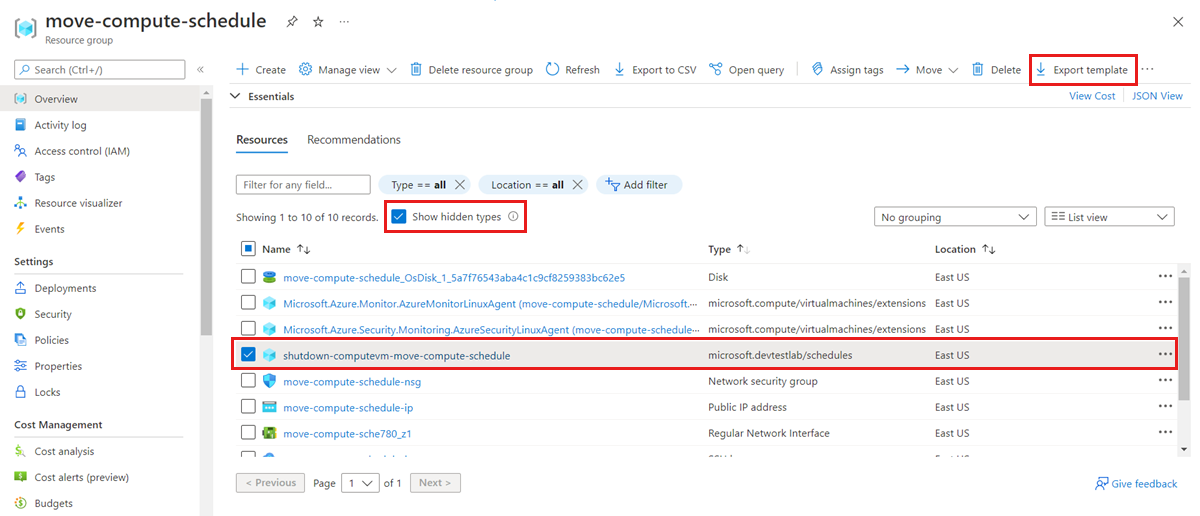
On the Export resource group template page, select Deploy.
On the Custom deployment page, select Edit template.
In the template code, change all instances of
"location": "<old location>"to"location": "<new location>"and then select Save.On the Custom deployment page, enter values that match the target VM:
Name Value Subscription Select an Azure subscription. Resource group Select the resource group name. Region Select a location for the lab schedule. For example, Central US. Schedule Name Must be a globally unique name. VirtualMachine_xxx_externalId Must be the target VM. 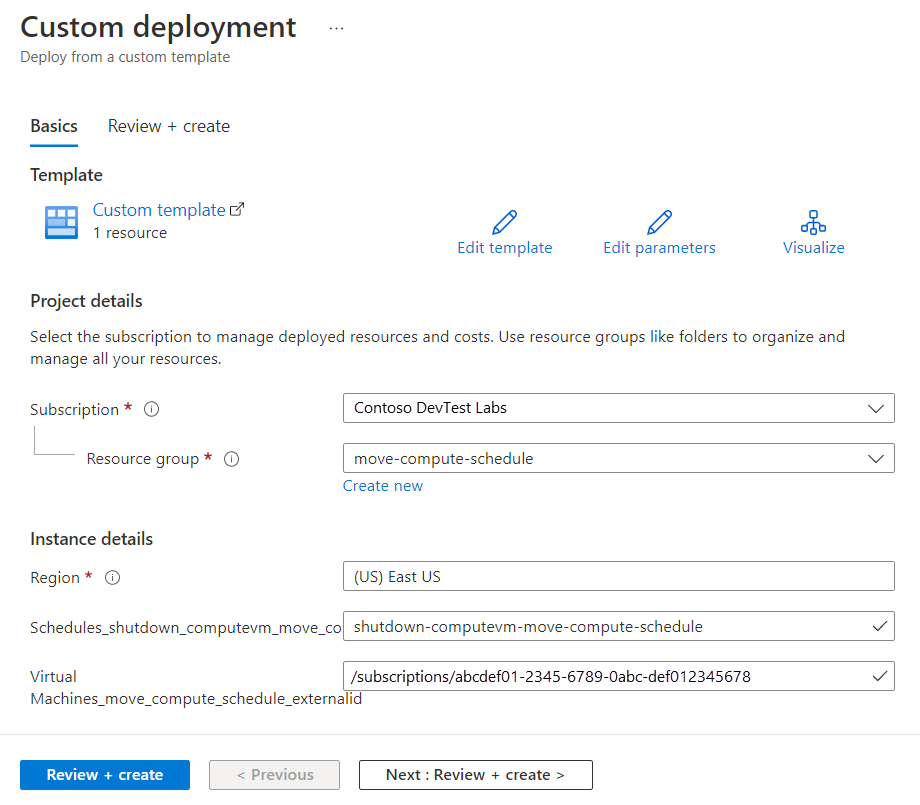
Important
Each schedule must have a globally unique name; you will need to change the schedule name for the new location.
Select Review and create to create the deployment.
When the deployment is complete, verify that the new schedule is configured correctly on the new VM.
Discard or clean up
After the deployment, if you want to start over, you can delete the target lab, and repeat the steps described in the Prepare and Move sections of this article.
To commit the changes and complete the move, you must delete the original lab.
To remove a lab by using the Azure portal:
In the Azure portal, expand the menu on the left side to open the menu of services, and choose DevTest Labs to display the list of labs.
Locate the target lab to delete, and right-click the More button (...) on the right side of the listing.
Select Delete, and confirm.
You can also choose to clean up the original schedules if they're no longer used. Go to the original schedule resource group (where you exported templates from in step 5 above) and delete the schedule resource.
Next steps
In this article, you moved DevTest Labs from one region to another and cleaned up the source resources. To learn more about moving resources between regions and disaster recovery in Azure, refer to: