Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
The Oracle to Azure Database for PostgreSQL schema conversion feature in the Visual Studio Code PostgreSQL extension helps you convert your existing Oracle database schema objects into PostgreSQL-compatible schema. This functionality is designed for relational schemas and ensures that the converted schema works seamlessly with Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server.
The tool provides a project-based user interface to automate schema conversion. If certain objects can't be converted automatically, the tool flags them as Review Tasks, which you can resolve manually by using GitHub Copilot Agents.
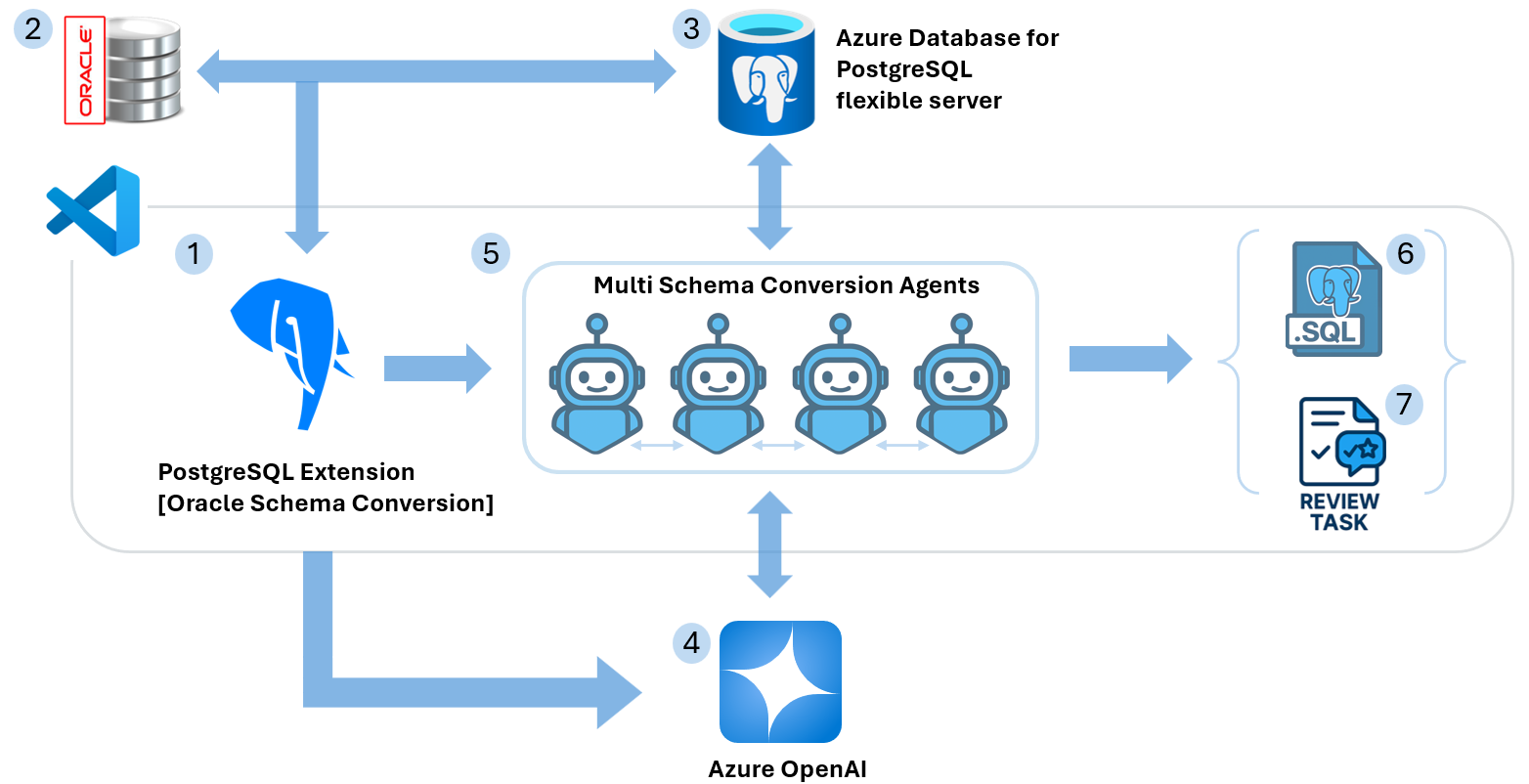
Architecture
The schema conversion process involves multiple components working together:
- Source Oracle Database: Your existing Oracle database containing the schema to convert
- Visual Studio Code PostgreSQL Extension: The primary interface for managing the conversion process
- Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server: Used as the scratch database for validation and testing
- Azure OpenAI: Provides intelligent transformation capabilities for complex schema objects
- Schema Conversion Agents: AI-powered agents that handle the automated conversion process
How it works
The schema conversion process uses an intelligent, multistage approach that combines automated transformation with human oversight:
- Connection and Discovery: The tool connects to your Oracle database and catalogs all schema objects. It analyzes their structure, dependencies, and complexity to create a conversion plan.
- AI-Powered Transformation: Schema Conversion Agents use Azure OpenAI to intelligently transform Oracle-specific constructs into PostgreSQL-compatible equivalents. The AI understands context, relationships, and best practices for both database platforms.
