Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This article shows you how to secure a Kubernetes online endpoint that's created through Azure Machine Learning.
You use HTTPS to restrict access to online endpoints and help secure the data that clients submit. HTTPS encrypts communications between a client and an online endpoint by using Transport Layer Security (TLS). TLS is sometimes still called Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), which was the predecessor of TLS.
Tip
- Specifically, Kubernetes online endpoints support TLS version 1.2 for Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) and Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes.
- TLS version 1.3 for Azure Machine Learning Kubernetes inference is unsupported.
TLS and SSL both rely on digital certificates, which help with encryption and identity verification. For more information on how digital certificates work, see the Wikipedia topic public_key_infrastructure.
Warning
If you don't use HTTPS for your online endpoints, data that's sent to and from the service might be visible to others on the internet.
HTTPS also enables the client to verify the authenticity of the server that it's connecting to. This feature protects clients against man-in-the-middle attacks.
The following is the general process to secure an online endpoint:
Important
You need to purchase your own certificate to get a domain name or TLS/SSL certificate, and then configure them in the Azure Machine Learning extension. For more detailed information, see the following sections of this article.
Get a domain name
If you don't already own a domain name, purchase one from a domain name registrar. The process and price differ among registrars. The registrar provides tools to manage the domain name. You use these tools to map an FQDN (such as www.contoso.com) to the IP address that hosts your online endpoint.
For more information on how to get the IP address of your online endpoints, see the Update your DNS with an FQDN section of this article.
Get a TLS/SSL certificate
There are many ways to get a TLS/SSL certificate (digital certificate). The most common is to purchase one from a certificate authority. Regardless of where you get the certificate, you need the following files:
- A certificate that contains the full certificate chain and is PEM encoded
- A key that's PEM encoded
Note
An SSL key in a PEM file with passphrase protection is not supported.
When you request a certificate, you must provide the FQDN of the address that you plan to use for the online endpoint (for example, www.contoso.com). The address that's stamped into the certificate and the address that the clients use are compared to verify the identity of the online endpoint. If those addresses don't match, the client gets an error message.
For more information on how to configure IP banding with an FQDN, see the Update your DNS with an FQDN section of this article.
Tip
If the certificate authority can't provide the certificate and key as PEM-encoded files, you can use a tool like OpenSSL to change the format.
Warning
Use self-signed certificates only for development. Don't use them in production environments. Self-signed certificates can cause problems in your client applications. For more information, see the documentation for the network libraries that your client application uses.
Configure TLS/SSL in the Azure Machine Learning extension
For a Kubernetes online endpoint that's set to use inference HTTPS for secure connections, you can enable TLS termination with deployment configuration settings when you deploy the Azure Machine Learning extension in a Kubernetes cluster.
At deployment time for the Azure Machine Learning extension, the allowInsecureConnections configuration setting is False by default. To ensure successful extension deployment, you need to specify either the sslSecret configuration setting or a combination of sslKeyPemFile and sslCertPemFile configuration-protected settings. Otherwise, you can set allowInsecureConnections=True to support HTTP and disable TLS termination.
Note
To support the HTTPS online endpoint, allowInsecureConnections must be set to False.
To enable an HTTPS endpoint for real-time inference, you need to provide a PEM-encoded TLS/SSL certificate and key. There are two ways to specify the certificate and key at deployment time for the Azure Machine Learning extension:
- Specify the
sslSecretconfiguration setting. - Specify a combination of
sslCertPemFileandslKeyPemFileconfiguration-protected settings.
Configure sslSecret
The best practice is to save the certificate and key in a Kubernetes secret in the azureml namespace.
To configure sslSecret, you need to save a Kubernetes secret in your Kubernetes cluster in the azureml namespace to store cert.pem (PEM-encoded TLS/SSL certificate) and key.pem (PEM-encoded TLS/SSL key).
The following code is a sample YAML definition of a TLS/SSL secret:
apiVersion: v1
data:
cert.pem: <PEM-encoded SSL certificate>
key.pem: <PEM-encoded SSL key>
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: <secret name>
namespace: azureml
type: Opaque
After you save the secret in your cluster, you can use the following Azure CLI command to specify sslSecret as the name of this Kubernetes secret. (This command will work only if you're using AKS.)
az k8s-extension create --name <extension-name> --extension-type Microsoft.AzureML.Kubernetes --config inferenceRouterServiceType=LoadBalancer sslSecret=<Kubernetes secret name> sslCname=<ssl cname> --cluster-type managedClusters --cluster-name <your-AKS-cluster-name> --resource-group <your-RG-name> --scope cluster
Configure sslCertPemFile and sslKeyPemFile
You can specify the sslCertPemFile configuration setting to be the path to the PEM-encoded TLS/SSL certificate file, and the sslKeyPemFile configuration setting to be the path to the PEM-encoded TLS/SSL key file.
