Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
APPLIES TO:
 Azure CLI ml extension v2 (current)
Azure CLI ml extension v2 (current)
 Python SDK azure-ai-ml v2 (current)
Python SDK azure-ai-ml v2 (current)
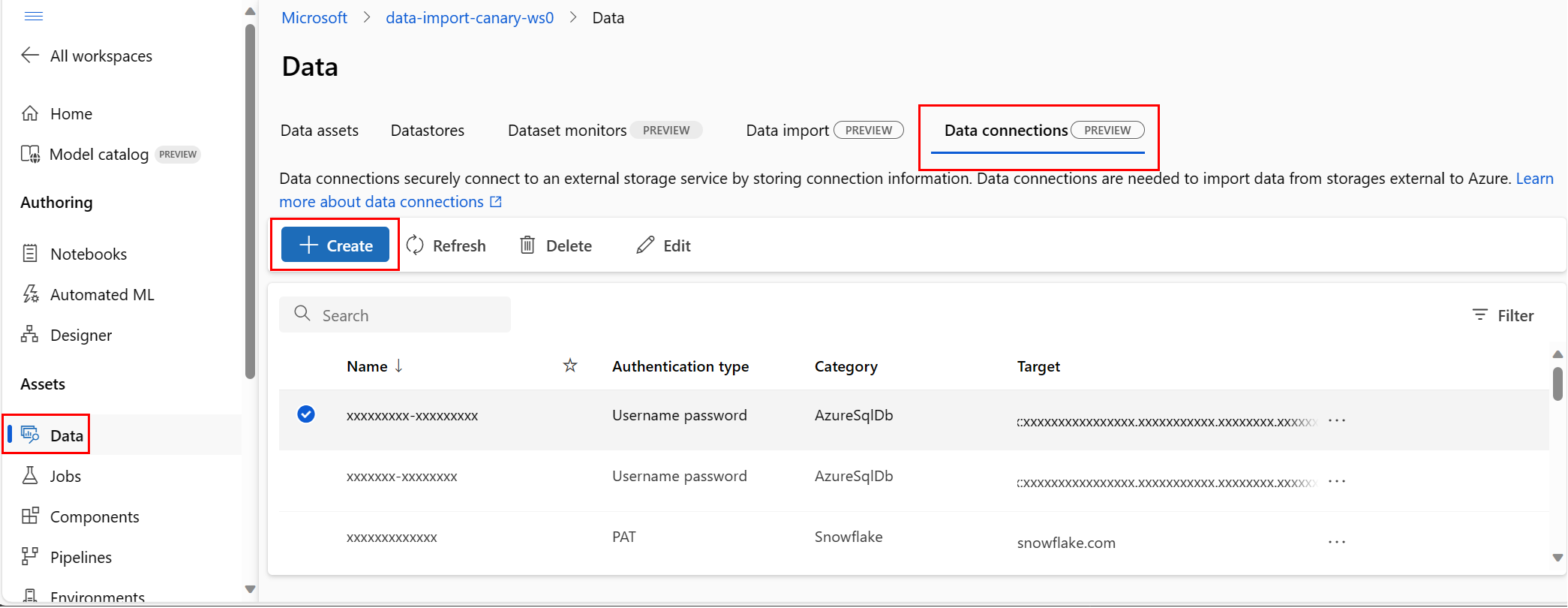
In this article, learn how to connect to data sources located outside of Azure, to make that data available to Azure Machine Learning services. Azure connections serve as key vault proxies, and interactions with connections are direct interactions with an Azure key vault. An Azure Machine Learning connection securely stores username and password data resources, as secrets, in a key vault. The key vault RBAC controls access to these data resources. For this data availability, Azure supports connections to these external sources:
- Snowflake DB
- Amazon S3
- Azure SQL DB
Important
This feature is currently in public preview. This preview version is provided without a service-level agreement, and we don't recommend it for production workloads. Certain features might not be supported or might have constrained capabilities.
For more information, see Supplemental Terms of Use for Microsoft Azure Previews.
Prerequisites
An Azure subscription. If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a free account before you begin. Try the free or paid version of Azure Machine Learning.
An Azure Machine Learning workspace.
Important
An Azure Machine Learning connection securely stores the credentials passed during connection creation in the Workspace Azure Key Vault. A connection references the credentials from the key vault storage location for further use. You don't need to directly deal with the credentials after they are stored in the key vault. You have the option to store the credentials in the YAML file. A CLI command or SDK can override them. We recommend that you avoid credential storage in a YAML file, because a security breach could lead to a credential leak.
Note
For a successful data import, please verify that you installed the latest azure-ai-ml package (version 1.5.0 or later) for SDK, and the ml extension (version 2.15.1 or later).
If you have an older SDK package or CLI extension, please remove the old one and install the new one with the code shown in the tab section. Follow the instructions for SDK and CLI as shown here:
Code versions
az extension remove -n ml
az extension add -n ml --yes
az extension show -n ml #(the version value needs to be 2.15.1 or later)
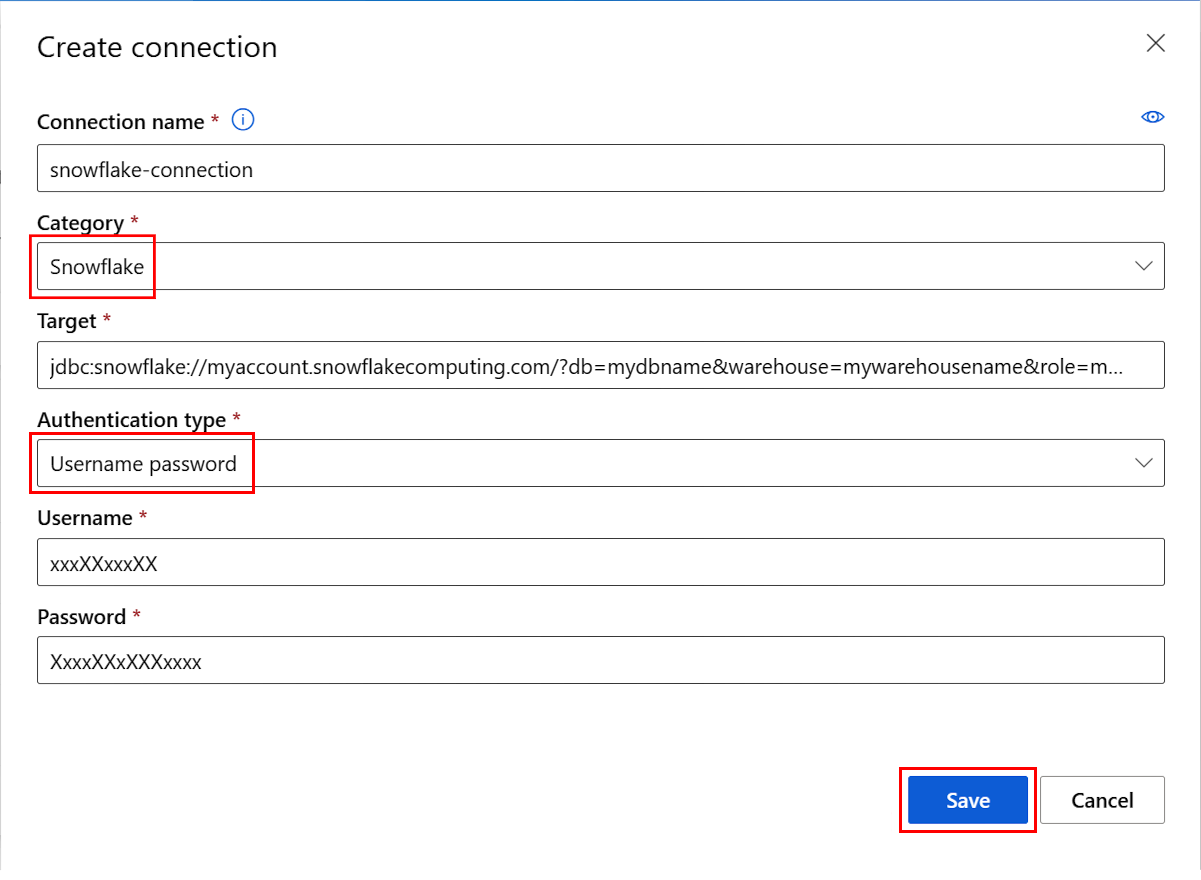
Create a Snowflake DB connection
This YAML file creates a Snowflake DB connection. Be sure to update the appropriate values:
# my_snowflakedb_connection.yaml
$schema: http://azureml/sdk-2-0/Connection.json
type: snowflake
name: my-sf-db-connection # add your datastore name here
target: jdbc:snowflake://<myaccount>.snowflakecomputing.com/?db=<mydb>&warehouse=<mywarehouse>&role=<myrole>
# add the Snowflake account, database, warehouse name and role name here. If no role name provided it will default to PUBLIC
credentials:
type: username_password
username: <username> # add the Snowflake database user name here or leave this blank and type in CLI command line
password: <password> # add the Snowflake database password here or leave this blank and type in CLI command line
Create the Azure Machine Learning connection in the CLI:
Option 1: Use the username and password in YAML file
az ml connection create --file my_snowflakedb_connection.yaml
Option 2: Override the username and password at the command line
az ml connection create --file my_snowflakedb_connection.yaml --set credentials.
username="<username>" credentials.
password="<password>"
Create a Snowflake DB connection that uses OAuth
The information in this section describes how to create a Snowflake DB connection that uses OAuth to authenticate.
Important
Before following the steps in this section, you must first Configure Azure to issue OAuth tokens on behalf of the client. This configuration creates a service principal, which is required for the OAuth connection. You need the following information to create the connection:
- Client ID: The ID of the service principal
- Client Secret: The secret of the service principal
- Tenant ID: The ID of the Microsoft Entra ID tenant
This YAML file creates a Snowflake DB connection that uses OAuth. Be sure to update the appropriate values:
# my_snowflakedb_connection.yaml
name: snowflake_service_principal_connection
type: snowflake
# Add the Snowflake account, database, warehouse name, and role name here. If no role name is provided, it will default to PUBLIC.
target: jdbc:snowflake://<myaccount>.snowflakecomputing.com/?db=<mydb>&warehouse=<mywarehouse>&scope=<scopeForServicePrincipal>
credentials:
type: service_principal
client_id: <client-id> # The service principal's client id
client_secret: <client-secret> # The service principal's client secret
tenant_id: <tenant-id> # The Microsoft Entra ID tenant id
Create the Azure Machine Learning connection in the CLI:
az ml connection create --file my_snowflakedb_connection.yaml
You can also override the information in the YAML file at the command line:
