Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This tutorial shows you how to set up Microsoft Entra authentication for Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server.
In this tutorial, you learn how to:
- Configure the Microsoft Entra Admin.
- Connect to Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server using Microsoft Entra ID.
Prerequisites
An Azure account with an active subscription.
If you don't have an Azure subscription, create an Azure free account before you begin.
Note
With an Azure free account, you can now try Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server for free for 12 months. For more information, see Use an Azure free account to try Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server for free.
Install or upgrade Azure CLI to the latest version. See Install Azure CLI.
Configure the Microsoft Entra Admin
To create a Microsoft Entra Admin user, follow the following steps.
In the Azure portal, select the instance of Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server that you want to enable for Microsoft Entra ID.
Under the Security pane, select Authentication:
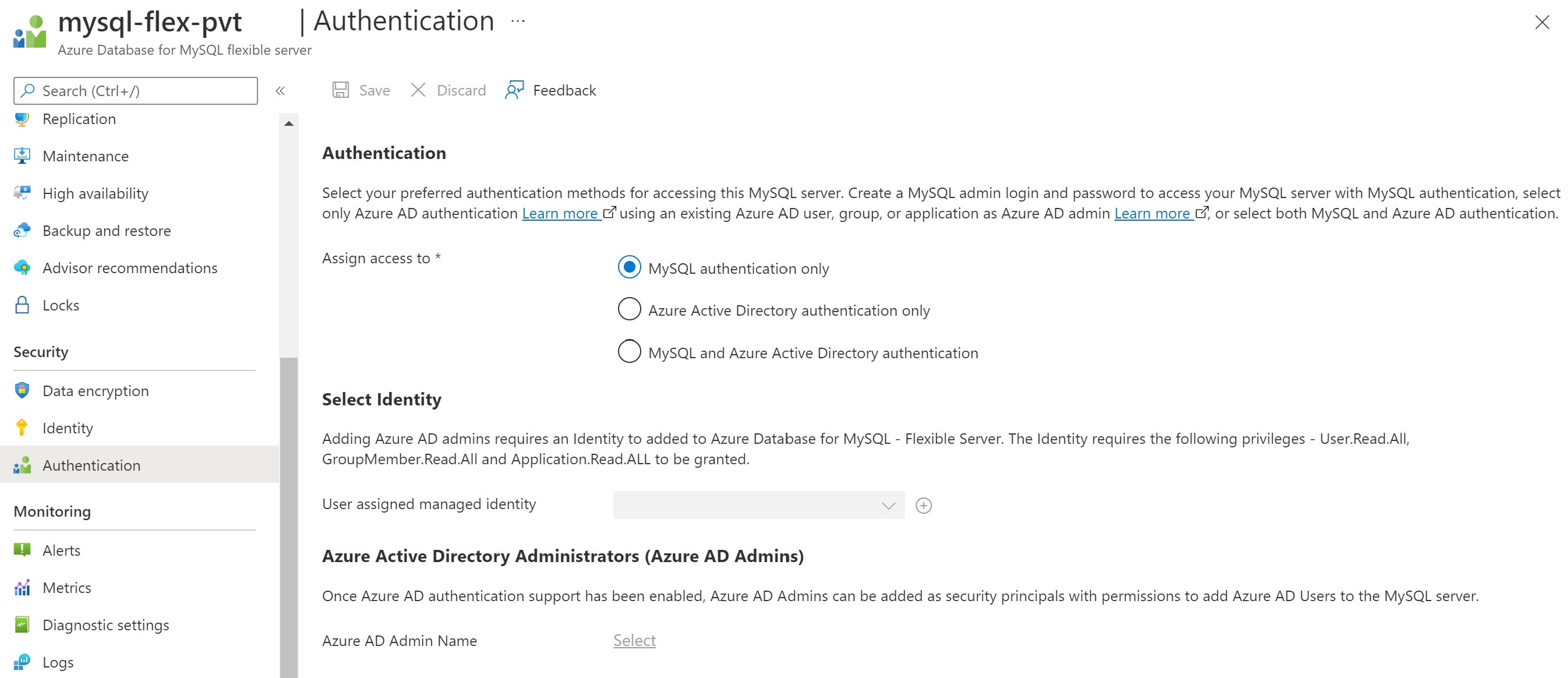
There are three types of authentication available:
MySQL authentication only – By default, MySQL uses the built-in mysql_native_password authentication plugin, which performs authentication using the native password hashing method
Microsoft Entra authentication only – Only allows authentication with a Microsoft Entra account. Disables mysql_native_password authentication and turns ON the server parameter aad_auth_only
MySQL and Microsoft Entra authentication – Allows authentication using a native MySQL password or a Microsoft Entra account. Turns OFF the server parameter aad_auth_only
Select Identity – Select/Add User assigned managed identity. The following permissions are required to allow the UMI to read from Microsoft Graph as the server identity. Alternatively, give the user-assigned managed identity the Directory Readers role.