The following example demonstrates how to use the Azure CLI to specify PEM files to the Azure Machine Learning extension that uses a TLS/SSL certificate that you purchased. The example assumes that you're using AKS.
az k8s-extension create --name <extension-name> --extension-type Microsoft.AzureML.Kubernetes --config enableInference=True inferenceRouterServiceType=LoadBalancer sslCname=<ssl cname> --config-protected sslCertPemFile=<file-path-to-cert-PEM> sslKeyPemFile=<file-path-to-cert-KEY> --cluster-type managedClusters --cluster-name <your-AKS-cluster-name> --resource-group <your-RG-name> --scope cluster
Note
- A PEM file with passphrase protection is not supported.
- Both
sslCertPemFIleandsslKeyPemFIleuse configuration-protected parameters. They don't configuresslSecretandsslCertPemFile/sslKeyPemFileat the same time.
Update your DNS with an FQDN
For model deployment on a Kubernetes online endpoint with a custom certificate, you must update your DNS record to point to the IP address of the online endpoint. The Azure Machine Learning inference router service (azureml-fe) provides this IP address. For more information about azureml-fe, see Managed Azure Machine Learning inference router.
To update the DNS record for your custom domain name:
Get the online endpoint's IP address from the scoring URI, which is usually in the format of
http://104.214.29.152:80/api/v1/service/<service-name>/score. In this example, the IP address is 104.214.29.152.After you configure your custom domain name, it replaces the IP address in the scoring URI. For Kubernetes clusters that use
LoadBalanceras the inference router service,azureml-feis exposed externally through a cloud provider's load balancer and TLS/SSL termination. The IP address of the Kubernetes online endpoint is the external IP address of theazureml-feservice deployed in the cluster.If you use AKS, you can get the IP address from the Azure portal. Go to your AKS resource page, go to Service and ingresses, and then find the azureml-fe service under the azuerml namespace. Then you can find the IP address in the External IP column.
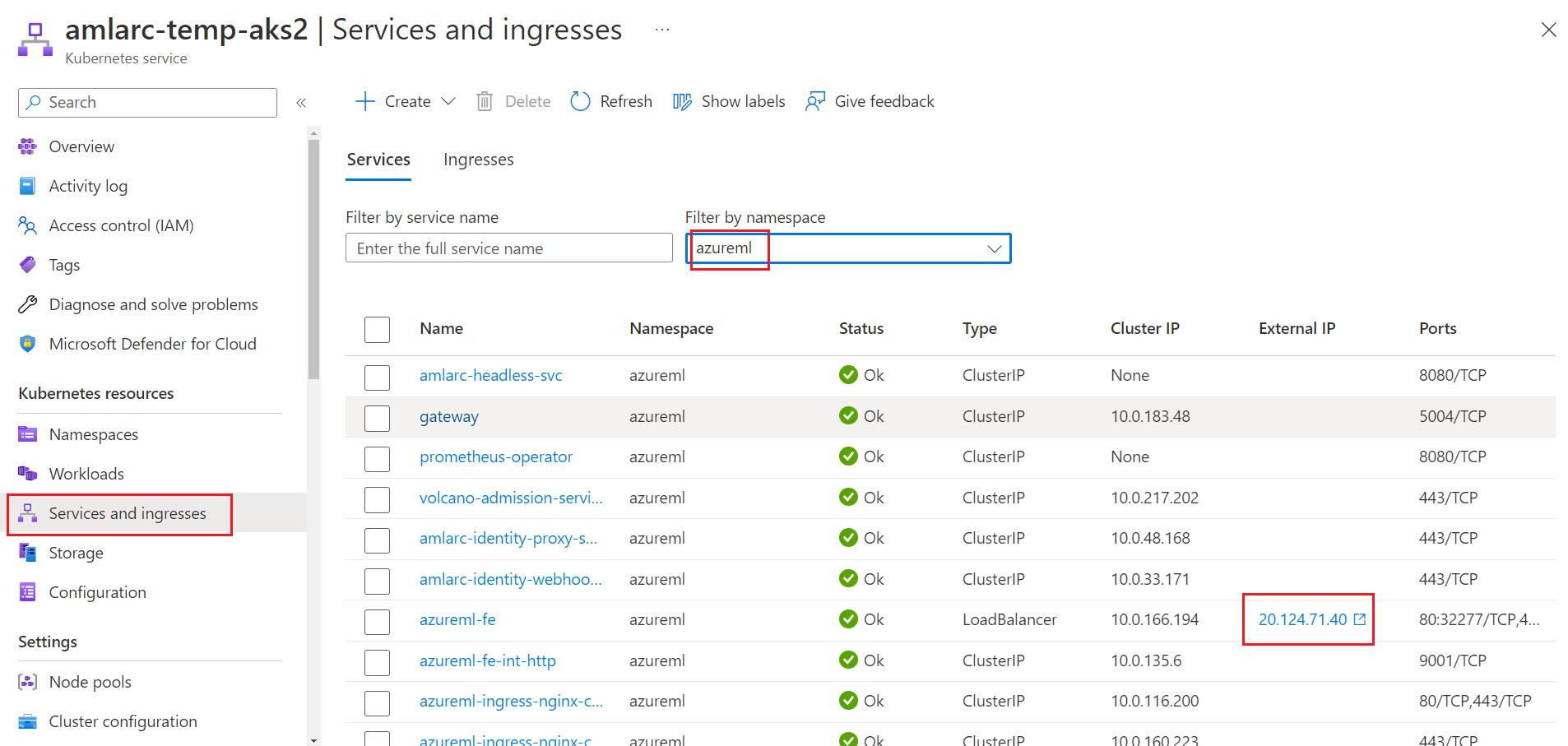
In addition, you can run the Kubernetes command
kubectl describe svc azureml-fe -n azuremlin your cluster to get the IP address from theLoadBalancer Ingressparameter in the output.Note
For Kubernetes clusters that use either
nodePortorclusterIPas the inference router service, you need to set up your own load-balancing solution and TLS/SSL termination forazureml-fe. You also need to get the IP address of theazureml-feservice in the cluster scope.Use the tools from your domain name registrar to update the DNS record for your domain name. The record maps the FQDN (for example,
www.contoso.com) to the IP address. The record must point to the IP address of the online endpoint.Tip
Microsoft is not responsible for updating the DNS for your custom DNS name or certificate. You must update it with your domain name registrar.
After the DNS record update, you can validate DNS resolution by using the
