Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
In this article, you learn how to fine tune, evaluate, and deploy foundation models in the Model Catalog.
You can quickly test out any pre-trained model using the Sample Inference form on the model card, providing your own sample input to test the result. Additionally, the model card for each model includes a brief description of the model and links to samples for code based inferencing, fine-tuning, and evaluation of the model.
How to evaluate foundation models using your own test data
You can evaluate a foundation model against your test dataset, using either the Evaluate UI form or by using the code based samples, linked from the model card.
Evaluating using the studio
You can invoke the Evaluate model form by selecting the Evaluate button on the model card for any foundation model.
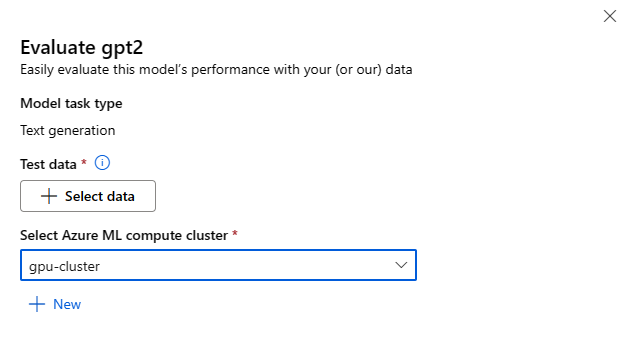
You can evaluate each model for the specific inference task that you use the model for.
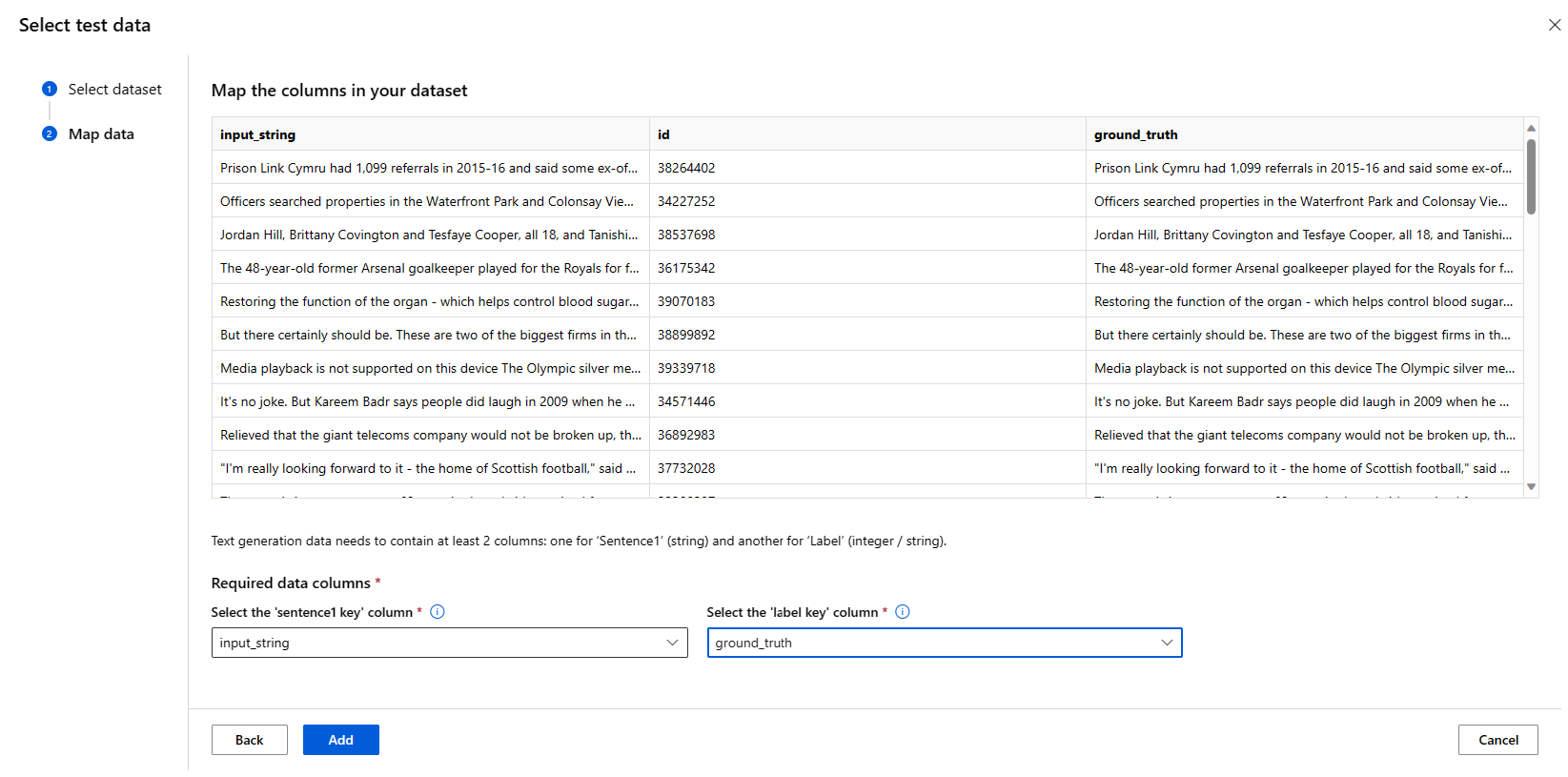
Test Data:
- Pass in the test data you would like to use to evaluate your model. You can choose to either upload a local file (in JSONL format) or select an existing registered dataset from your workspace.