az ml connection create --file my_snowflakedb_connection.yaml --set credentials.client_id="my-client-id" credentials.client_secret="my-client-secret" credentials.tenant_id="my-tenant-id"
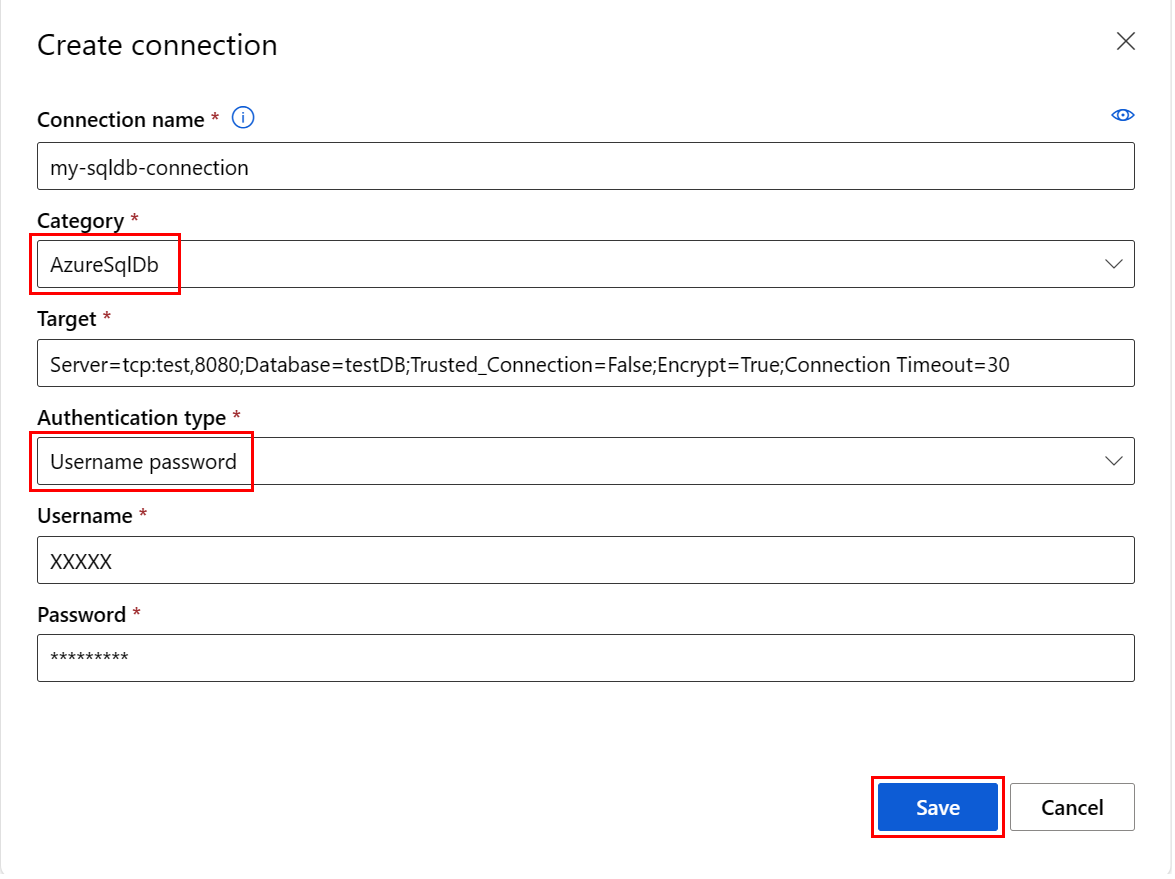
Create an Azure SQL DB connection
This YAML script creates an Azure SQL DB connection. Be sure to update the appropriate values:
# my_sqldb_connection.yaml
$schema: http://azureml/sdk-2-0/Connection.json
type: azure_sql_db
name: my-sqldb-connection
target: Server=tcp:<myservername>,<port>;Database=<mydatabase>;Trusted_Connection=False;Encrypt=True;Connection Timeout=30
# add the sql servername, port addresss and database
credentials:
type: sql_auth
username: <username> # add the sql database user name here or leave this blank and type in CLI command line
password: <password> # add the sql database password here or leave this blank and type in CLI command line
Create the Azure Machine Learning connection in the CLI:
Option 1: Use the username / password from YAML file
az ml connection create --file my_sqldb_connection.yaml
Option 2: Override the username and password in YAML file
az ml connection create --file my_sqldb_connection.yaml --set credentials.
username="<username>" credentials.
password="<password>"
Create Amazon S3 connection
Create an Amazon S3 connection with the following YAML file. Be sure to update the appropriate values:
# my_s3_connection.yaml
$schema: http://azureml/sdk-2-0/Connection.json
type: s3
name: my_s3_connection
target: <mybucket> # add the s3 bucket details
credentials:
type: access_key
access_key_id: bbbbbbbb-1c1c-2d2d-3e3e-444444444444 # add access key id
secret_access_key: H4iJ5kL6mN7oP8qR9sT0uV1wX2yZ3a # add access key secret
Create the Azure Machine Learning connection in the CLI:
az ml connection create --file my_s3_connection.yaml
Non-data connections
You can use these connection types to connect to Git:
- Python feed
- Azure Container Registry
- a connection that uses an API key
These connections aren't data connections, but are used to connect to external services for use in your code.
