Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
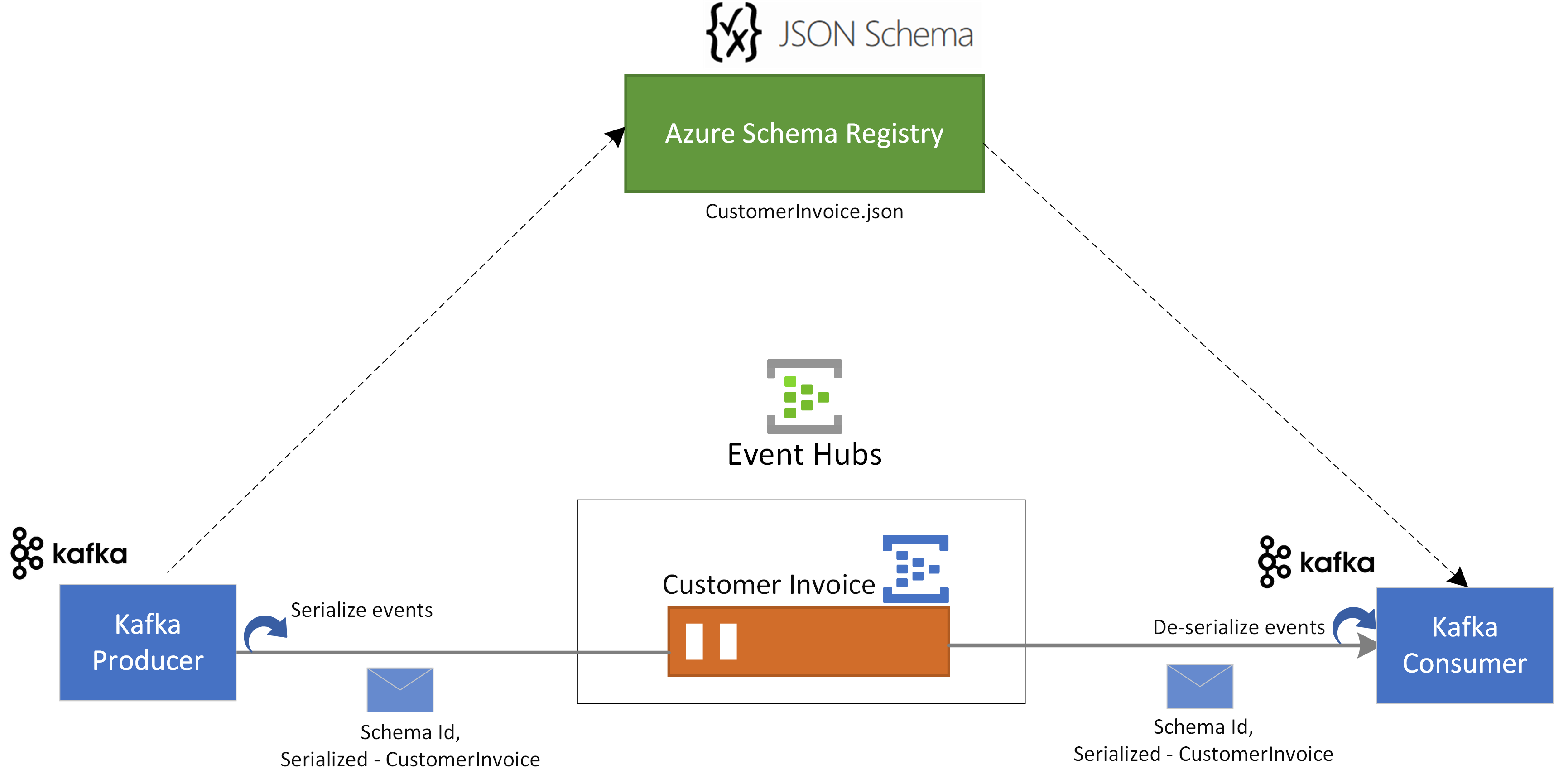
This tutorial walks you through a scenario where you use JSON Schemas to serialize and deserialize event using Azure Schema Registry in Event Hubs.
In this use case a Kafka producer application uses JSON schema stored in Azure Schema Registry to, serialize the event and publish them to a Kafka topic/event hub in Azure Event Hubs. The Kafka consumer deserializes the events that it consumes from Event Hubs. For that it uses schema ID of the event and JSON schema, which is stored in Azure Schema Registry.
Prerequisites
If you're new to Azure Event Hubs, see Event Hubs overview before you do this quickstart.
To complete this quickstart, you need the following prerequisites:
- If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a free account before you begin.
- In your development environment, install the following components:
- Java Development Kit (JDK) 1.7+.
- Download and install a Maven binary archive.
- Git
- Clone the Azure Schema Registry for Kafka repository.
Create an event hub
Follow instructions from the quickstart: Create an Event Hubs namespace and an event hub to create an Event Hubs namespace and an event hub. Then, follow instructions from Get the connection string to get a connection string to your Event Hubs namespace.
Note down the following settings that you use in the current quickstart:
- Connection string for the Event Hubs namespace
- Name of the event hub
Create a schema
Follow instructions from Create schemas using Schema Registry to create a schema group and a schema.
Create a schema group named contoso-sg using the Schema Registry portal. Use JSON Schema as the serialization type.