- Once you selected the dataset, you need to map the columns from your input data, based on the schema needed for the task. For example, map the column names that correspond to the 'sentence' and 'label' keys for Text Classification
Compute:
Provide the Azure Machine Learning Compute cluster you would like to use for fine-tuning the model. Evaluation needs to run on GPU compute. Ensure that you have sufficient compute quota for the compute SKUs you wish to use.
Select Finish in the Evaluate form to submit your evaluation job. Once the job completes, you can view evaluation metrics for the model. Based on the evaluation metrics, you might decide if you would like to fine-tune the model using your own training data. Additionally, you can decide if you would like to register the model and deploy it to an endpoint.
Evaluating using code based samples
To enable you to get started with model evaluation, we provide samples (both Python notebooks and CLI examples) in the Evaluation samples in azureml-examples git repo. Each model card also links to evaluation samples for corresponding tasks
How to fine-tune foundation models using your own training data
In order to improve model performance in your workload, you might want to fine tune a foundation model using your own training data. You can easily fine-tune these foundation models by using either the fine-tune settings in the studio or by using the code based samples linked from the model card.
Fine-tune using the studio
You can invoke the fine-tune settings form by selecting on the Fine-tune button on the model card for any foundation model.
Fine-tune Settings:
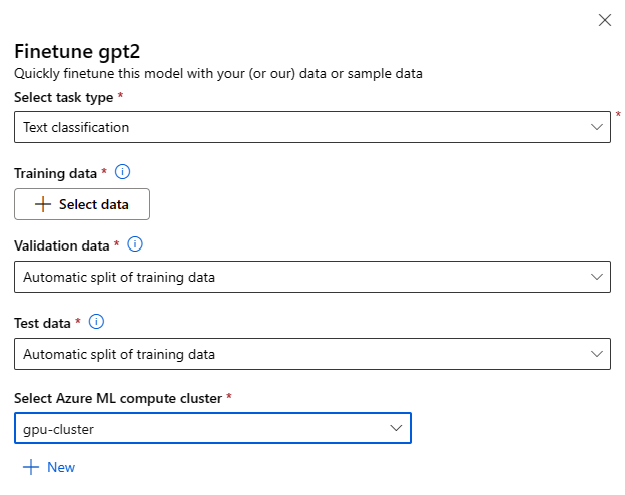
Fine-tuning task type
- Every pre-trained model from the model catalog can be fine-tuned for a specific set of tasks (For Example: Text classification, Token classification, Question answering). Select the task you would like to use from the drop-down.