nslookup custom-domain-namecommand. If the DNS record is correctly updated, the custom domain name will point to the IP address of the online endpoint.There can be a delay of minutes or hours before clients can resolve the domain name, depending on the registrar and the time to live (TTL) that's configured for the domain name.
For more information on DNS resolution with Azure Machine Learning, see How to use your workspace with a custom DNS server.
Update the TLS/SSL certificate
TLS/SSL certificates expire and must be renewed. Typically, this happens every year. Use the information in the following steps to update and renew your certificate for models deployed to Kubernetes (AKS and Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes):
Use the documentation from the certificate authority to renew the certificate. This process creates new certificate files.
Update your Azure Machine Learning extension and specify the new certificate files by using the
az k8s-extension updatecommand.If you used a Kubernetes secret to configure TLS/SSL before, you need to first update the Kubernetes secret with the new cert.pem and key.pem configuration in your Kubernetes cluster. Then run the extension update command to update the certificate:
az k8s-extension update --name <extension-name> --extension-type Microsoft.AzureML.Kubernetes --config inferenceRouterServiceType=LoadBalancer sslSecret=<Kubernetes secret name> sslCname=<ssl cname> --cluster-type managedClusters --cluster-name <your-AKS-cluster-name> --resource-group <your-RG-name> --scope clusterIf you directly configured the PEM files in the extension deployment command before, you need to run the extension update command and specify the new PEM file's path:
az k8s-extension update --name <extension-name> --extension-type Microsoft.AzureML.Kubernetes --config sslCname=<ssl cname> --config-protected sslCertPemFile=<file-path-to-cert-PEM> sslKeyPemFile=<file-path-to-cert-KEY> --cluster-type managedClusters --cluster-name <your-AKS-cluster-name> --resource-group <your-RG-name> --scope cluster
Disable TLS
To disable TLS for a model deployed to Kubernetes:
Update the Azure Machine Learning extension with
allowInsecureConnectionsset toTrue.Remove the
sslCnameconfiguration setting, along with thesslSecretorsslPemconfiguration settings.Run the following Azure CLI command in your Kubernetes cluster, and then perform an update. This command assumes that you're using AKS.
az k8s-extension update --name <extension-name> --extension-type Microsoft.AzureML.Kubernetes --config enableInference=True inferenceRouterServiceType=LoadBalancer allowInsecureConnections=True --cluster-type managedClusters --cluster-name <your-AKS-cluster-name> --resource-group <your-RG-name> --scope cluster
Warning
By default, the Azure Machine Learning extension deployment expects configuration settings for HTTPS support. We recommend HTTP support only for development or testing purposes. The allowInsecureConnections=True configuration setting provides HTTP support.
Next steps
Learn how to: