Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
The DICOM® service in Azure Health Data Services supports cross-origin resource sharing (CORS). CORS allows you to configure settings so that applications from one domain (origin) can access resources from a different domain, known as a cross-domain request.
CORS is often used in a single-page app that must call a RESTful API to a different domain.
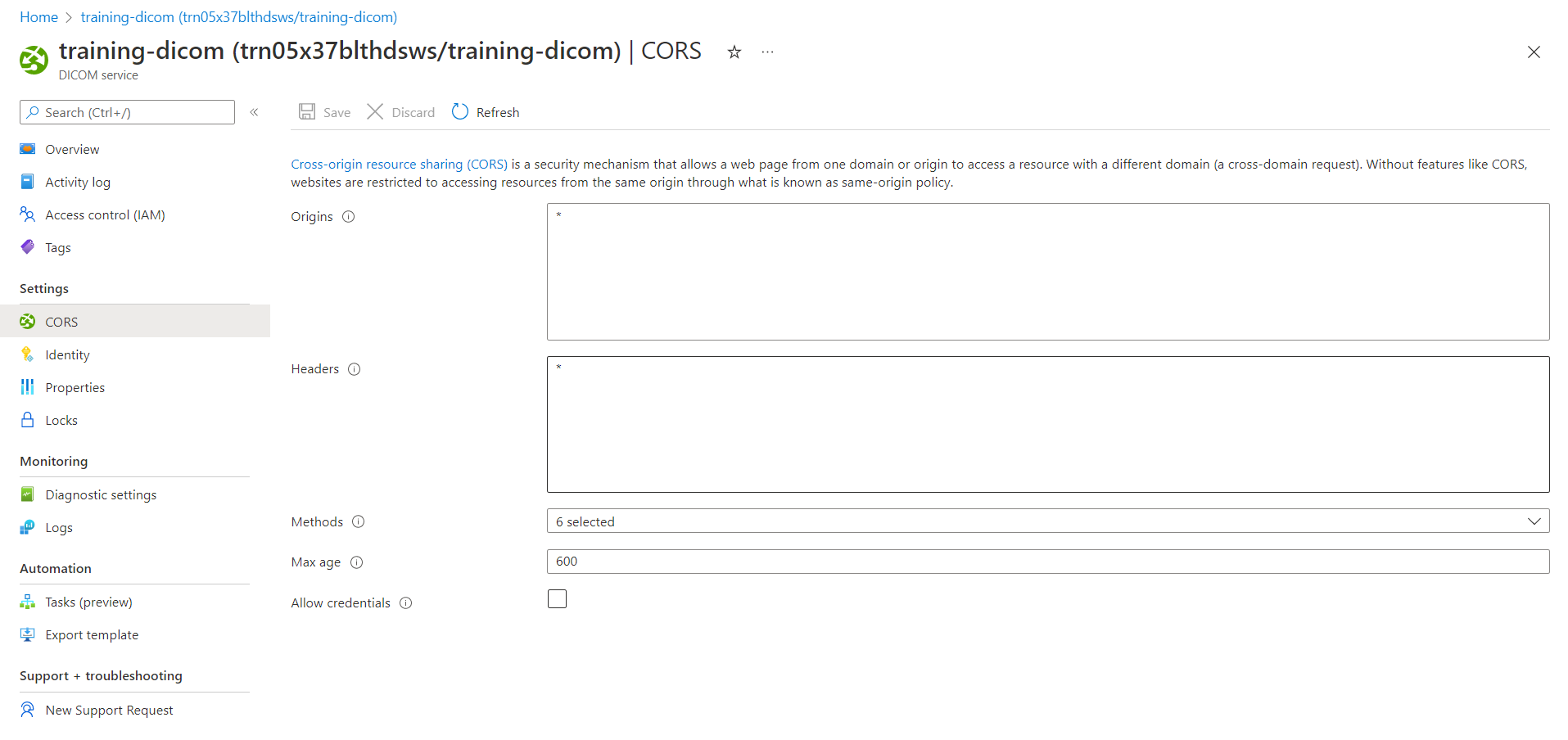
Cross-origin resource sharing configuration settings
To configure a CORS setting in the DICOM service, specify the following settings:
- Origins (Access-Control-Allow-Origin). A list of domains allowed to make cross-origin requests to the DICOM service. Each domain (origin) must be entered in a separate line. You can enter an asterisk (*) to allow calls from any domain, but we don't recommend it because it's a security risk.
Note
You can't specify different settings for different domain origins. All settings (Headers, Methods, Max age, and Allow credentials) apply to all origins specified in the Origins setting.
Headers (Access-Control-Allow-Headers). A list of headers that the origin request will contain. To allow all headers, enter an asterisk (*).
Methods (Access-Control-Allow-Methods). The allowed methods (PUT, GET, POST, and so on) in an API call. Choose Select all for all methods.
Max age (Access-Control-Max-Age). The value in seconds to cache preflight request results for Access-Control-Allow-Headers and Access-Control-Allow-Methods.
Allow credentials (Access-Control-Allow-Credentials). CORS requests normally don’t include cookies to prevent cross-site request forgery (CSRF) attacks. If you select this setting, the request can be made to include credentials, such as cookies. You can't configure this setting if you already set Origins with an asterisk (*).
Note
DICOM® is the registered trademark of the National Electrical Manufacturers Association for its Standards publications relating to digital communications of medical information.