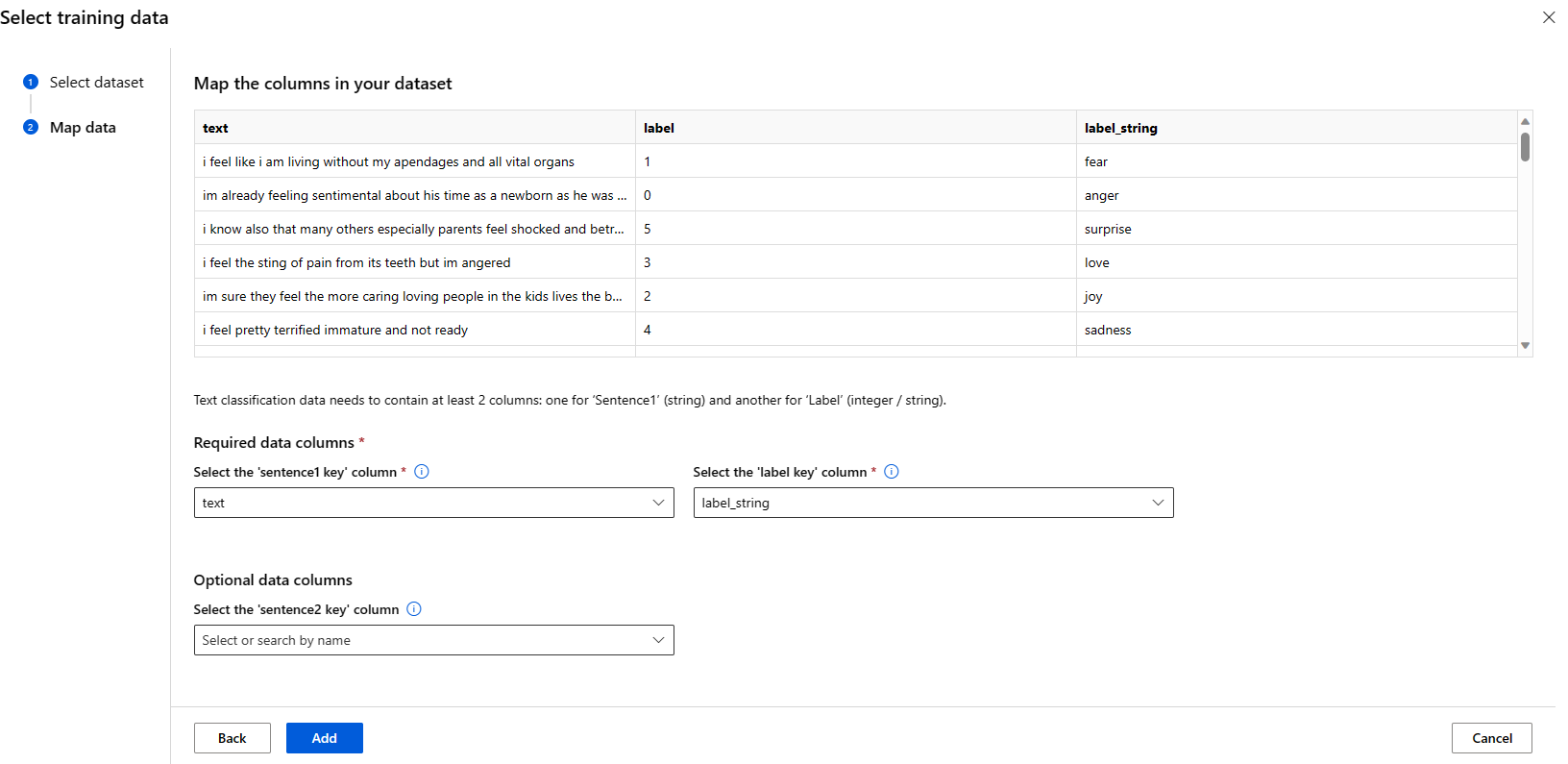
Training Data
Pass in the training data you would like to use to fine-tune your model. You can choose to either upload a local file (in JSONL, CSV or TSV format) or select an existing registered dataset from your workspace.
Once you select the dataset, you need to map the columns from your input data, based on the schema needed for the task. For example: map the column names that correspond to the 'sentence' and 'label' keys for Text Classification
- Validation data: Pass in the data you would like to use to validate your model. Selecting Automatic split reserves an automatic split of training data for validation. Alternatively, you can provide a different validation dataset.
- Test data: Pass in the test data you would like to use to evaluate your fine-tuned model. Selecting Automatic split reserves an automatic split of training data for test.
- Compute: Provide the Azure Machine Learning Compute cluster you would like to use for fine-tuning the model. Fine-tuning needs to run on GPU compute. We recommend using compute SKUs with A100 / V100 GPUs when fine tuning. Ensure that you have sufficient compute quota for the compute SKUs you wish to use.
- Select Finish in the fine-tune form to submit your fine-tuning job. Once the job completes, you can view evaluation metrics for the fine-tuned model. You can then register the fine-tuned model output by the fine-tuning job and deploy this model to an endpoint for inferencing.
Fine-tuning using code based samples
Currently, Azure Machine Learning supports fine-tuning models for the following language tasks:
- Text classification
- Token classification
- Question answering
- Summarization
- Translation
To enable users to quickly get started with fine-tuning, we have published samples (both Python notebooks and CLI examples) for each task in the azureml-examples git repo fine-tune samples. Each model card also links to fine-tuning samples for supported fine-tuning tasks.
Deploying foundation models to endpoints for inferencing
You can deploy foundation models (both pre-trained models from the model catalog, and fine-tuned models, once they're registered to your workspace) to an endpoint that can then be used for inferencing. Deployment to both standard deployments and managed compute is supported. You can deploy these models by using either the Deploy UI wizard or by using the code based samples linked from the model card.
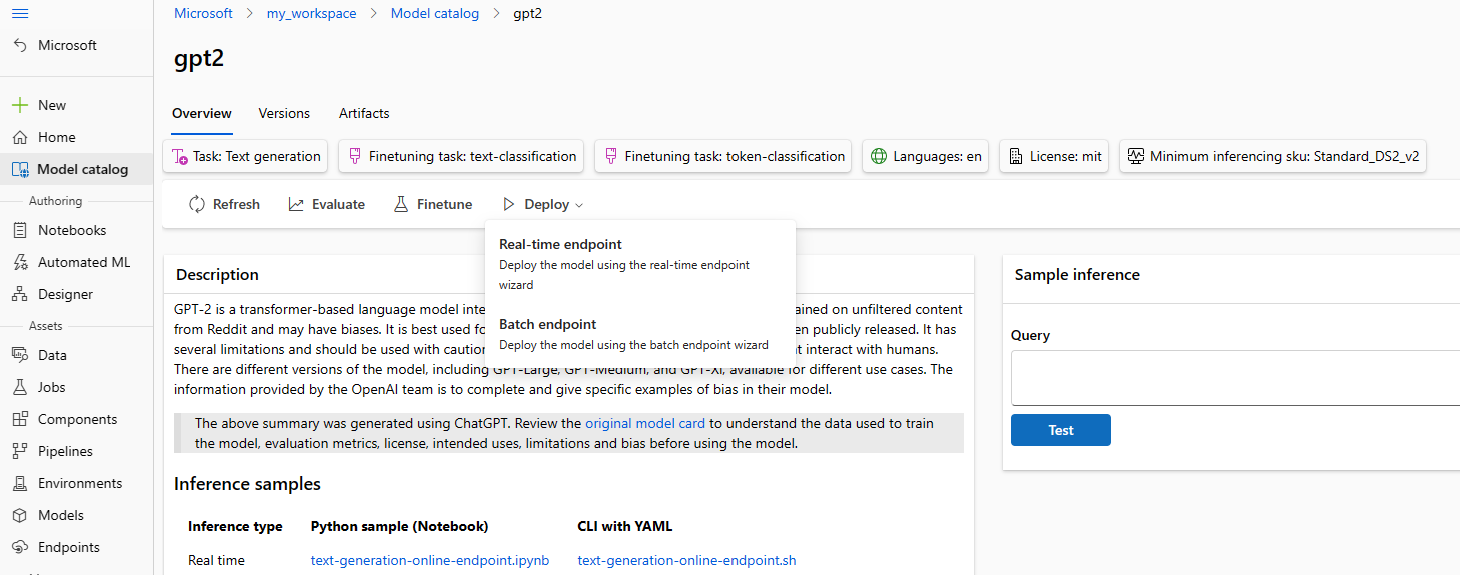
Deploying using the studio
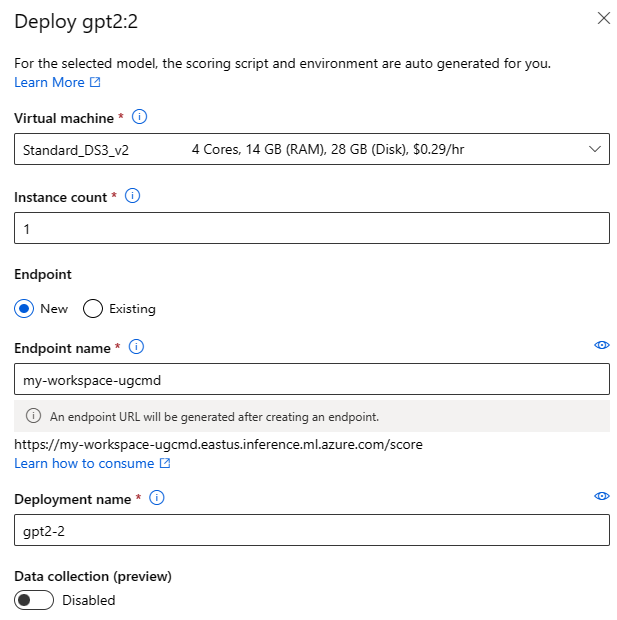
You can invoke the Deploy UI form by selecting the Deploy button on the model card for any foundation model, and selecting either standard deployment with Azure AI Content Safety or Managed Compute without Azure AI Content Safety
