Quickstart: Create Apache Spark cluster in Azure HDInsight using Bicep
In this quickstart, you use Bicep to create an Apache Spark cluster in Azure HDInsight. You then create a Jupyter Notebook file, and use it to run Spark SQL queries against Apache Hive tables. Azure HDInsight is a managed, full-spectrum, open-source analytics service for enterprises. The Apache Spark framework for HDInsight enables fast data analytics and cluster computing using in-memory processing. Jupyter Notebook lets you interact with your data, combine code with markdown text, and do simple visualizations.
If you're using multiple clusters together, you'll want to create a virtual network, and if you're using a Spark cluster you'll also want to use the Hive Warehouse Connector. For more information, see Plan a virtual network for Azure HDInsight and Integrate Apache Spark and Apache Hive with the Hive Warehouse Connector.
Bicep is a domain-specific language (DSL) that uses declarative syntax to deploy Azure resources. It provides concise syntax, reliable type safety, and support for code reuse. Bicep offers the best authoring experience for your infrastructure-as-code solutions in Azure.
Prerequisites
If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a free account before you begin.
Review the Bicep file
The Bicep file used in this quickstart is from Azure Quickstart Templates.
@description('The name of the HDInsight cluster to create.')
param clusterName string
@description('These credentials can be used to submit jobs to the cluster and to log into cluster dashboards. The username must consist of digits, upper or lowercase letters, and/or the following special characters: (!#$%&\'()-^_`{}~).')
@minLength(2)
@maxLength(20)
param clusterLoginUserName string
@description('The password must be at least 10 characters in length and must contain at least one digit, one upper case letter, one lower case letter, and one non-alphanumeric character except (single-quote, double-quote, backslash, right-bracket, full-stop). Also, the password must not contain 3 consecutive characters from the cluster username or SSH username.')
@minLength(10)
@secure()
param clusterLoginPassword string
@description('These credentials can be used to remotely access the cluster. The sshUserName can only consit of digits, upper or lowercase letters, and/or the following special characters (%&\'^_`{}~). Also, it cannot be the same as the cluster login username or a reserved word')
@minLength(2)
param sshUserName string
@description('SSH password must be 6-72 characters long and must contain at least one digit, one upper case letter, and one lower case letter. It must not contain any 3 consecutive characters from the cluster login name')
@minLength(6)
@maxLength(72)
@secure()
param sshPassword string
@description('Location for all resources.')
param location string = resourceGroup().location
@description('This is the headnode Azure Virtual Machine size, and will affect the cost. If you don\'t know, just leave the default value.')
@allowed([
'Standard_A4_v2'
'Standard_A8_v2'
'Standard_E2_v3'
'Standard_E4_v3'
'Standard_E8_v3'
'Standard_E16_v3'
'Standard_E20_v3'
'Standard_E32_v3'
'Standard_E48_v3'
])
param headNodeVirtualMachineSize string = 'Standard_E8_v3'
@description('This is the workernode Azure Virtual Machine size, and will affect the cost. If you don\'t know, just leave the default value.')
@allowed([
'Standard_A4_v2'
'Standard_A8_v2'
'Standard_E2_v3'
'Standard_E4_v3'
'Standard_E8_v3'
'Standard_E16_v3'
'Standard_E20_v3'
'Standard_E32_v3'
'Standard_E48_v3'
])
param workerNodeVirtualMachineSize string = 'Standard_E8_v3'
resource defaultStorageAccount 'Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts@2021-08-01' = {
name: 'storage${uniqueString(resourceGroup().id)}'
location: location
sku: {
name: 'Standard_LRS'
}
kind: 'StorageV2'
}
resource cluster 'Microsoft.HDInsight/clusters@2021-06-01' = {
name: clusterName
location: location
properties: {
clusterVersion: '4.0'
osType: 'Linux'
tier: 'Standard'
clusterDefinition: {
kind: 'spark'
configurations: {
gateway: {
'restAuthCredential.isEnabled': true
'restAuthCredential.username': clusterLoginUserName
'restAuthCredential.password': clusterLoginPassword
}
}
}
storageProfile: {
storageaccounts: [
{
name: replace(replace(defaultStorageAccount.properties.primaryEndpoints.blob, 'https://', ''), '/', '')
isDefault: true
container: clusterName
key: defaultStorageAccount.listKeys('2021-08-01').keys[0].value
}
]
}
computeProfile: {
roles: [
{
name: 'headnode'
targetInstanceCount: 2
hardwareProfile: {
vmSize: headNodeVirtualMachineSize
}
osProfile: {
linuxOperatingSystemProfile: {
username: sshUserName
password: sshPassword
}
}
}
{
name: 'workernode'
targetInstanceCount: 2
hardwareProfile: {
vmSize: workerNodeVirtualMachineSize
}
osProfile: {
linuxOperatingSystemProfile: {
username: sshUserName
password: sshPassword
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
output storage object = defaultStorageAccount.properties
output cluster object = cluster.properties
Two Azure resources are defined in the Bicep file:
- Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts: create an Azure Storage Account.
