Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
In this guide, you learn how to use MQTT v5 Request-Response messaging pattern to implement command-response flow with MQTT broker. Consider a sample scenario, in which a cloud application sends commands to devices and receives responses from the devices.
Prerequisites
- You have an Event Grid namespace created with MQTT broker enabled. Refer to this Quickstart - Publish and subscribe on an MQTT topic to create the namespace, subresources, and to publish/subscribe on an MQTT topic.
Configuration needed in Event Grid namespace to implement Request-Response messaging pattern
Here's the sample configuration to achieve Request-Response messaging pattern using MQTT broker.
CA certificate
Add the CA certificate that is used to sign the client certificates.
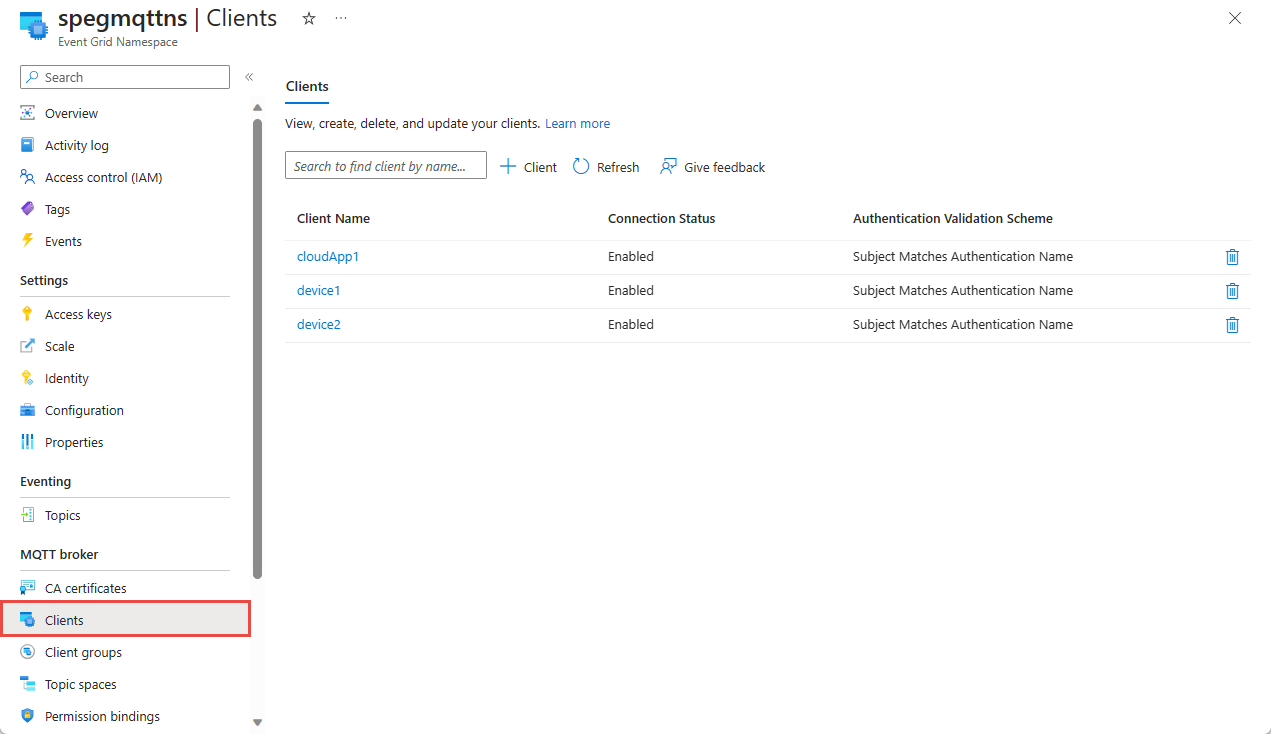
Clients
- Register the cloud application as a client in the namespace. Add an attribute called "type" to the client, with value as "cloudApp".
- Register the devices as clients in the namespace. Add the "type" attribute to the clients, with value as "device".
You can use any supported authentication method. This sample configuration shows CA certificate chain based authentication and assumes that the client authentication name is in the Subject field of client certificate.
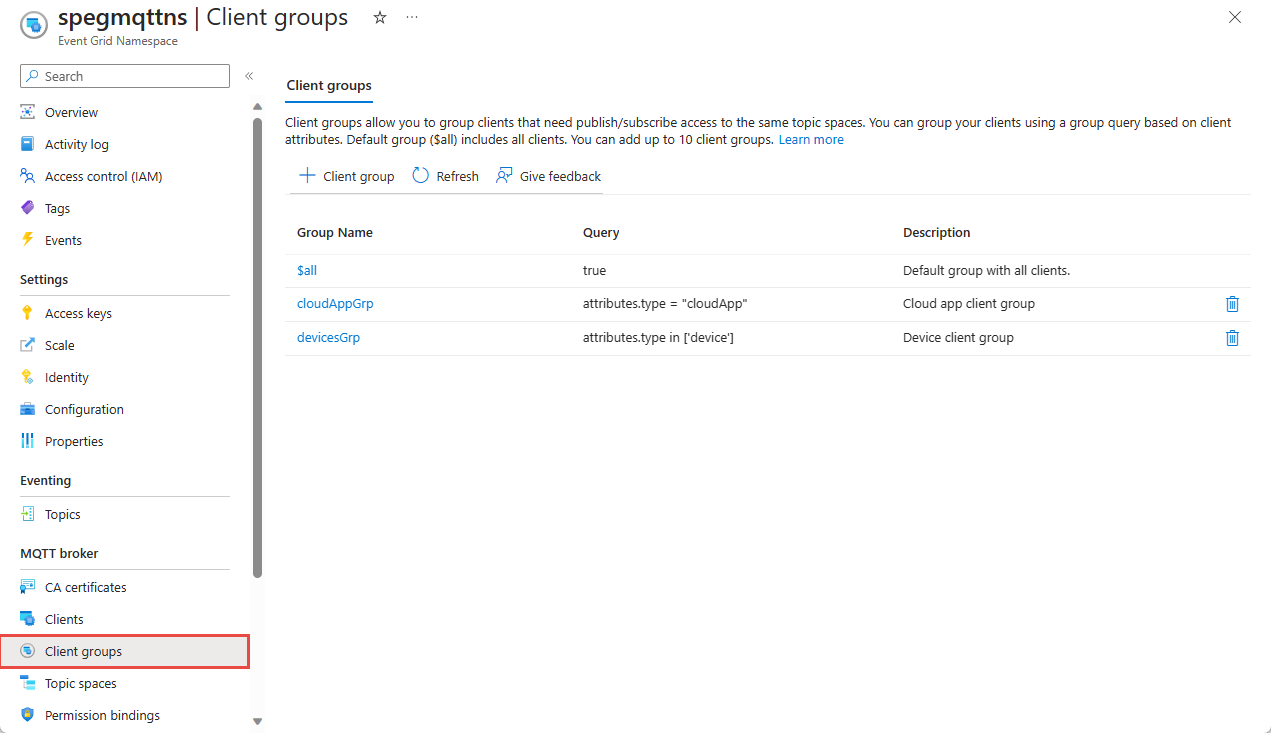
Client groups
Create two client groups, one for the cloud application client and another for all the devices.
"cloudAppGrp" client group includes the clients with "type" attribute's value set to "cloudApp".
"devicesGrp" client group includes all the clients of type "device".
Topic spaces
Create "requestDesiredProperties" topic space with topic template "devices/+/desired" to which cloud application publishes desired-property requests. Wildcard allows the cloud application to publish a request to any device.
Create "responseReportedProperties" topic space with topic template "devices/+/reported" to which cloud application subscribes to receive reported-property responses from devices.
Create "deviceDesiredSub" topic space with topic template "devices/${client.authenticationName}/desired" to which devices subscribe to receive the desired-property requests from the cloud application. Authentication name variable is used to ensure a device can receive messages meant only for that device.
Create "deviceReportedPub" topic space with topic template "devices/${client.authenticationName}/reported" to which devices publish reported-property responses.
