Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Applies to: Azure Logic Apps (Consumption + Standard)
Azure Logic Apps supports all content types like JSON, XML, flat files, and binary data. While some content types have native support, meaning they don't need casting or conversion, other content types need some work to give you the required format.
To help determine the best way to handle content or data in workflows, Azure Logic Apps uses the Content-Type header value in the HTTP requests that workflows get from external callers.
The following list includes some example Content-Type values that a workflow can encounter:
- application/json (native type)
- text/plain (native type)
- application/xml and application/octet-stream
- Other content types
This guide describes how Azure Logic Apps handles different content types and shows how to correctly cast or convert these types when necessary.
application/json
For an HTTP request where the Content-Type header value is application/json, Azure Logic Apps stores and handles the content as a JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) object. By default, you can parse JSON content without any casting or conversion. You can also parse this content by using an expression.
For example, the following expression uses the body() function with My_action, which is the JSON name for a predecessor action in the workflow:
body('My_action')['client']['animal-type'][0]
The following steps describe how the expression works without casting or conversion:
The
body()function gets thebodyoutput object from theMy_actionaction.From the returned
bodyobject, the function accesses theclientobject.The
clientobject contains theanimal-typeproperty, which is set to an array.The function accesses the first item in the array and directly returns the value dog without casting or conversion.
If you work with JSON data that doesn't use a Content-Type header, you can manually convert that data to JSON by using the json() function, for example:
json(triggerBody())['client']['animal-type']
The
triggerBody()function gets thebodyobject from the workflow's trigger output. This object is typically a JSON object.The source for the
bodyobject originates from the inbound HTTP request or event received by the workflow trigger.The
json()function explicitly parses thebodyobject returned from thetriggerBody()function as a JSON object.This behavior is useful, for example, when the trigger body is a string that requires handling as JSON.
The remaining expression behavior is similar to the previous example.
Create tokens for JSON properties
In Azure Logic Apps, you can generate user-friendly tokens that represent the properties in JSON content. You can then use these tokens so you can more easily reference these properties and their values in your workflow.
The following list describes common workflow operations and the corresponding ways that you can generate tokens for properties in JSON content:
Request trigger named When a HTTP request is received
When you work in the designer with the Request trigger, you can optionally provide a JSON schema that defines the JSON objects, properties, and the expected data types for each property value. If you don't have a JSON schema, you can provide an example payload to generate a JSON schema that you can use.
The trigger uses the schema to parse JSON content from incoming HTTP requests and generate tokens that represent the properties in the JSON content. You can then easily reference and use these properties and their values in subsequent actions in your workflow.
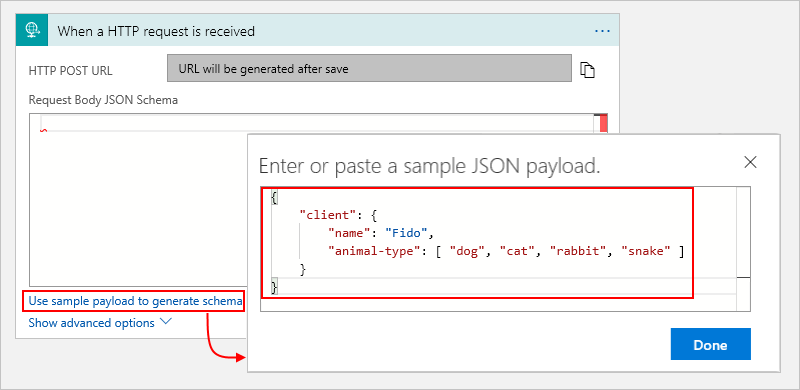
The following steps describe how you can provide an example payload to generate a JSON schema:
On the designer, select the Request trigger to open the information pane.
On the Parameters tab, under the Request Body JSON Schema box, select Use sample payload to generate schema.
In the Enter or paste a sample JSON payload box, enter a sample payload, then select Done.
The generated schema now appears in your trigger.
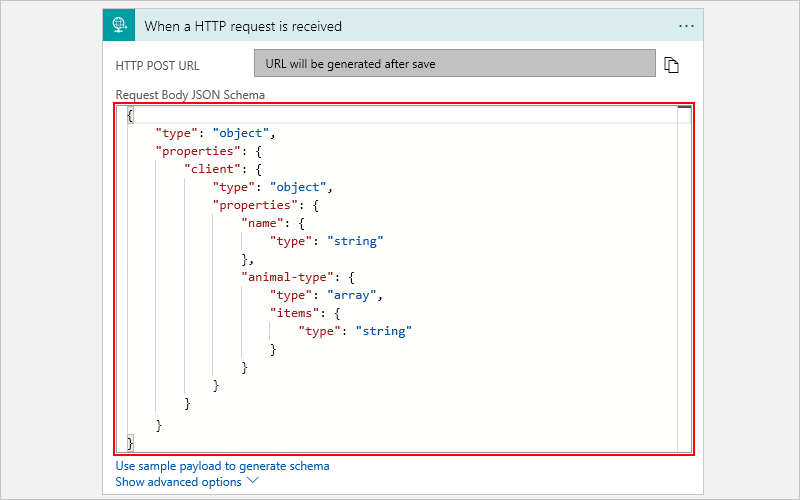
In the code view editor, you can review the underlying JSON definition for the Request trigger:
"triggers": { "When_an_HTTP_request_is_received": { "type": "Request", "kind": "Http", "inputs": { "schema": { "type": "object", "properties": { "client": { "type": "object", "properties": { "animal-type": { "type": "array", "items": { "type": "string" }, }, "name": { "type": "string" } } } } } } } }To trigger your workflow, get the Workflow URL or the trigger's HTTP URL, which is generated after you save the workflow for the first time.
