Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
The LangChain Python library is a framework for developing applications powered by large language models (LLMs), agents, and dependency tools. This article shows you how to supercharge your LangChain development with Azure Machine Learning prompt flow.
The integration of LangChain with prompt flow is a powerful combination that can help you build and test your custom language models with ease. You can use LangChain modules to build the flow, then use the prompt flow process to scale experiments for bulk testing, evaluation, and eventual deployment. For example, you can conduct large scale experiments based on larger datasets.
If you already have a local prompt flow based on LangChain code, you can easily convert it into an Azure Machine Learning prompt flow for further experimentation. Or if you prefer to use LangChain SDK classes and functions directly, you can easily build Azure Machine Learning flows with Python nodes that use your custom LangChain code.
Prerequisites
- A local LangChain flow that's properly tested and ready for deployment.
- A compute session that can run the Machine Learning prompt flow by adding packages listed in the requirements.txt file, including
langchain. For more information, see Manage prompt flow compute session.
Convert LangChain code into a prompt flow
Use the following process to convert your local LangChain code to a runnable Azure Machine Learning prompt flow.
Convert credentials to a prompt flow connection
Your LangChain code might define environment variables to store credentials, such as the AzureOpenAI API key necessary for invoking AzureOpenAI models. For example, the following code shows environmental variables being set for OpenAI API type, key, base, and version.
os.environ["OPENAI_API_TYPE"] = "azure"
os.environ["OPENAI_API_VERSION"] = "2023-05-15"
os.environ["OPENAI_API_BASE"] = "https://contosobamiopenai.openai.azure.com/"
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "abc123abc123abc123abc123abc123ab"
When you run an Azure Machine Learning prompt flow in the cloud, it's better not to expose credentials as environment variables. To securely store and manage credentials separately from your code, you should convert the environmental variables into a prompt flow connection.
To create a connection that securely stores custom credentials such as your LLM API key or other required keys, follow these instructions:
On the Prompt flow page in your Azure Machine Learning workspace, select the Connections tab, and then select Create.
Select a connection type from the dropdown list. For this example, select Custom.
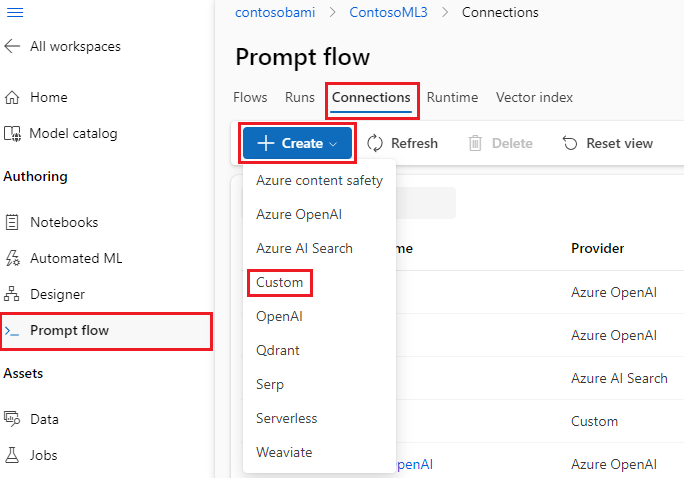
In the right pane, define your connection Name, and then add Key-value pairs to store your credentials and keys by selecting Add key-value pairs.
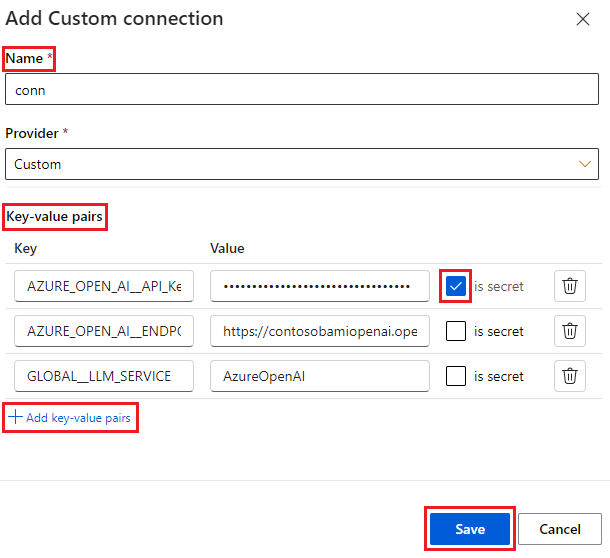
To store an encrypted value for a key, select the is secret checkbox next to one or more key-value pairs. You must set at least one value as secret to successfully create a custom connection.