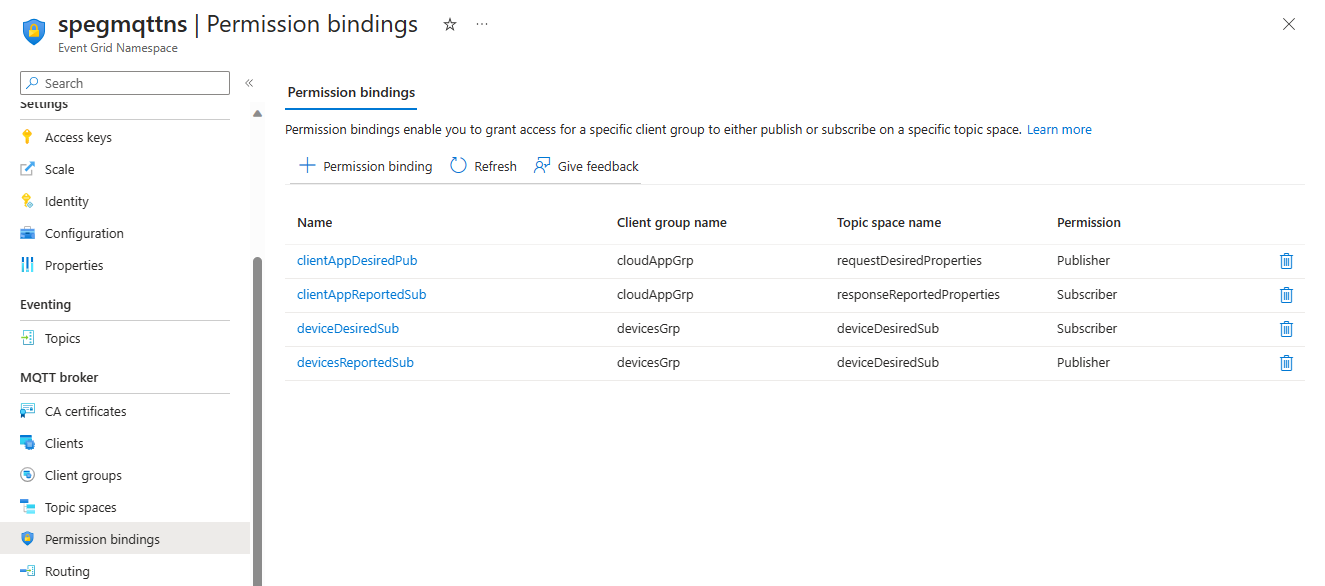
Permission bindings
Create permission bindings that allow cloud application group to publish on request topic, and subscribe to response topic. Devices group subscribes to request topic and publishes to response topic.
Create "clientAppDesiredPub" permission binding that grants "cloudAppGrp" with publisher access to "requestDesiredProperties" topic space.
Create "clientAppReportedSub" permission binding that grants "cloudAppGrp" with subscriber access to "responseReportedProperties" topic space.
Create "deviceDesiredSub" permission binding that grants "devicesGrp" with subscriber access to "deviceDesiredSub" topic space.
Create "deviceReportedPub" permission binding that grants "devicesGrp" with publisher access to "deviceReportedPub" topic space.
Showing Request-Response messages using MQTTX application
Connect the cloud application and devices to the MQTT broker using the MQTTX application.
Add "devices/+/reported" as subscription to cloud application client
Add their own request topics as subscriptions to devices. For example, add "devices/device1/desired" as subscription to "device1" client.