- Microsoft.HDInsight/cluster: create an HDInsight cluster.
Deploy the Bicep file
Save the Bicep file as main.bicep to your local computer.
Deploy the Bicep file using either Azure CLI or Azure PowerShell.
az group create --name exampleRG --location eastus az deployment group create --resource-group exampleRG --template-file main.bicep --parameters clusterName=<cluster-name> clusterLoginUserName=<cluster-username> sshUserName=<ssh-username>You need to provide values for the parameters:
- Replace <cluster-name> with the name of the HDInsight cluster to create.
- Replace <cluster-username> with the credentials used to submit jobs to the cluster and to log in to cluster dashboards. The username has a minimum length of two characters and a maximum length of 20 characters. It must consist of digits, upper or lowercase letters, and/or the following special characters: (!#$%&'()-^_`{}~).').
- Replace <ssh-username> with the credentials used to remotely access the cluster. The username has a minimum length of two characters. It must consist of digits, upper or lowercase letters, and/or the following special characters: (%&'^_`{}~). It cannot be the same as the cluster username.
You'll be prompted to enter the following:
- clusterLoginPassword, which must be at least 10 characters long and must contain at least one digit, one uppercase letter, one lowercase letter, and one non-alphanumeric character except single-quote, double-quote, backslash, right-bracket, full-stop. It also must not contain three consecutive characters from the cluster username or SSH username.
- sshPassword, which must be 6-72 characters long and must contain at least one digit, one uppercase letter, and one lowercase letter. It must not contain any three consecutive characters from the cluster login name.
Note
When the deployment finishes, you should see a message indicating the deployment succeeded.
If you run into an issue with creating HDInsight clusters, it could be that you don't have the right permissions to do so. For more information, see Access control requirements.
Review deployed resources
Use the Azure portal, Azure CLI, or Azure PowerShell to list the deployed resources in the resource group.
az resource list --resource-group exampleRG
Create a Jupyter Notebook file
Jupyter Notebook is an interactive notebook environment that supports various programming languages. You can use a Jupyter Notebook file to interact with your data, combine code with markdown text, and perform simple visualizations.
Open the Azure portal.
Select HDInsight clusters, and then select the cluster you created.
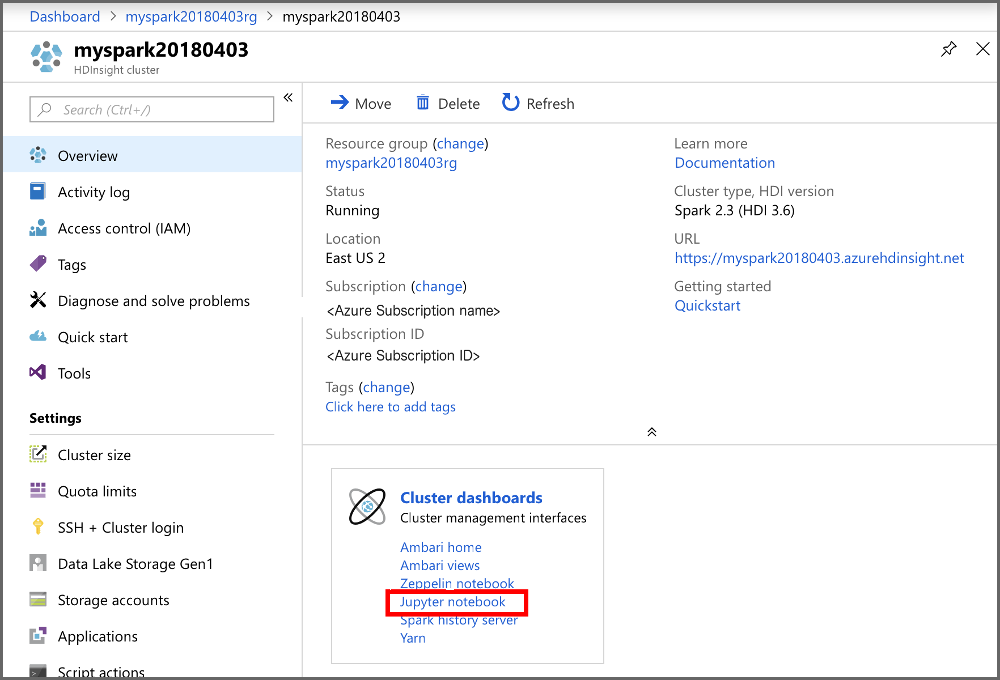
From the portal, in Cluster dashboards section, select Jupyter Notebook. If prompted, enter the cluster login credentials for the cluster.
