Regulatory Compliance in Azure Policy
Regulatory Compliance in Azure Policy provides built-in initiative definitions to view a list of the
controls and compliance domains based on responsibility (Customer, Microsoft, Shared).
For Microsoft-responsible controls, we provide additional details of our audit results based on
third-party attestation and our implementation details to achieve that compliance.
Microsoft-responsible controls are of policyType static.
Note
Regulatory Compliance is a Preview feature. For updated built-ins, the initiatives controls map to the corresponding compliance standard. Existing compliance standard initiatives are in the process of being updated to support Regulatory Compliance.
Regulatory Compliance defined
Regulatory Compliance is built on the
grouping portion of an initiative
definition. In built-ins, each grouping in the initiative definition defines a name (control), a
category (compliance domain), and provides a reference to the
policyMetadata object that has information
about that control. A Regulatory Compliance initiative definition must have the category
property set to Regulatory Compliance. As an otherwise standard initiative definition,
Regulatory Compliance initiatives support
parameters to create dynamic assignments.
Customers can create their own Regulatory Compliance initiatives. These definitions can be original or copied from existing built-in definitions. If using a built-in Regulatory Compliance initiative definition as a reference, it's recommended to monitor the source of the Regulatory Compliance definitions in the Azure Policy GitHub repo.
To link a custom Regulatory Compliance initiative to your Microsoft Defender for Cloud dashboard, see Create custom security initiatives and policies.
Regulatory Compliance in portal
When an initiative definition has been created with groups, the Compliance details page in portal for that initiative has additional information.