To test the workflow, use a client tool or app from where you can send an HTTP request to the workflow URL or trigger URL. Make sure that the request includes a header named Content-Type and the header value is set to application/json.
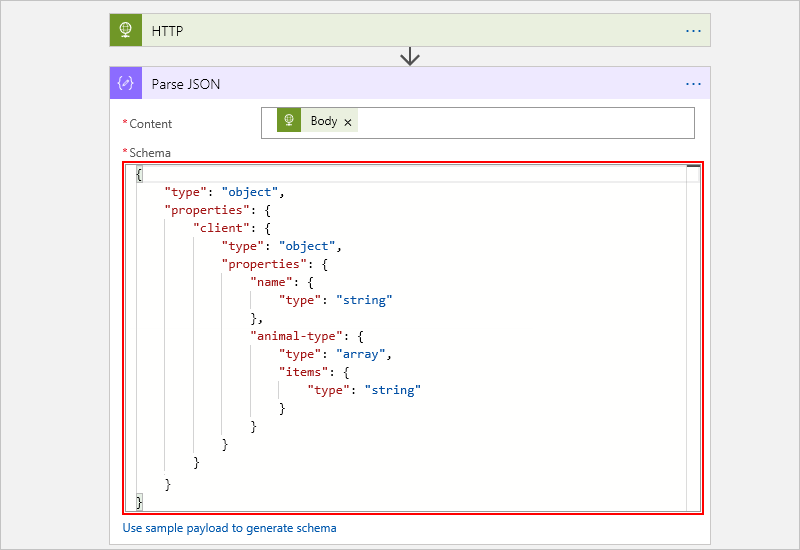
Parse JSON action
When you use this action in the designer, you can parse JSON output and generate user-friendly tokens that represent the properties in your JSON content. You can then easily reference and use those properties throughout your logic app's workflow.
Similar to the Request trigger, you can provide or generate a JSON schema that describes the JSON content you want to parse. That way, you can more easily consume data from Azure Service Bus, Azure Cosmos DB, and so on.
text/plain
If your workflow receives HTTP requests where the Content-Type header value is text/plain. Azure Logic Apps stores and handles the content in raw form. If you reference or use this content in subsequent workflow actions without casting or conversion, outbound requests also have the Content-Type header value set to text/plain.
For example, suppose you're working with a flat file, and the inbound HTTP request has the Content-Type header value set to text/plain:
Date,Name,Address
Oct-1,Frank,123 Ave
If you send this request to a subsequent action that uses the request body to send another request, the second request also has the Content-Type header value set to text/plain. If you work with data in plain text but didn't specify a header, you can manually cast this data to text by using the string() function, for example:
string(triggerBody())
application/xml and application/octet-stream
Azure Logic Apps always preserves the Content-Type header value in an inbound HTTP request or response. If your workflow receives content with Content-Type set to application/octet-stream, and you include that content in a subsequent action without casting, the outbound request also sets Content-Type to application/octet-stream. This approach makes sure that data doesn't get lost while moving through the workflow. In stateful workflows, the subsequent action's state, inputs, and outputs are stored in a JSON object while the state moves through the workflow.
Converter functions
To preserve some data types, Azure Logic Apps converts content to a binary base64-encoded string. This string has the appropriate metadata that preserves both the $content payload and the $content-type, which are automatically converted.
The following list describes how Azure Logic Apps converts content when you use specific functions:
json(): Casts data toapplication/json.xml(): Casts data toapplication/xml.binary(): Casts data toapplication/octet-stream.string(): Casts data totext/plain.base64(): Converts content to a base64-encoded string.base64toString(): Converts a base64-encoded string totext/plain.base64toBinary(): Converts a base64-encoded string toapplication/octet-stream.dataUri(): Converts a string to a data URI.dataUriToBinary(): Converts a data URI to a binary string.dataUriToString(): Converts a data URI to a string.
For example, suppose your workflow trigger receives an HTTP request where Content-Type set to application/xml where the content looks like the following sample:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<CustomerName>Frank</CustomerName>
You can cast this content by using the following expression, which uses the xml() and triggerBody() functions:
xml(triggerBody())
You can then use the resulting content with subsequent actions in the workflow. Or, you might use the following expression that uses the xpath() and xml() functions instead:
xpath(xml(triggerBody()), '/CustomerName')
Other content types
Azure Logic Apps supports other content types but might require that you manually get the message body from an HTTP request by decoding the $content variable.
For example, suppose your workflow receives an HTTP request where Content-Type is set to application/x-www-url-formencoded. To preserve all the data, the request body includes the $content variable where the payload is encoded as a base64 string:
CustomerName=Frank&Address=123+Avenue
This content type isn't in plain text or JSON format, so Azure Logic Apps stores CustomerName=Frank&Address=123+Avenue using the following $content-type and $content variables:
"body": {
"$content-type": "application/x-www-url-formencoded",
"$content": "AAB1241BACDFA=="
}
Azure Logic Apps also includes native functions to handle form data, for example:
Or, you can manually access the data by using an expression such as the following example:
string(body('formdataAction'))
To make an outbound request use application/x-www-url-formencoded as the Content-Type header value, add the request content to the action body without any casting by using an expression such as body('formdataAction'). This method works only if the action body is the only parameter in the body inputs object. If you use the body('formdataAction') expression in a request where the content type is application/json, you get a runtime error because the body is sent encoded.