In that schema group, create a new JSON schema with schema name:
Microsoft.Azure.Data.SchemaRegistry.example.CustomerInvoiceusing the following schema content.{ "$id": "https://example.com/person.schema.json", "$schema": "https://json-schema.org/draft/2020-12/schema", "title": "CustomerInvoice", "type": "object", "properties": { "invoiceId": { "type": "string" }, "merchantId": { "type": "string" }, "transactionValueUsd": { "type": "integer" }, "userId": { "type": "string" } } }
Register an application to access schema registry
You can use Microsoft Entra ID to authorize your Kafka producer and consumer application to access Azure Schema Registry resources. To enable it, you need to register your client application with a Microsoft Entra tenant from the Azure portal.
To register a Microsoft Entra application named example-app see Register your application with a Microsoft Entra tenant.
- tenant.id - sets the tenant ID of the application
- client.id - sets the client ID of the application
- client.secret - sets the client secret for authentication
And if you're using managed identity, you would need:
- use.managed.identity.credential - indicates that MSI credentials should be used, should be used for MSI-enabled VM
- managed.identity.clientId - if specified, it builds MSI credential with given client ID managed.identity.resourceId - if specified, it builds MSI credential with given resource ID
Add user to Schema Registry Reader role
Add your user account to the Schema Registry Reader role at the namespace level. You can also use the Schema Registry Contributor role, but that's not necessary for this quickstart.
- On the Event Hubs namespace page, select Access control (IAM) on the left menu.
- On the Access control (IAM) page, select + Add -> Add role assignment on the menu.
- On the Assignment type page, select Next.
- On the Roles page, select Schema Registry Reader, and then select Next at the bottom of the page.
- Use the + Select members link to add the
example-appapplication that you created in the previous step to the role, and then select Next. - On the Review + assign page, select Review + assign.
Update client application configuration of Kafka applications
You need to update the client configuration of the Kafka producer and consumer applications with the Microsoft Entra application details and with the schema registry information.
To update the Kafka Producer configuration, navigate to azure-schema-registry-for-kafka/tree/master/java/json/samples/kafka-producer.
Update the configuration of the Kafka application in src/main/resources/app.properties by following Kafka Quickstart guide for Event Hubs.
Update the configuration details for the producer in src/main/resources/app.properties using schema registry related configuration and Microsoft Entra application that you created in the previous step as follows:
schema.group=contoso-sg schema.registry.url=https://<NAMESPACENAME>.servicebus.windows.net tenant.id=<> client.id=<> client.secret=<>Follow the same instructions and update the azure-schema-registry-for-kafka/tree/master/java/json/samples/kafka-consumer configuration as well.
For both Kafka producer and consumer applications, following JSON schema is used:
{ "$id": "https://example.com/person.schema.json", "$schema": "https://json-schema.org/draft/2020-12/schema", "title": "CustomerInvoice", "type": "object", "properties": { "invoiceId": { "type": "string" }, "merchantId": { "type": "string" }, "transactionValueUsd": { "type": "integer" }, "userId": { "type": "string" } } }
Using Kafka producer with JSON schema validation
To run the Kafka producer application, navigate to azure-schema-registry-for-kafka/tree/master/java/json/samples/kafka-producer.
You can run the producer application so that it can produce JSON Schema specific records or generic records. For specific records mode you need to first generate the classes against either the producer schema using the following maven command:
mvn generate-sourcesThen you can run the producer application using the following commands.
mvn clean package mvn -e clean compile exec:java -Dexec.mainClass="com.azure.schemaregistry.samples.producer.App"Upon successful execution of the producer application, it prompts you to choose the producer scenario. For this quickstart, you can choose option 1 - produce SpecificRecords.
Enter case number: 1 - produce SpecificRecordsUpon successful data serialization and publishing, you should see the following console logs in your producer application:
INFO com.azure.schemaregistry.samples.producer.KafkaJsonSpecificRecord - Sent Order Invoice 0 INFO com.azure.schemaregistry.samples.producer.KafkaJsonSpecificRecord - Sent Order Invoice 1 INFO com.azure.schemaregistry.samples.producer.KafkaJsonSpecificRecord - Sent Order Invoice 2
Using Kafka consumer with JSON schema validation
To run the Kafka consumer application, navigate to azure-schema-registry-for-kafka/tree/master/java/json/samples/kafka-consumer.
You can run the consumer application so that it can consume JSON Schema specific records or generic records. For specific records mode you need to first generate the classes against either the producer schema using the following maven command:
mvn generate-sourcesThen you can run the consumer application using the following command.
mvn clean package mvn -e clean compile exec:java -Dexec.mainClass="com.azure.schemaregistry.samples.consumer.App"Upon successful execution of the consumer application, it prompts you to choose the producer scenario. For this quickstart, you can choose option 1 - consume SpecificRecords.
Enter case number: 1 - consume SpecificRecordsUpon successful data consumption and deserialization, you should see the following console logs in your producer application:
INFO com.azure.schemaregistry.samples.consumer.KafkaJsonSpecificRecord - Invoice received: {invoiceId=Invoice 0, merchantId=Merchant Id 0, transactionValueUsd=0, userId=User Id 0} INFO com.azure.schemaregistry.samples.consumer.KafkaJsonSpecificRecord - Invoice received: {invoiceId=Invoice 1, merchantId=Merchant Id 1, transactionValueUsd=1, userId=User Id 1} INFO com.azure.schemaregistry.samples.consumer.KafkaJsonSpecificRecord - Invoice received: {invoiceId=Invoice 2, merchantId=Merchant Id 2, transactionValueUsd=2, userId=User Id 2}
Clean up resources
Delete the Event Hubs namespace or delete the resource group that contains the namespace.