Deployment settings
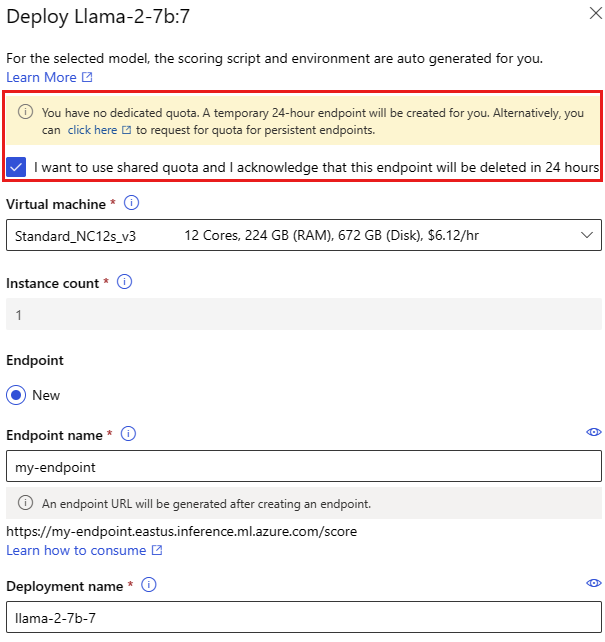
Since the scoring script and environment are automatically included with the foundation model, you only need to specify the Virtual machine SKU to use, number of instances and the endpoint name to use for the deployment.
Shared quota
If you're deploying a Llama-2, Phi, Nemotron, Mistral, Dolly or Deci-DeciLM model from the model catalog but don't have enough quota available for the deployment, Azure Machine Learning allows you to use quota from a shared quota pool for a limited time. For more information on shared quota, see Azure Machine Learning shared quota.
Deploying using code based samples
To enable you to quickly get started with deployment and inferencing, we provide samples in the Inference samples in the azureml-examples git repo. The published samples include Python notebooks and CLI examples. Each model card also links to Inference samples for Real time and Batch inferencing.
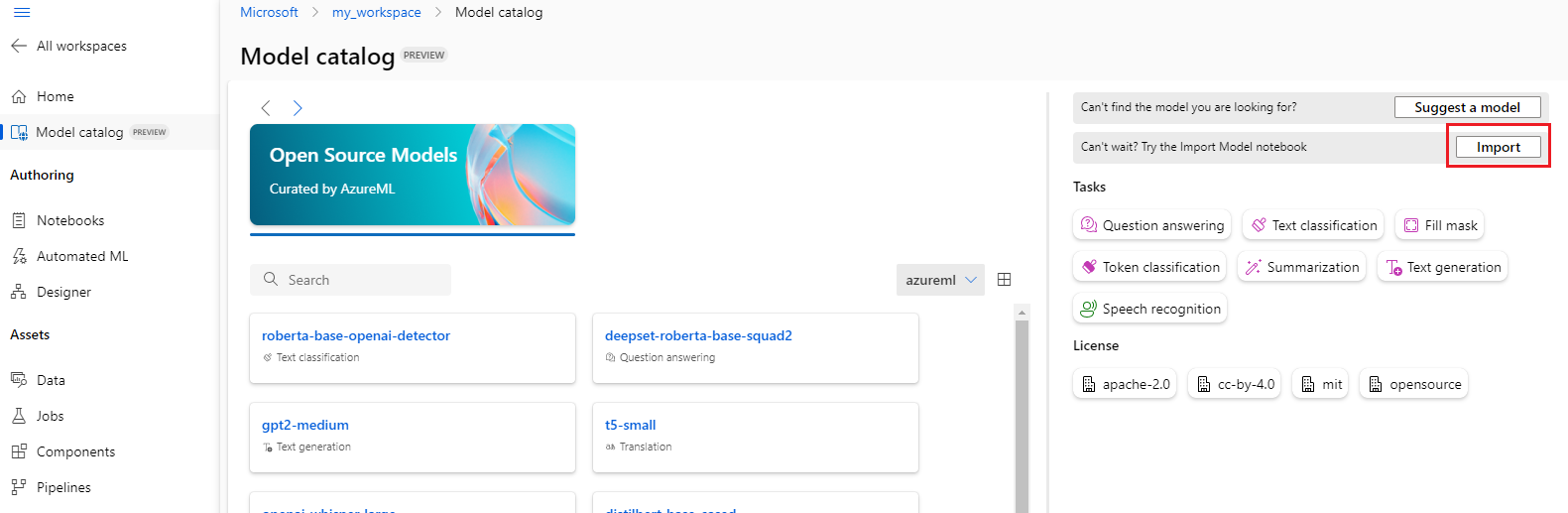
Import foundation models
If you search the model catalog and don't find the open source model you need, you can import it from Hugging Face into your Azure Machine Learning workspace. The Import button appears in the model catalog only when your search returns no results.
Hugging Face is an open-source library for natural language processing (NLP) that provides pre-trained models for popular NLP tasks. Currently, model import supports importing models for the following tasks, as long as the model meets the requirements listed in the Model Import Notebook:
- fill-mask
- token-classification
- question-answering
- summarization
- text-generation
- text-classification
- translation
- image-classification
- text-to-image
Note
Models from Hugging Face are subject to third-party license terms available on the Hugging Face model details page. It is your responsibility to comply with the model's license terms.
When your search returns no results, select Import model notebook to use the Model Import Notebook.
The model import notebook is also included in the azureml-examples git repo here.
In order to import the model, you need to pass in the MODEL_ID of the model you wish to import from Hugging Face. Browse models on Hugging Face hub and identify the model to import. Make sure the task type of the model is among the supported task types. Copy the model ID, which is available in the URI of the page or can be copied using the copy icon next to the model name. Assign it to the variable 'MODEL_ID' in the Model import notebook. For example:
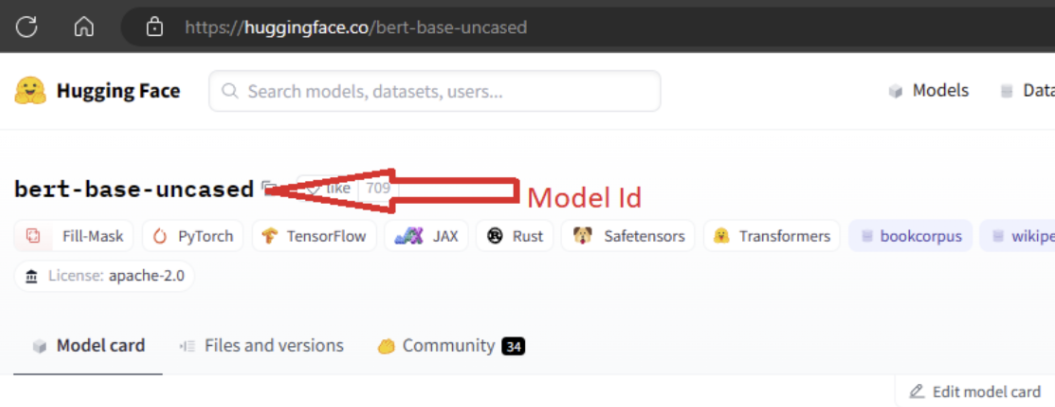
You need to provide compute for the Model import to run. Running the Model Import results in the specified model being imported from Hugging Face and registered to your Azure Machine Learning workspace. You can then fine-tune this model or deploy it to an endpoint for inferencing.
Learn more
- Explore the Model Catalog in Azure Machine Learning studio. You need an Azure Machine Learning workspace to explore the catalog.
- Explore the Model Catalog and Collections