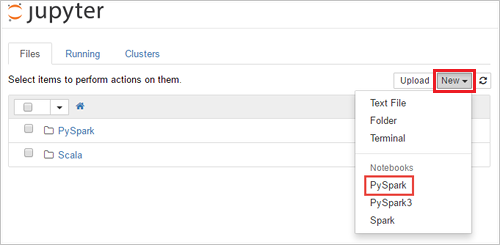
Select New > PySpark to create a notebook.
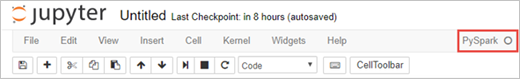
A new notebook is created and opened with the name Untitled(Untitled.pynb).
Run Apache Spark SQL statements
SQL (Structured Query Language) is the most common and widely used language for querying and transforming data. Spark SQL functions as an extension to Apache Spark for processing structured data, using the familiar SQL syntax.
Verify the kernel is ready. The kernel is ready when you see a hollow circle next to the kernel name in the notebook. Solid circle denotes that the kernel is busy.
When you start the notebook for the first time, the kernel performs some tasks in the background. Wait for the kernel to be ready.
Paste the following code in an empty cell, and then press SHIFT + ENTER to run the code. The command lists the Hive tables on the cluster:
%%sql SHOW TABLESWhen you use a Jupyter Notebook file with your HDInsight cluster, you get a preset
sparksession that you can use to run Hive queries using Spark SQL.%%sqltells Jupyter Notebook to use the presetsparksession to run the Hive query. The query retrieves the top 10 rows from a Hive table (hivesampletable) that comes with all HDInsight clusters by default. The first time you submit the query, Jupyter will create a Spark application for the notebook. It takes about 30 seconds to complete. Once the Spark application is ready, the query is executed in about a second and produces the results. The output looks like: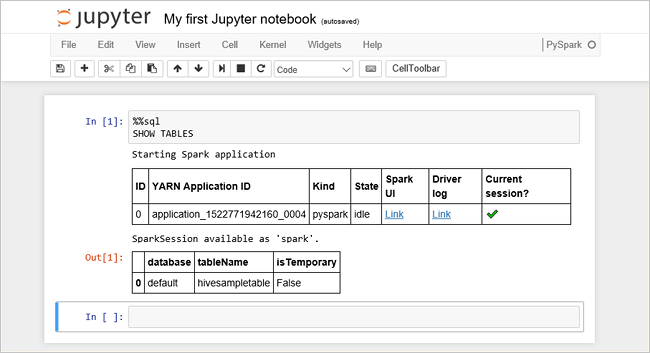
Every time you run a query in Jupyter, your web browser window title shows a (Busy) status along with the notebook title. You also see a solid circle next to the PySpark text in the top-right corner.
Run another query to see the data in
hivesampletable.%%sql SELECT * FROM hivesampletable LIMIT 10The screen should refresh to show the query output.
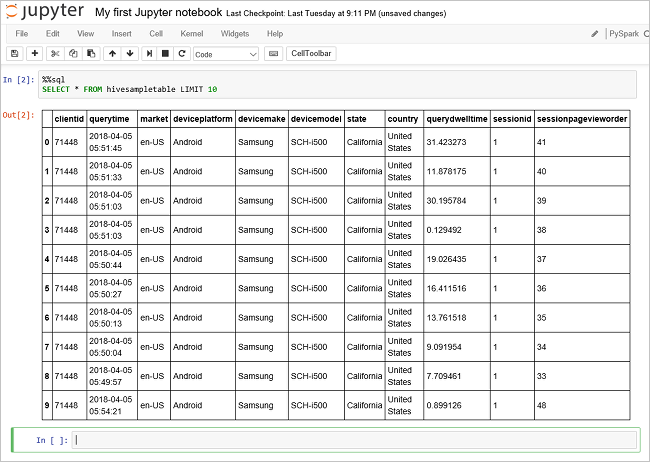
From the File menu on the notebook, select Close and Halt. Shutting down the notebook releases the cluster resources, including Spark application.
Clean up resources
When no longer needed, use the Azure portal, Azure CLI, or Azure PowerShell to delete the resource group and its resources.
az group delete --name exampleRG
Next steps
In this quickstart, you learned how to create an Apache Spark cluster in HDInsight and run a basic Spark SQL query. Advance to the next tutorial to learn how to use an HDInsight cluster to run interactive queries on sample data.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for