Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
In this article, you learn how to manage access (authorization) to an Azure load testing resource. Azure role-based access control (Azure RBAC) is used to manage access to Azure resources, such as the ability to create new resources or use existing ones. You can grant role-based access to users using the Azure portal, Azure Command-Line tools, or Azure Management APIs.
Prerequisites
To assign Azure roles, your Azure account must have:
Microsoft.Authorization/roleAssignments/writepermissions, such as User Access Administrator or Owner.
To create a new load testing resource, your Azure account must have:
- Permission to create resources in the resource group for the load testing resource, such as the Contributor or Owner role.
Roles in Azure Load Testing
In Azure Load Testing, access is granted by assigning the appropriate Azure role to users, groups, and applications at the load testing resource scope. Following are the built-in roles supported by a load testing resource:
| Role | Description |
|---|---|
| Load Test Reader | Read-only actions in the Load Testing resource. Readers can list and view tests, test runs, test profiles and test profile runs in the resource. Readers can't create, update, or run tests and test profiles. |
| Load Test Contributor | View, create, edit, or delete (where applicable) tests, test runs, test profiles and test profile runs in a Load Testing resource. |
| Load Test Owner | Full access to the Load Testing resource, including the ability to view, create, edit, or delete (where applicable) assets in a resource. For example, you can modify or delete the Load Testing resource. |
If you have the Owner, Contributor, or Load Test Owner role at the subscription level, you automatically have the same permissions as the Load Test Owner at the resource level.
Important
Role access can be scoped to multiple levels in Azure. For example, someone with owner access to a resource might not have owner access to the resource group that contains the resource. For more information, see How Azure RBAC works.
Role permissions
The following tables describe the specific permissions given to each role. These permissions can include Actions, which give permissions, and Not Actions, which restrict them.
Load Test Owner
A Load Test Owner can manage everything, including access. The following table shows the permissions granted for the role:
| Actions | Description |
|---|---|
| Microsoft.Resources/deployments/* | Create and manage resource group deployments. |
| Microsoft.Resources/subscriptions/resourceGroups/read | Gets or lists resource groups. |
| Microsoft.Insights/alertRules/* | Create and manage alert rules. |
| Microsoft.Authorization/*/read | Read authorization. |
| Microsoft.LoadTestService/* | Create and manage load testing resources. |
| DataActions | Description |
|---|---|
| Microsoft.LoadTestService/loadtests/* | Start, stop, manage load tests and test profiles. |
Load Test Contributor
A Load Test Contributor can manage everything except access. The following table shows the permissions granted for the role:
| Actions | Description |
|---|---|
| Microsoft.Resources/deployments/* | Create and manage resource group deployments. |
| Microsoft.Resources/subscriptions/resourceGroups/read | Gets or lists resource groups. |
| Microsoft.Insights/alertRules/* | Create and manage alert rules. |
| Microsoft.Authorization/*/read | Read authorization. |
| Microsoft.LoadTestService/*/read | Create and manage load testing resources. |
| DataActions | Description |
|---|---|
| Microsoft.LoadTestService/loadtests/* | Start, stop, and manage load tests. |
| Microsoft.LoadTestService/testProfiles/* | Create and manage load test profiles. |
| Microsoft.LoadTestService/testProfileRuns/* | Start, stop, and manage load test profile runs. |
Load Test Reader
A Load Test Reader can view all the resources in a load testing resource but can't make any changes. The following table shows the permissions granted for the role:
| Actions | Description |
|---|---|
| Microsoft.Resources/deployments/* | Create and manage resource group deployments. |
| Microsoft.Resources/subscriptions/resourceGroups/read | Gets or lists resource groups. |
| Microsoft.Insights/alertRules/* | Create and manage alert rules. |
| Microsoft.Authorization/*/read | Read authorization. |
| Microsoft.LoadTestService/*/read | Create and manage load testing resources. |
| DataActions | Description |
|---|---|
| Microsoft.LoadTestService/loadtests/readTest/action | Read load tests. |
| Microsoft.LoadTestService/testProfiles/read | Read load test profiles. |
| Microsoft.LoadTestService/testProfileRuns/read | Read load test profile runs. |
Configure Azure RBAC for your load testing resource
The following section shows you how to configure Azure RBAC on your load testing resource through the Azure portal and PowerShell.
Configure Azure RBAC using the Azure portal
Sign in to the Azure portal and open your load testing resource from the Azure Load Testing page.
Select Access control (IAM) and select a role from the list of available roles. You can choose any of the available built-in roles that an Azure load testing resource supports or any custom role you might have defined. Assign the role to a user to which you want to give permissions.
For detailed steps, see Assign Azure roles using the Azure portal.
Remove role assignments from a user
You can remove the access permission for a user who isn't managing the Azure load testing resource, or who no longer works for the organization. The following steps show how to remove the role assignments from a user. For detailed steps, see Remove Azure role assignments:
Open Access control (IAM) at a scope, such as management group, subscription, resource group, or resource, where you want to remove access.
Select the Role assignments tab to view all the role assignments at this scope.
In the list of role assignments, add a checkmark next to the user with the role assignment you want to remove.
Select Remove, and then select Yes to confirm.
Configure Azure RBAC using PowerShell
You can also configure role-based access to a load testing resource using the following Azure PowerShell cmdlets:
Get-AzRoleDefinition lists all Azure roles that are available in Microsoft Entra ID. You can use this cmdlet with the Name parameter to list all the actions that a specific role can perform.
Get-AzRoleDefinition -Name 'Load Test Contributor'The following snippet is the example output:
Name : Load Test Contributor Id : 00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000 IsCustom : False Description : View, create, update, delete and execute load tests. View and list load test resources but can not make any changes. Actions : {Microsoft.LoadTestService/*/read, Microsoft.Authorization/*/read, Microsoft.Resources/deployments/*, Microsoft.Resources/subscriptions/resourceGroups/read…} NotActions : {} DataActions : {Microsoft.LoadTestService/loadtests/*} NotDataActions : {} AssignableScopes : {/}Get-AzRoleAssignment lists Azure role assignments at the specified scope. Without any parameters, this cmdlet returns all the role assignments made under the subscription. Use the
ExpandPrincipalGroupsparameter to list access assignments for the specified user, and the groups that the user belongs to.Example: Use the following cmdlet to list all the users and their roles within a load testing resource.
Get-AzRoleAssignment -Scope '/subscriptions/<SubscriptionID>/resourcegroups/<Resource Group Name>/Providers/Microsoft.LoadTestService/loadtests/<Load Test Name>'Use New-AzRoleAssignment to assign access to users, groups, and applications to a particular scope.
Example: Use the following command to assign the "Load Test Reader" role for a user in the load testing resource scope.
New-AzRoleAssignment -SignInName <sign-in Id of a user you wish to grant access> -RoleDefinitionName 'Load Test Reader' -Scope '/subscriptions/<SubscriptionID>/resourcegroups/<Resource Group Name>/Providers/Microsoft.LoadTestService/loadtests/<Load Testing resource name>'Use Remove-AzRoleAssignment to remove access of a specified user, group, or application from a particular scope.
Example: Use the following command to remove the user from the Load Test Reader role in the load testing resource scope.
Remove-AzRoleAssignment -SignInName <sign-in Id of a user you wish to remove> -RoleDefinitionName 'Load Test Reader' -Scope '/subscriptions/<SubscriptionID>/resourcegroups/<Resource Group Name>/Providers/Microsoft.LoadTestService/loadtests/<Load Testing resource name>'
Troubleshooting
This section lists steps to troubleshoot common problems with user access in Azure Load Testing.
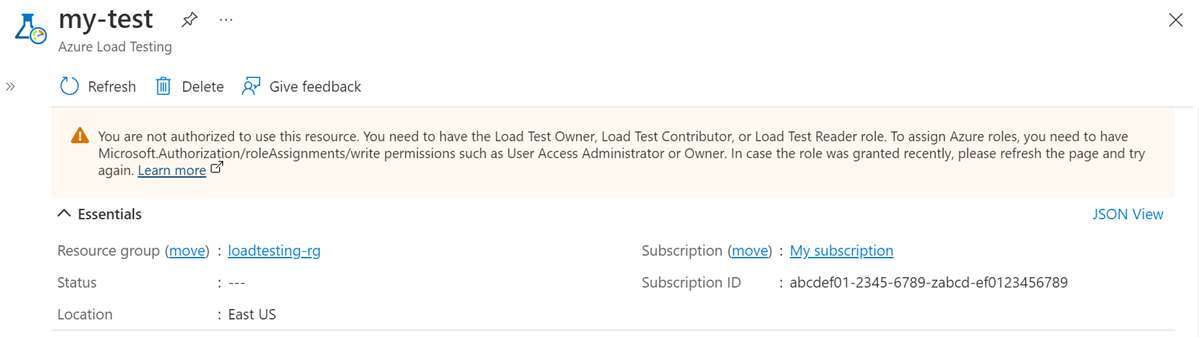
Unable to create or run a test with You are not authorized to use this resource
You encounter this message if your Azure account doesn't have the necessary permissions to manage tests. Make sure to grant the user the Load Test Owner or Load Test Contributor role on the load testing resource.
Related content
- Learn more about Using managed identities.
- Learn more about Identifying performance bottlenecks (tutorial).