Select Save.
The custom connection can replace keys and credentials or corresponding environmental variables explicitly defined in your LangChain code. To use the custom connection in the flow, see Configure connection.
Convert LangChain code to a runnable flow
To create a flow, select Create on the Prompt flow page in Azure Machine Learning studio, and choose a flow type. On the flow authoring page, start your compute session before you author the flow. Select tool types at the top of the page to insert corresponding nodes into the flow. For detailed flow authoring instructions, see Develop prompt flow.
All your LangChain code can directly run in Python nodes in your flow, as long as your compute session contains the langchain package dependency.
There are two ways to convert your LangChain code into an Azure Machine Learning prompt flow. The type of flow to implement depends on your use case.
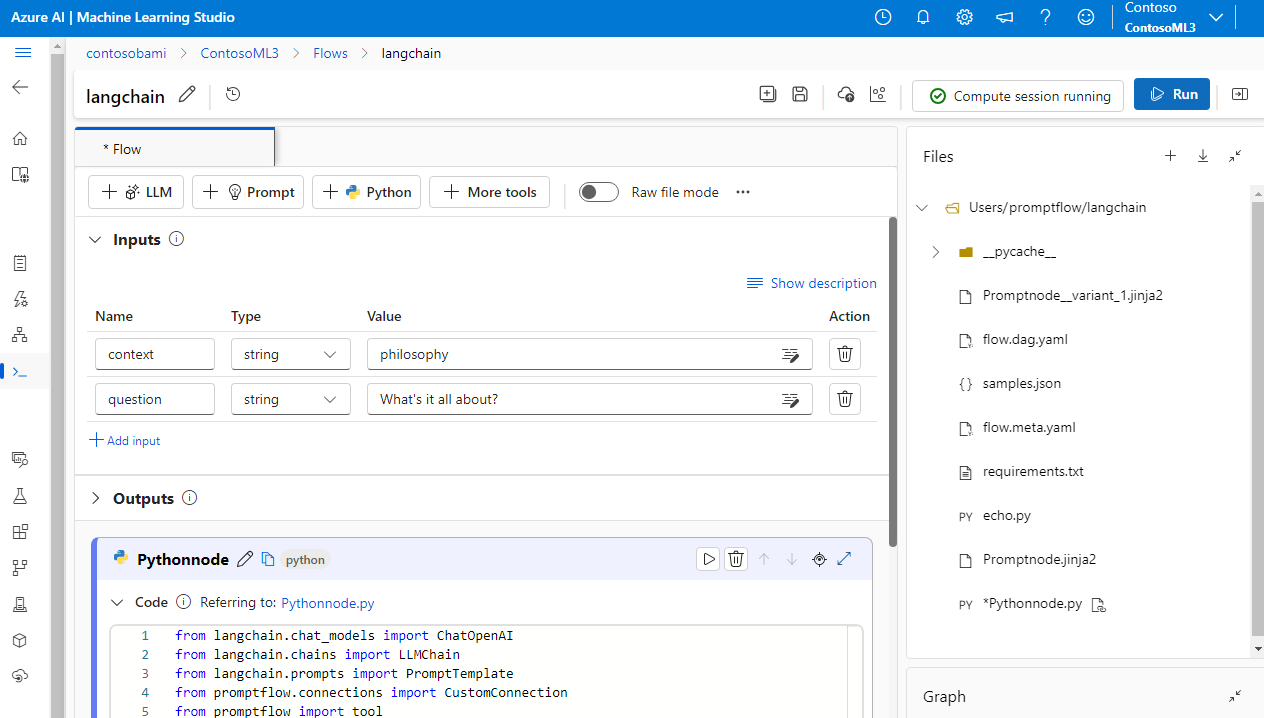
For better experiment management, you can convert your code to use Azure Machine Learning Python and prompt tools in the flow. You extract the prompt template from your code into a prompt node, and put the remaining code in single or multiple Python nodes or tools. This option helps you easily tune prompts by running variants and lets you choose optimal prompts based on evaluation results.