- User.Read.All: Allows access to Microsoft Entra user information.
- GroupMember.Read.All: Allows access to Microsoft Entra group information.
- Application.Read.ALL: Allows access to Microsoft Entra service principal (application) information.
Important
Only a user with at least the Privileged Role Administrator role can grant these permissions.
Select a valid Microsoft Entra user or a Microsoft Entra group in the customer tenant to be Microsoft Entra administrator. Once Microsoft Entra authentication support has been enabled, Microsoft Entra Admins can be added as security principals with permission to add Microsoft Entra users to the MySQL server.
Note
Only one Microsoft Entra admin can be created per MySQL server, and selecting another overwrites the existing Microsoft Entra admin configured for the server.
Grant permissions to User assigned managed identity
The following sample PowerShell script grants the necessary permissions for a UMI. This sample assigns permissions to the UMI umiservertest.
To run the script, you must sign in as a user with a Global Administrator or Privileged Role Administrator role.
The script grants the User.Read.All, GroupMember.Read.All, and Application.Read.ALL permissions to a UMI to access Microsoft Graph.
# Script to assign permissions to the UMI "umiservertest"
import-module Az.Resources
import-module Microsoft.Entra
$tenantId = '<tenantId>' # Your Azure AD tenant ID
Connect-Entra -TenantID $tenantId
# Log in as a user with a "Global Administrator" or "Privileged Role Administrator" role
# Script to assign permissions to an existing UMI
# The following Microsoft Graph permissions are required:
# User.Read.All
# GroupMember.Read.All
# Application.Read.ALL
# Search for Microsoft Graph
$AAD_SP = Get-AzADServicePrincipal -DisplayNameStartsWith "Microsoft Graph"
$AAD_SP
# Use Microsoft Graph; in this example, this is the first element $AAD_SP[0]
#Output
#ObjectId AppId DisplayName
#-------- ----- -----------
#47d73278-e43c-4cc2-a606-c500b66883ef 00000003-0000-0000-c000-000000000000 Microsoft Graph
#44e2d3f6-97c3-4bc7-9ccd-e26746638b6d 0bf30f3b-4a52-48df-9a82-234910c4a086 Microsoft Graph #Change
$MSIName = "<managedIdentity>"; # Name of your user-assigned
$MSI = Get-AzADServicePrincipal -DisplayNameStartsWith $MSIName
if($MSI.Count -gt 1)
{
Write-Output "More than 1 principal found, please find your principal and copy the right object ID. Now use the syntax $MSI = Get-AzureADServicePrincipal -ObjectId <your_object_id>"
# Choose the right UMI
Exit
}
# If you have more UMIs with similar names, you have to use the proper $MSI[ ]array number
# Assign the app roles
$AAD_AppRole = $AAD_SP.AppRole | Where-Object {$_.Value -eq "User.Read.All"}
New-AzADServicePrincipalAppRoleAssignment -ServicePrincipalId $MSI.Id -ResourceId $AAD_SP.Id -AppRoleId $AAD_AppRole.Id
$AAD_AppRole = $AAD_SP.AppRole | Where-Object {$_.Value -eq "GroupMember.Read.All"}
New-AzADServicePrincipalAppRoleAssignment -ServicePrincipalId $MSI.Id -ResourceId $AAD_SP.Id -AppRoleId $AAD_AppRole.Id
$AAD_AppRole = $AAD_SP.AppRole | Where-Object {$_.Value -eq "Application.Read.All"}
New-AzADServicePrincipalAppRoleAssignment -ServicePrincipalId $MSI.Id -ResourceId $AAD_SP.Id -AppRoleId $AAD_AppRole.Id
In the final steps of the script, if you have more UMIs with similar names, you have to use the proper $MSI[ ]array number. An example is $AAD_SP.ObjectId[0].
Check permissions for user-assigned managed identity
To check permissions for a UMI, go to the Azure portal. In the Microsoft Entra ID resource, go to Enterprise applications. Select All Applications for Application type, and search for the UMI that was created.
Select the UMI, and go to the Permissions settings under Security.
After you grant the permissions to the UMI, they're enabled for all servers created with the UMI assigned as a server identity.
Connect to Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server using Microsoft Entra ID
1 - Authenticate with Microsoft Entra ID
Start by authenticating with Microsoft Entra ID using the Azure CLI tool.
(This step isn't required in Azure Cloud Shell.)
Sign in to Azure account using az login command. Note the ID property, which refers to the Subscription ID for your Azure account:
az login
The command launches a browser window to the Microsoft Entra authentication page. It requires you to give your Microsoft Entra user ID and password.
If you have multiple subscriptions, choose the appropriate subscription using the az account set command:
az account set --subscription \<subscription id\>
2 - Retrieve Microsoft Entra access token
Invoke the Azure CLI tool to acquire an access token for the Microsoft Entra authenticated user from step 1 to access Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server.
Example (for Public Cloud):
az account get-access-token --resource https://ossrdbms-aad.database.windows.netThe above resource value must be specified exactly as shown. For other clouds, the resource value can be looked up using the following:
az cloud showFor Azure CLI version 2.0.71 and later, the command can be specified in the following more convenient version for all clouds:
az account get-access-token --resource-type oss-rdbmsUsing PowerShell, you can use the following command to acquire access token:
$accessToken = Get-AzAccessToken -ResourceUrl https://ossrdbms-aad.database.windows.net $accessToken.Token | out-file C:\temp\MySQLAccessToken.txt
After authentication is successful, Microsoft Entra ID returns an access token:
{
"accessToken": "TOKEN",
"expiresOn": "...",
"subscription": "...",
"tenant": "...",
"tokenType": "Bearer"
}
The token is a Base 64 string that encodes all the information about the authenticated user and is targeted to the Azure Database for MySQL service.
The access token validity is anywhere between 5 minutes to 60 minutes. We recommend you get the access token before initiating the sign-in to Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server.
- You can use the following PowerShell command to see the token validity.
$accessToken.ExpiresOn.DateTime
3 - Use a token as a password for logging in with MySQL
You need to use the access token as the MySQL user password when connecting. You can use the method described above to retrieve the token using GUI clients such as MySQL workbench.
Connect to Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server using MySQL CLI
When using the CLI, you can use this shorthand to connect:
Example (Linux/macOS):
mysql -h mydb.mysql.database.azure.com \
--user user@tenant.onmicrosoft.com \
--enable-cleartext-plugin \
--password=`az account get-access-token --resource-type oss-rdbms --output tsv --query accessToken`
Example (PowerShell):
mysql -h mydb.mysql.database.azure.com \
--user user@tenant.onmicrosoft.com \
--enable-cleartext-plugin \
--password=$(az account get-access-token --resource-type oss-rdbms --output tsv --query accessToken)
mysql -h mydb.mysql.database.azure.com \
--user user@tenant.onmicrosoft.com \
--enable-cleartext-plugin \
--password=$((Get-AzAccessToken -ResourceUrl https://ossrdbms-aad.database.windows.net).Token)
Connect to Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server using MySQL Workbench
- Launch MySQL Workbench and Select the Database option, then select Connect to database.
- In the hostname field, enter the MySQL FQDN for example, mysql.database.azure.com.
- In the username field, enter the MySQL Microsoft Entra administrator name. For example, user@tenant.onmicrosoft.com.
- In the password field, select Store in Vault and paste in the access token from the file for example, C:\temp\MySQLAccessToken.txt.
- Select the advanced tab and ensure that you check Enable Cleartext Authentication Plugin.
- Select OK to connect to the database.
Important considerations when connecting
user@tenant.onmicrosoft.comis the name of the Microsoft Entra user or group you're trying to connect as- Make sure to use the exact way the Microsoft Entra user or group name is spelled
- Microsoft Entra user and group names are case sensitive
- When connecting as a group, use only the group name (for example,
GroupName) - If the name contains spaces, use
\before each space to escape it
Note
The "enable-cleartext-plugin" setting – you need to use a similar configuration with other clients to make sure the token gets sent to the server without being hashed.
You're now authenticated to your MySQL flexible server using Microsoft Entra authentication.
Other Microsoft Entra admin commands
Manage server Active Directory administrator
az mysql flexible-server ad-adminCreate an Active Directory administrator
az mysql flexible-server ad-admin createExample: Create Active Directory administrator with user 'john@contoso.com', administrator ID '00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000' and identity 'test-identity'
az mysql flexible-server ad-admin create -g testgroup -s testsvr -u john@contoso.com -i 00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000 --identity test-identityDelete an Active Directory administrator
az mysql flexible-server ad-admin deleteExample: Delete Active Directory administrator
az mysql flexible-server ad-admin delete -g testgroup -s testsvrList all Active Directory administrators
az mysql flexible-server ad-admin listExample: List Active Directory administrators
az mysql flexible-server ad-admin list -g testgroup -s testsvrGet an Active Directory administrator
az mysql flexible-server ad-admin showExample: Get Active Directory administrator
az mysql flexible-server ad-admin show -g testgroup -s testsvrWait for the Active Directory administrator to satisfy certain conditions
az mysql flexible-server ad-admin waitExamples:
- Wait until the Active Directory administrator exists
az mysql flexible-server ad-admin wait -g testgroup -s testsvr --exists- Wait for the Active Directory administrator to be deleted
az mysql flexible-server ad-admin wait -g testgroup -s testsvr –deleted
Create Microsoft Entra users in Azure Database for MySQL
To add a Microsoft Entra user to your Azure Database for MySQL database, perform the following steps after connecting:
- First ensure that the Microsoft Entra user
<user>@yourtenant.onmicrosoft.comis a valid user in Microsoft Entra tenant. - Sign in to your Azure Database for MySQL instance as the Microsoft Entra Admin user.
- Create user
<user>@yourtenant.onmicrosoft.comin Azure Database for MySQL.
Example:
CREATE AADUSER 'user1@yourtenant.onmicrosoft.com';
For user names that exceed 32 characters, it's recommended you use an alias instead, to be used when connecting:
Example:
CREATE AADUSER 'userWithLongName@yourtenant.onmicrosoft.com' as 'userDefinedShortName';
Note
- MySQL ignores leading and trailing spaces, so the user name should not have any leading or trailing spaces.
- Authenticating a user through Microsoft Entra ID does not give the user any permissions to access objects within the Azure Database for MySQL database. You must grant the user the required permissions manually.
Create Microsoft Entra groups in Azure Database for MySQL
To enable a Microsoft Entra group for access to your database, use the exact mechanism as for users, but instead specify the group name:
Example:
CREATE AADUSER 'Prod_DB_Readonly';
When logging in, group members use their personal access tokens but sign in with the group name specified as the username.
Compatibility with application drivers
Most drivers are supported; however, make sure to use the settings for sending the password in clear text, so the token gets sent without modification.
C/C++
- libmysqlclient: Supported
- mysql-connector-c++: Supported
Java
- Connector/J (mysql-connector-java): Supported, must utilize
useSSLsetting
- Connector/J (mysql-connector-java): Supported, must utilize
Python
- Connector/Python: Supported
Ruby
- mysql2: Supported
.NET
- mysql-connector-net: Supported, need to add plugin for mysql_clear_password
- mysql-net/MySqlConnector: Supported
Node.js
- mysqljs: Not supported (doesn't send the token in cleartext without patch)
- node-mysql2: Supported
Perl
- DBD::mysql: Supported
- Net::MySQL: Not supported
Go
- go-sql-driver: Supported, add
?tls=true&allowCleartextPasswords=trueto connection string
- go-sql-driver: Supported, add
PHP
mysqli extension: Supported
PDO_MYSQL driver: Supported