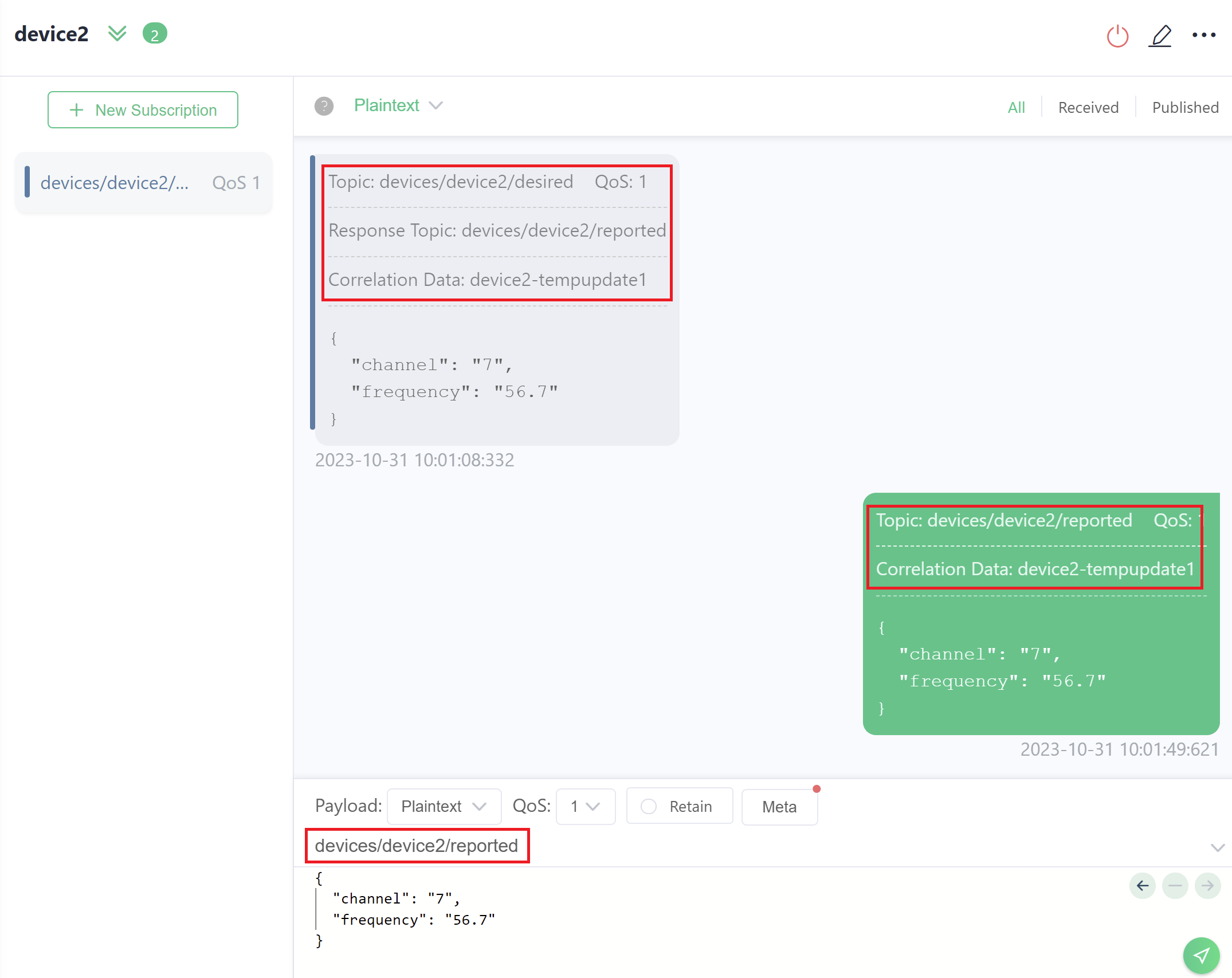
Cloud application publishes a request to device2 on "devices/device2/desired" topic, and includes a response topic "devices/device2/reported". Cloud application includes Correlation Data as "device2-tempupdate1".
The device2 receives the message on "devices/device2/desired" topic and reports its current properties state on the response topic "devices/device2/reported" to the cloud application client. Also, device2 includes Correlation Data as "device2-tempupdate1", which allows cloud application to trace the response back to the original request.
Note
- These MQTT messages can be routed via Event Grid subscriptions and written to a storage or cache to keep track of the desired and current state of a device.
- Client life cycle events such as "connected" and "disconnected" can be used to keep track of a device's availability to resend any requests as needed.
- Request-Response message pattern can also be achieved in MQTT v3.1.1, by including the Response topic in the request message payload. The device client needs to parse the message payload, identifies the Response topic, and publishes the response on that topic.