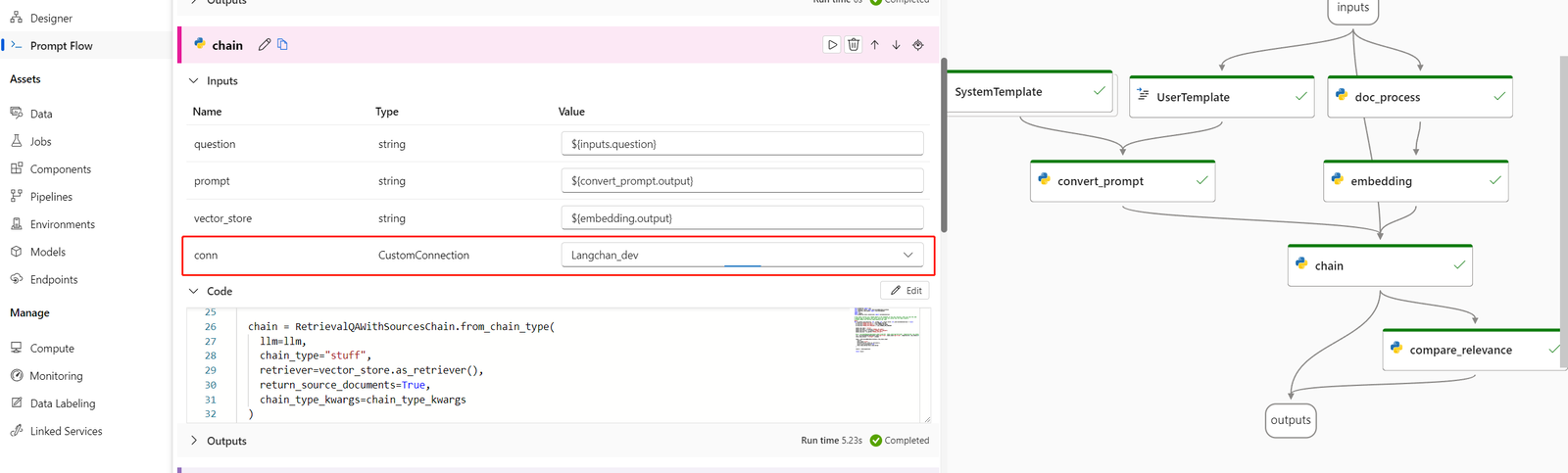
The following example shows a flow that uses both prompt nodes and Python nodes:
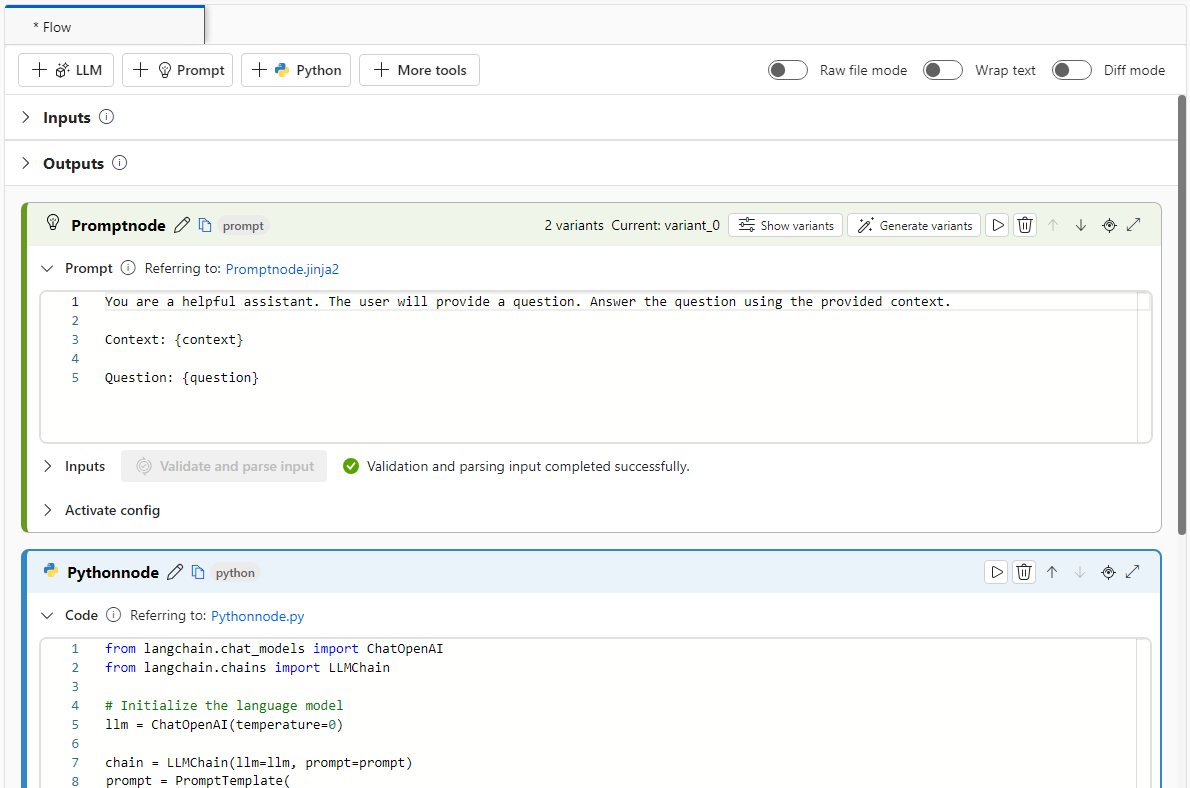
For a simpler conversion process, you can call the LangChain LLM library directly from within Python nodes. All your code runs in Python nodes, including prompt definitions. This option supports faster batch testing based on larger datasets or other configurations.