A new tab, Controls is added to the page. Filtering is available by compliance domain and
policy definitions are grouped by the title field from the policyMetadata object. Each row
represents a control that shows its compliance state, the compliance domain it's part of,
responsibility information, and how many non-compliant and compliant policy definitions make up that
control.
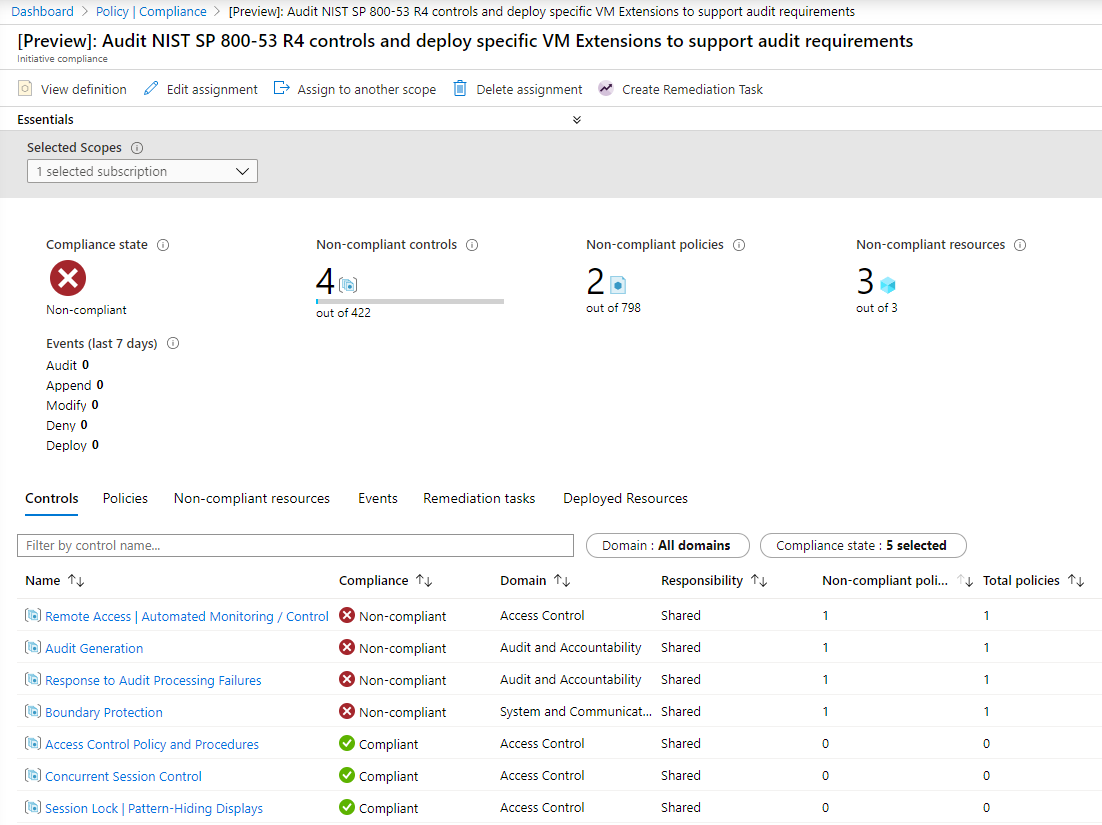
Selecting a control opens a page of details about that control. The Overview contains the
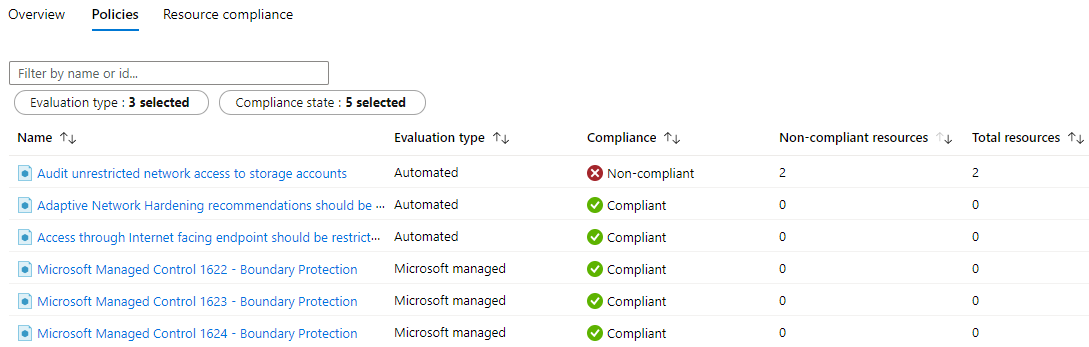
information from description and requirements. Under the Policies tab are all the individual
policy definitions in the initiative that contribute to this control. The Resource
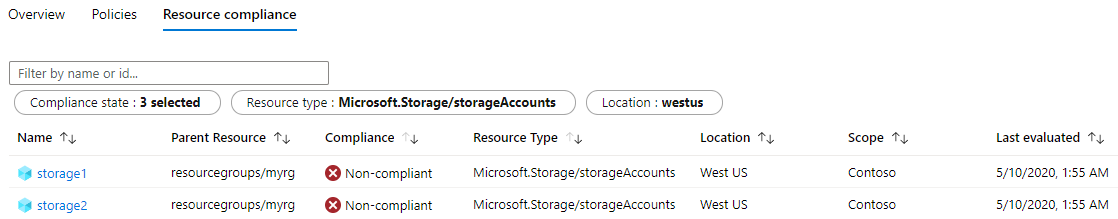
compliance tab provides a granular view of each resource that's evaluated by a member policy of
the currently viewed control.
Note
An evaluation type of Microsoft managed is for a static policy definition policyType.
From the same control page, changing to the Resource compliance tab shows all resources this control's policy definitions include. Filters are available for name or ID, compliance state, resource type, and location.
Regulatory Compliance in SDK
If Regulatory Compliance is enabled on an initiative definition, the evaluation scan record, events, and policy states SDK each return additional properties. These additional properties are grouped by compliance state and provide information on how many groups are in each state.
The following code is an example of added results from a summarize call:
"policyGroupDetails": [{
"complianceState": "noncompliant",
"count": 4
},
{
"complianceState": "compliant",
"count": 76
}
]
Next steps
- See the initiative definition structure
- Review examples at Azure Policy samples.
- Review Understanding policy effects.
- Learn how to remediate non-compliant resources.