Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Running a Replicate changes Migration, with our offline scenario with "Enable Transactional Consistency" enables businesses to migrate their databases to Azure while the databases remain operational. In other words, migrations can be completed with minimum downtime for critical applications, limiting the impact on service level availability and inconvenience to their end customers.
Current implementation
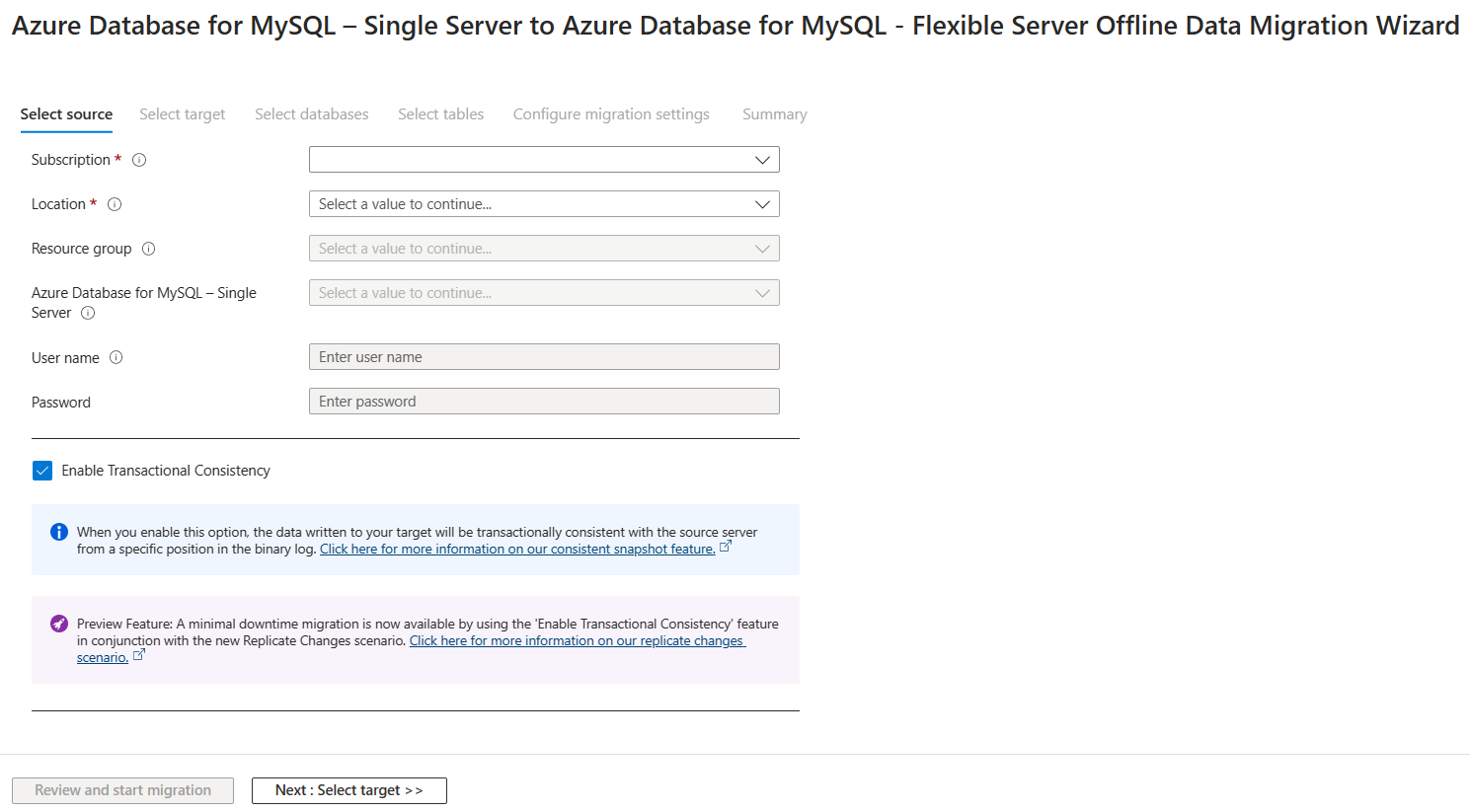
You must run an offline migration scenario with "Enable Transactional Consistency" to get the bin log file and position to replicate the incoming changes. The DMS portal UI shows the binary log filename and position aligned to the time the locks were obtained on the source for the consistent snapshot. You can use this value in our replicate changes migration to stream the incoming changes.
While running the replicate changes migration, when your target is almost caught up with the source server, stop all incoming transactions to the source database and wait until all pending transactions have been applied to the target database. To confirm that the target database is up-to-date on the source server, run the query 'SHOW MASTER STATUS;', then compare that position to the last committed binlog event (displayed under Migration Progress). When the two positions are the same, the target has caught up with all changes, and you can start the cutover.
How Replicate Changes works
The current implementation is based on streaming binlog changes from the source server and applying them to the target server. Like Data-in replication, this is easier to set up and doesn't require a physical connection between the source and the target servers.
The server can send Binlog as a stream that contains binary data as documented here. The client can specify the initial log position to start the stream with. The log file name describes the log position, the position within that file, and optionally GTID (Global Transaction ID) if gtid mode is enabled at the source.
The data changes are sent as "row" events, which contain data for individual rows (prior and/or after the change depending on the operation type, which is insert, delete, or update). The row events are then applied in their raw format using a BINLOG statement: MySQL 8.0 Reference Manual :: 13.7.8.1 BINLOG Statement. But for a DMS migration to a 5.7 server, DMS doesn't apply changes as BINLOG statements (since DMS doesn't have necessary privileges to do so) and instead translates the row events into INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE statements.
Prerequisites
To complete the replicate changes migration successfully, ensure that the following prerequisites are in place:
Use the MySQL command line tool of your choice to determine whether
log_binis enabled on the source server. The Binlog isn't always turned on by default, so verify that it's enabled before starting the migration. To determine whether log_bin is enabled on the source server, run the command:SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'log_bin'Ensure that the user has
REPLICATION_APPLIERorBINLOG_ADMINpermission on target server for applying the bin log.Ensure that the user has
REPLICATION REPLICApermission on the target server.Ensure that the user has
REPLICATION CLIENTandREPLICATION REPLICApermission on the source server for reading and applying the bin log.Run an offline migration scenario with Enable Transactional Consistency to get the bin log file and position.
If you're targeting a replicate changes migration, configure the binlog_expire_logs_seconds parameter on the source server to ensure that binlog files aren't purged before the replica commits the changes. We recommend at least two days, to begin with. After a successful cutover, the value can be reset.
Limitations
- When performing a replicate changes migration, the name of the database on the target server must be the same as the name on the source server.
- Support is limited to the ROW binlog format.
- DDL changes replication is supported only when you have selected the option for Replicate data definition and administration statements for selected objects on DMS UI. The replication feature supports replicating data definition and administration statements that occur after the initial load and are logged in the binary log to the target.
- Renaming databases or tables isn't supported when replicating changes.