The following example shows a flow that uses Python nodes only:
Configure connection
After you structure your flow and move your code to specific tool nodes, you need to replace your original environment variables with the corresponding keys from your connection. To use the custom connection you created, follow these steps:
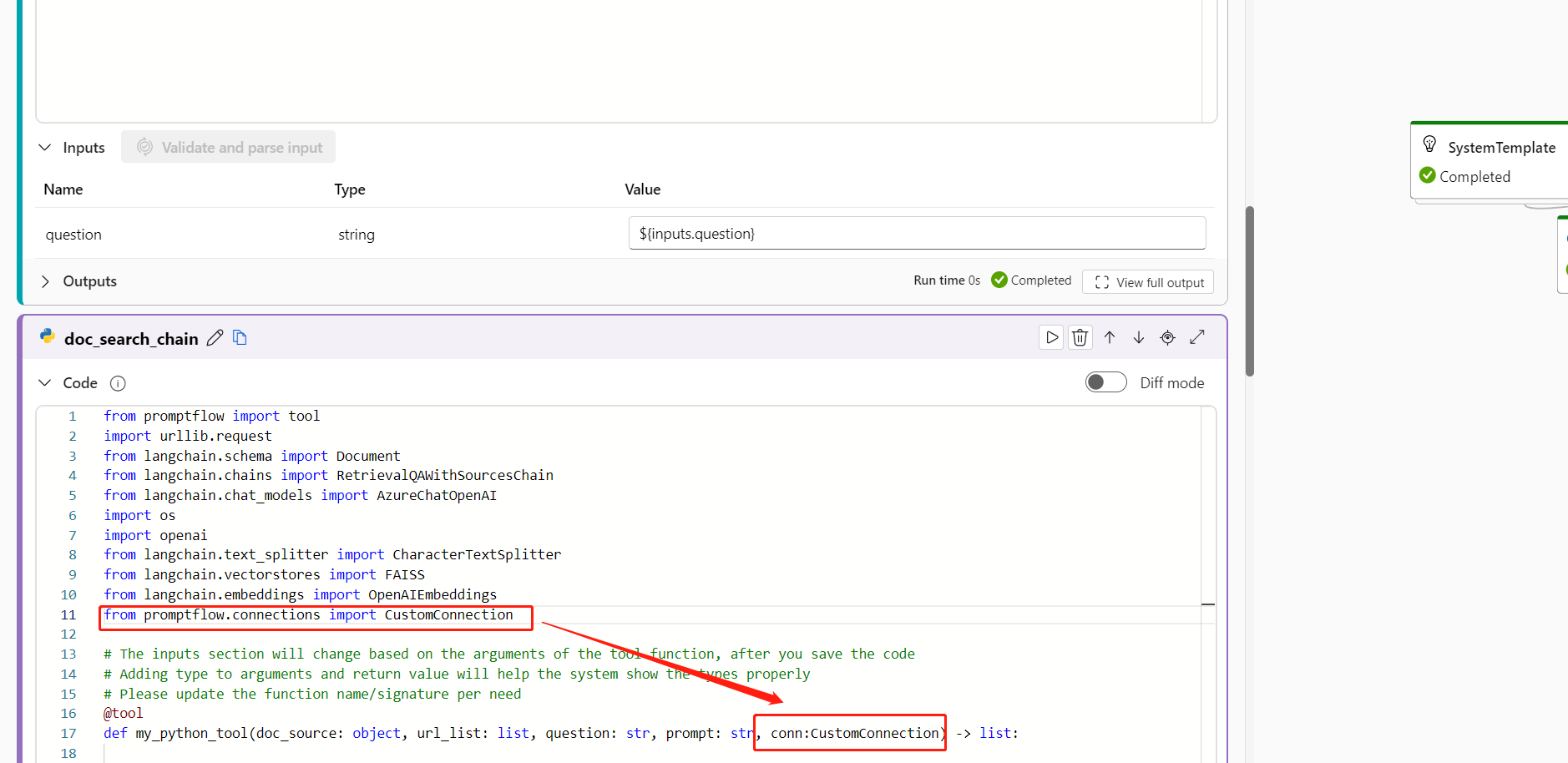
In your Python code, import the custom connection library by entering
from promptflow.connections import CustomConnection.Note
To import an Azure OpenAI connection, use
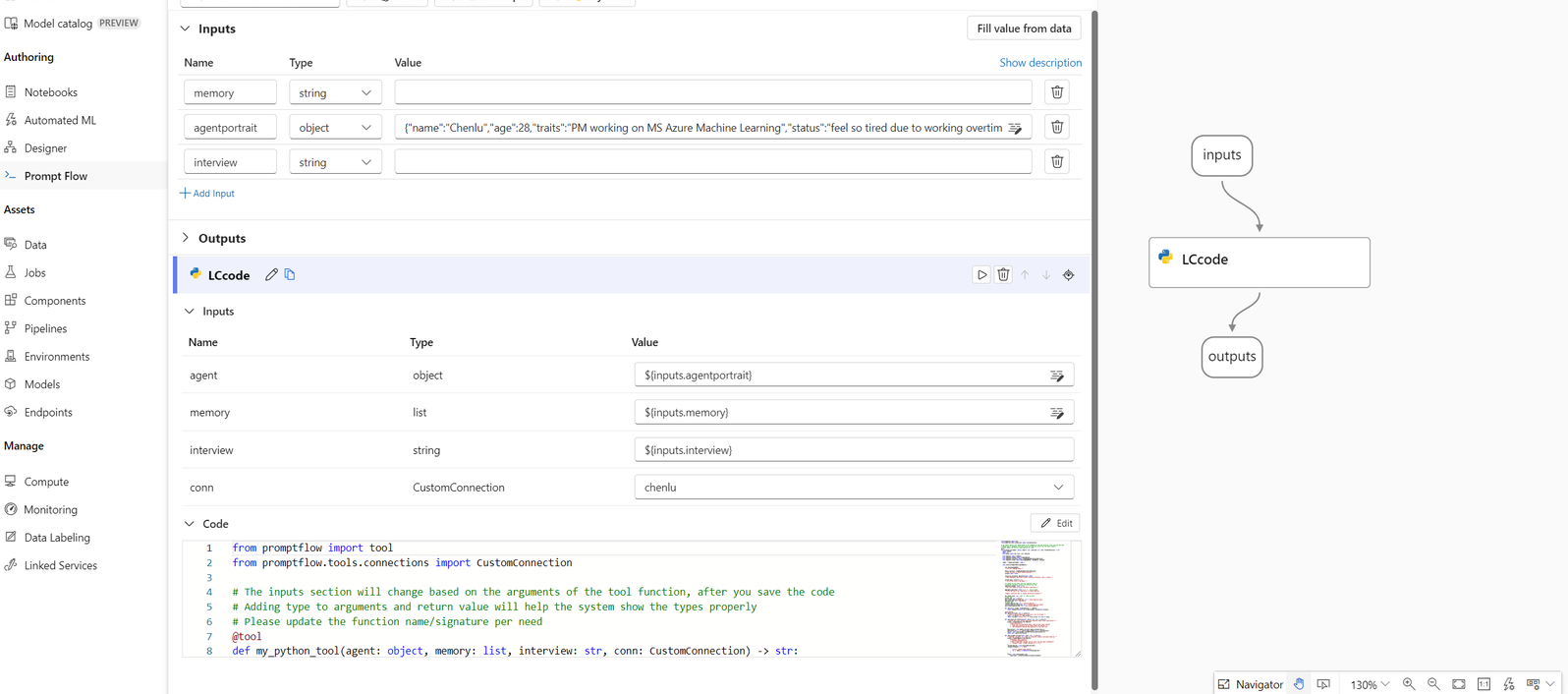
from promptflow.connections import AzureOpenAIConnection.In your tool function, define an input parameter of the type
CustomConnection.Replace environment variables that originally defined the keys or credentials with the corresponding keys from the connection.
Parse the input to the input section of the node UI, and then select your custom connection from the Value dropdown list in the UI.
Be sure to also configure the connection parameters in any other nodes that require them, such as LLM nodes.
Configure inputs and outputs
Before you run the flow, configure the node inputs and outputs and the overall flow inputs and outputs. This step is crucial to ensure that all the required data passes properly through the flow and produces desired results. For more information, see Flow inputs and outputs.