- Validation in Scratch Environment: The tool tests all converted objects in the Azure Database for PostgreSQL database (scratch database) environment. This step ensures syntax correctness and compatibility before final output generation.
- Review Task Generation: The tool flags objects that can't be fully automated or require human judgment as Review Tasks. These objects might include complex business logic or Oracle-specific features that need manual attention.
- Guided Resolution: GitHub Copilot Agent Mode provides intelligent assistance for completing Review Tasks. It offers context-aware suggestions and Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server best practices to help you make informed decisions.
- Output Generation: The tool converts successfully validated objects into organized PostgreSQL
.sqlfiles, ready for deployment to your target environment.
Install the extension
The Oracle to PostgreSQL Schema Conversion functionality is built into the PostgreSQL extension for Visual Studio Code. You don't need a separate extension - it's included as a comprehensive feature within the main PostgreSQL extension.
Installation steps
- Open Extensions Marketplace: In Visual Studio Code, select the Extensions icon in the Activity Bar on the left side, or use the keyboard shortcut
Ctrl+Shift+X(Windows/Linux) orCmd+Shift+X(macOS). - Search for PostgreSQL: In the Extensions Marketplace search box, type "PostgreSQL" to find the extension.
- Install the Extension: Locate the PostgreSQL extension in the search results and select Install.
- Access Schema Conversion: When the extension is installed, you see an elephant icon in the Visual Studio Code sidebar representing the PostgreSQL extension. You can access the Schema Conversion feature through this extension interface.
Schema conversion workflow
This section explains the core concepts used throughout the Oracle to PostgreSQL schema conversion workflow - including conversion units (schemas, tables, indexes, views, and procedures), review tasks for human oversight, scratch database validation, AI-powered schema conversion agents, and the resulting PostgreSQL SQL artifacts. Understanding these concepts helps you interpret conversion results, prioritize and resolve flagged items, and prepare converted files for deployment to Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server.
Scratch database
An Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server that you use during conversion for validation purposes to ensure compatibility. This approach ensures that:
- Converted objects are syntactically correct
- Dependencies are properly resolved
- Performance characteristics are maintained
- Azure-specific features are applied appropriately
Review tasks
The tool flags items for manual review when the AI can't fully convert an object or recommends a second look. Common review tasks include:
- Complex PL/SQL procedures that need manual optimization
- Oracle-specific data types with multiple PostgreSQL alternatives
- Custom functions with Oracle-specific logic
GitHub Copilot agent mode
An integrated feature in Visual Studio Code that provides guided prompts to help you complete review tasks and align schema with your application requirements. The agent mode offers:
- Context-aware suggestions for schema modifications
- Best practice recommendations for Azure Database for PostgreSQL
- Code completion for complex transformations
- Integration with your existing development workflow
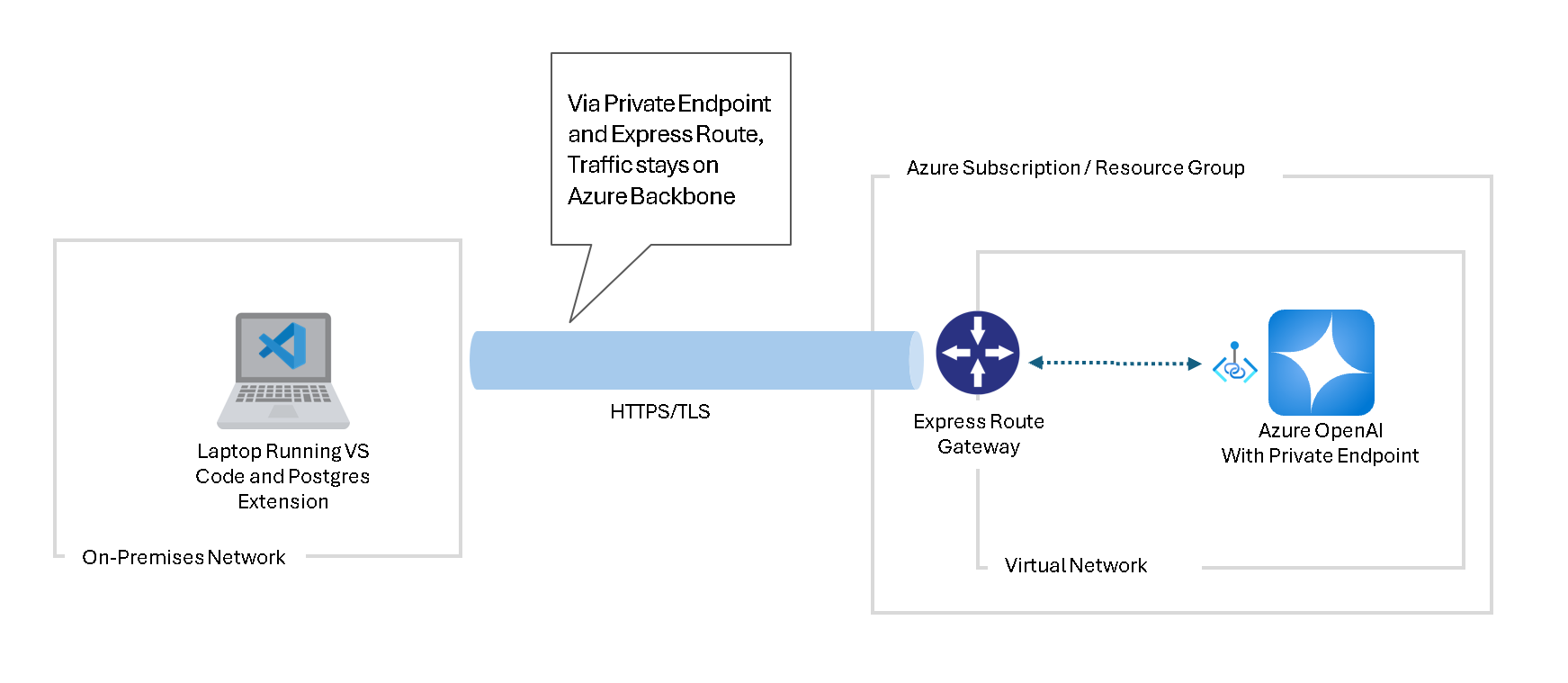
Security and networking
When you use the schema conversion feature, make sure your Visual Studio Code environment can securely connect to both your source Oracle database and the Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server instance that you use as the scratch database.