Git
Create a Git connection with one of following YAML file. Be sure to update the appropriate values:
Connect using a personal access token (PAT):
#Connection.yml name: test_ws_conn_git_pat type: git target: https://github.com/contoso/contosorepo credentials: type: pat pat: dummy_patConnect to a public repo (no credentials):
#Connection.yml name: git_no_cred_conn type: git target: https://https://github.com/contoso/contosorepo
Create the Azure Machine Learning connection in the CLI:
az ml connection create --file connection.yaml
Python feed
Create a connection to a Python feed with one of following YAML files. Be sure to update the appropriate values:
Connect using a personal access token (PAT):
#Connection.yml name: test_ws_conn_python_pat type: python_feed target: https://test-feed.com credentials: type: pat pat: dummy_patConnect using a username and password:
name: test_ws_conn_python_user_pass type: python_feed target: https://test-feed.com credentials: type: username_password username: <username> password: <password>Connect to a public feed (no credentials):
name: test_ws_conn_python_no_cred type: python_feed target: https://test-feed.com3
Create the Azure Machine Learning connection in the CLI:
az ml connection create --file connection.yaml
Container Registry
Create a connection to an Azure Container Registry with one of following YAML files. Be sure to update the appropriate values:
Connect using a username and password:
name: test_ws_conn_cr_user_pass type: container_registry target: https://test-feed.com2 credentials: type: username_password username: <username> password: <password>
Create the Azure Machine Learning connection in the CLI:
az ml connection create --file connection.yaml
API key
The following example creates an API key connection:
from azure.ai.ml.entities import WorkspaceConnection
from azure.ai.ml.entities import UsernamePasswordConfiguration, ApiKeyConfiguration
name = "my_api_key"
target = "https://L6mN7oP8q.core.windows.net/mycontainer"
wps_connection = WorkspaceConnection(
name=name,
type="apikey",
target=target,
credentials=ApiKeyConfiguration(key="9sT0uV1wX"),
)
ml_client.connections.create_or_update(workspace_connection=wps_connection)
Generic Container Registry
Using the GenericContainerRegistry workspace connection, you can specify an external registry, such as Nexus or Artifactory, for image builds. Environment images are pushed from the specified registry, and the previous cache is ignored.
Create a connection using the following YAML files. Be sure to update the appropriate values:
#myenv.yml
$schema: https://azuremlschemas.azureedge.net/latest/environment.schema.json
name: docker-image-plus-conda-example
image: mcr.microsoft.com/azureml/openmpi4.1.0-ubuntu20.04
type: python_feed
conda_file: conda_dep.yml
description: Environment created from a Docker image plus Conda environment
#conda_dep.yml
name: project_environment
dependencies:
- python=3.10
- pip:
- azureml-defaults
channels:
- anaconda
- conda-forge
#connection.yml
name: ws_conn_generic_container_registry
type: container_registry
target: https://test-registry.com
credentials:
type: username_password
username: <username>
password: <password>
#hello_world_job.yml
$schema: https://azuremlschemas.azureedge.net/latest/commandJob.schema.json
command: echo "hello world"
environment: azureml:<env name>@latest
Create connection from YAML file with your credentials:
az ml connection create --file connection.yaml --credentials username=<username> password=<password> --resource-group my-resource-group --workspace-name my-workspace
Create environment
az ml environment create --name my-env --version 1 --file my_env.yml --conda-file conda_dep.yml --image mcr.microsoft.com/azureml/openmpi4.1.0-ubuntu20.04 --resource-group my-resource-group --workspace-name my-workspace
You can verify that the environment was successfully created
az ml environment show --name my-env --version 1 --resource-group my-resource-group --workspace-name my-workspace
Related content
If you use a data connection (Snowflake DB, Amazon S3, or Azure SQL DB), these articles offer more information: