Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Egress lockdown provides access to the URLs and endpoints an Azure Red Hat OpenShift cluster needs to function effectively.
Egress lockdown ensures that you have access to URLs, such as management.azure.com, so you can create another worker node backed by Azure VMs. Egress lockdown ensures access even if the outbound (egress) traffic is restricted by a firewall appliance or other means.
Egress lockdown takes a collection of domains required for an Azure Red Hat OpenShift cluster to function and proxies calls to these domains through the Azure Red Hat OpenShift service. The domains, which are region-specific, can't be configured by customers.
Egress lockdown doesn't rely on customer internet access for Azure Red Hat OpenShift services to work. In order for clusters to reach any Azure Red Hat OpenShift service, cluster traffic exits through an Azure private endpoint created within the cluster resource group where all of the Azure Red Hat OpenShift resources are available.
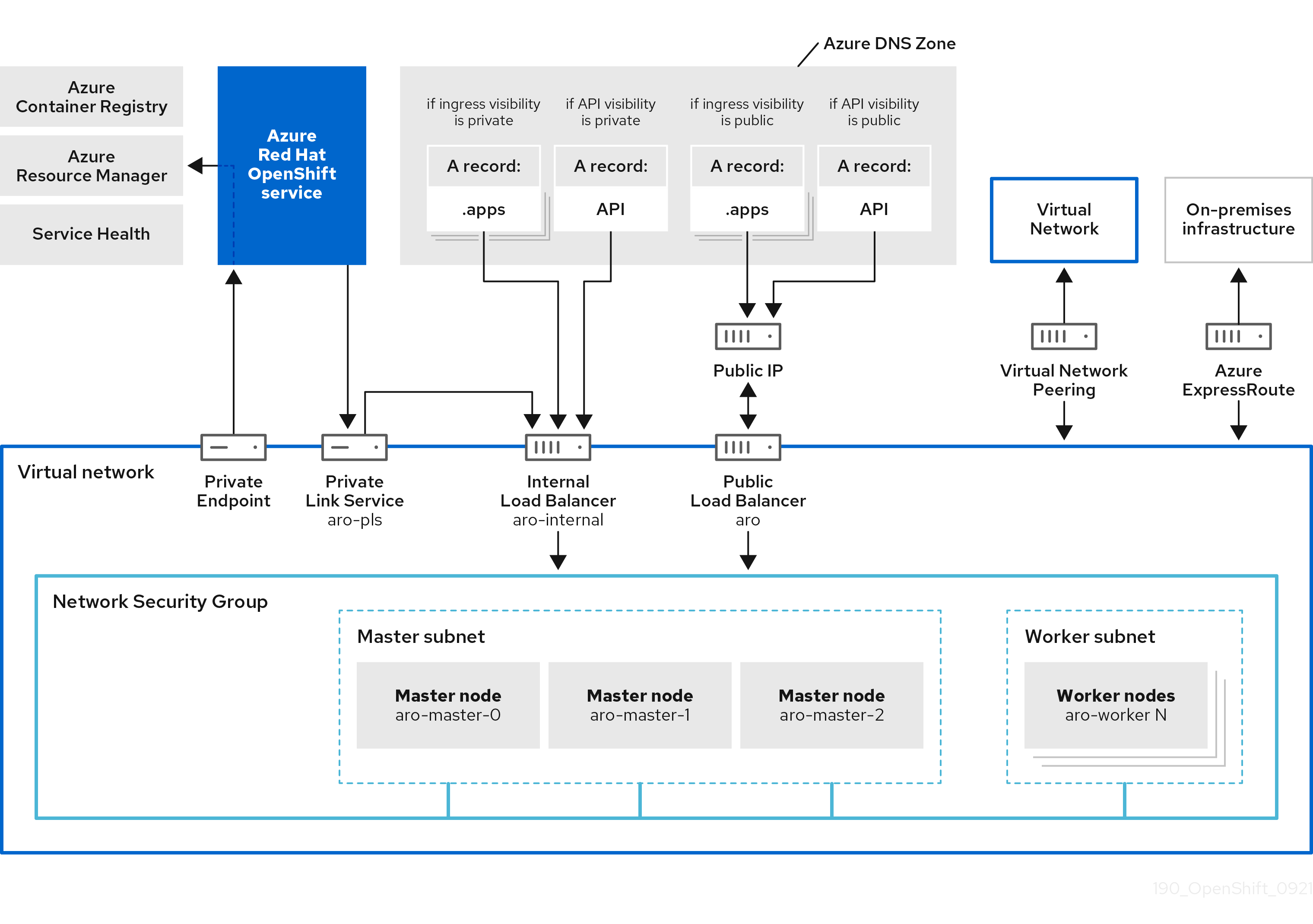
The following image displays the architecture changes that encompass egress lockdown.
A well-known subset of domains (that the Azure Red Hat OpenShift clusters need to function) validates the destination of the cluster traffic. Finally, the traffic passes through the Azure Red Hat OpenShift service to connect to these URLs and endpoints.
Enable egress lockdown
In order to function, egress lockdown relies on the Server Name Indication (SNI) extension to the Transport Layer Security (TLS). All customer workloads that communicate with the well-known subset of domains must have SNI enabled.
Egress lockdown is enabled by default for new cluster creation. However, to enable egress lockdown on existing clusters, you must have SNI enabled on the customer workloads. To enable egress lockdown on your existing clusters, submit a support case to either Microsoft Support or Red Hat Support.
Verify egress lockdown is enabled on a cluster
To verify whether egress lockdown is enabled on a cluster, sign in to your Azure cluster and run the following command:
$ oc get cluster.aro.openshift.io cluster -o go-template='{{ if .spec.gatewayDomains }}{{ "Egress Lockdown Feature Enabled" }}{{ else }}{{ "Egress Lockdown Feature Disabled" }}{{ end }}{{ "\n" }}'
Depending on whether egress lockdown is enabled or disabled, you'll see one of the following messages:
Egress Lockdown Feature EnabledEgress Lockdown Feature Disabled
Relation to storage lockdown
Storage lockdown is another feature of Azure Red Hat OpenShift that enhances cluster security. Storage Accounts created with the cluster are configured to restrict any public access. Exceptions are added for the Azure Red Hat OpenShift Resource Provisioner subnets as well as the subnet of egress lockdown gateway. Cluster components that utilize this storage, for example, OpenShift Image Registry, rely on egress lockdown functionality instead of accessing the storage accounts directly.
Next steps
For more information on controlling egress traffic on your Azure Red Hat OpenShift cluster, see Control egress traffic for your Azure Red Hat OpenShift (ARO) cluster (preview).