Microsoft recommends connecting to an Azure OpenAI resource by using a private endpoint. For more information, see Create a private endpoint for Azure OpenAI.
For more information on securing your Azure OpenAI connections, visit Data, privacy, and security for Azure Direct Models in Azure AI Foundry.
Important
Customer validation responsibility: The same AI engine used for schema conversion can also assist with validation and review. AI systems can occasionally confirm their own mistakes. To prevent data loss, functional regressions, or security issues, independently validate all converted objects and review-task resolutions before deploying to production. As part of your controls, consider enabling Azure AI Foundry content filtering to help reduce harmful or undesired outputs. For guidance, see Content filtering in Azure AI Foundry.
Why use the schema conversion feature?
Converting Oracle schemas to Azure Database for PostgreSQL streamlines migration and modernization. It reduces manual effort and risk by automating transformations, validating results in a scratch database, and providing AI-assisted review and Azure-optimized output ready for deployment.
- Automated conversion: Reduces manual effort by automatically converting compatible schema objects
- AI-powered intelligence: Uses Azure OpenAI for smart transformation decisions
- Validation-first approach: Uses the scratch database to ensure converted objects work correctly
- Integrated workflow: Works seamlessly within Visual Studio Code development environment
- Review and refinement: Provides clear guidance for manual review tasks
- Azure optimization: Designed for Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server
Supported schema objects
The conversion tool supports a broad range of Oracle schema and code objects, including data definition elements, schema-level components, and procedural code. While you can convert many common objects automatically, you might need to manually review or customize the mapping for certain Oracle-specific features or proprietary extensions. For detailed lists of supported objects and known limitations, see the sections in this article.
Database schema objects
The conversion tool supports the following Oracle database objects:
- Tables - Table definitions, column specifications, and table-level constraints
- Constraints - Primary keys, foreign keys, unique constraints, check constraints
- Indexes - B-tree indexes, unique indexes, composite indexes
- Sequences - Oracle sequence objects for autoincrementing values
- Triggers - Row-level and statement-level triggers
- Views - Standard database views
- Materialized Views - Oracle materialized views and refresh logic
- Schemas - Schema-level objects and organization
- Synonyms - Public and private synonyms (with limitations)
Oracle code objects
Advanced Oracle code constructs supported for conversion:
- Triggers - Complex trigger logic and event handling
- Packages - Oracle package specifications and bodies
- Functions - User-defined functions with complex logic
- Stored Procedures - Oracle stored procedures and parameter handling
Supported Oracle versions
This section summarizes the database engine versions that support automated schema conversion and highlights compatibility considerations. Use the listed supported Oracle and PostgreSQL releases for the best results. Validate conversions in a nonproduction test environment, and use the latest minor patch of each supported major release. If your environment uses an unsupported version or includes Oracle proprietary features, you might need to perform extra manual mapping or review before deployment.
The following Oracle database versions support schema conversion:
- Oracle 21c
- Oracle 18c
- Oracle 19c
- Oracle 12.2
- Oracle 12.1
Feedback and support
For bugs, feature requests, and issues related to the Schema Conversion feature or the PostgreSQL extension, use the built-in feedback tool in Visual Studio Code. You can access this tool in two ways:
Help menu
Go to Help > Report Issue
Command Palette
- Open the Command Palette with
Ctrl+Shift+P(Windows/Linux) orCmd+Shift+P(macOS). - Run the command: PGSQL: Report Issue.
When you create your issue or provide feedback, include Schema Conversion: as a prefix in your title. This prefix helps the development team quickly identify and prioritize Schema Conversion-related feedback. This feedback mechanism helps the development team continuously improve the Schema Conversion functionality and address any issues you encounter during your Oracle to PostgreSQL migration projects.