Provision read access to Azure Storage using Microsoft Purview Data owner policies (preview)
Important
This feature is currently in preview. The Supplemental Terms of Use for Microsoft Azure Previews include additional legal terms that apply to Azure features that are in beta, in preview, or otherwise not yet released into general availability.
Data owner policies are a type of Microsoft Purview access policies. They allow you to manage access to user data in sources that have been registered for Data Policy Enforcement in Microsoft Purview. These policies can be authored directly in the Microsoft Purview governance portal, and after publishing, they get enforced by the data source.
This guide covers how a data owner can delegate in Microsoft Purview management of access to Azure Storage datasets. Currently, these two Azure Storage sources are supported:
- Blob storage
- Azure Data Lake Storage (ADLS) Gen2
Prerequisites
An Azure account with an active subscription. Create an account for free.
A new or existing Microsoft Purview account. Follow this quickstart guide to create one.
Region support
- All Microsoft Purview regions are supported.
- Storage accounts in the following regions are supported without the need for additional configuration. However, zone-redundant storage (ZRS) accounts are not supported.
- Australia Central
- Australia East
- Australia Southeast
- Brazil South
- Canada Central
- Canada East
- Central India
- Central US
- East Asia
- East US 2
- East US
- France Central
- Germany West Central
- Japan East
- Japan West
- Korea Central
- North Central US
- North Europe
- Norway East
- Poland Central
- Qatar Central
- South Central US
- South Africa North
- Southeast Asia
- South India
- Sweden Central
- Switzerland North
- West Central US
- West Europe
- West US
- West US 2
- West US 3
- UAE North
- UK South
- UK West
- Storage accounts in other regions in Public Cloud are supported after setting feature flag AllowPurviewPolicyEnforcement, as outlined in the next section. Newly created ZRS Storage accounts are supported, if created after setting the feature flag AllowPurviewPolicyEnforcement.
If needed, you can create a new Storage account by following this guide.
Configure the subscription where the Azure Storage account resides for policies from Microsoft Purview
This step is only necessary in certain regions (see prior section). To enable Microsoft Purview to manage policies for one or more Azure Storage accounts, execute the following PowerShell commands in the subscription where you'll deploy your Azure Storage account. These PowerShell commands will enable Microsoft Purview to manage policies on all Azure Storage accounts in that subscription.
If you’re executing these commands locally, be sure to run PowerShell as an administrator. Alternatively, you can use the Azure Cloud Shell in the Azure portal: https://shell.azure.com.
# Install the Az module
Install-Module -Name Az -Scope CurrentUser -Repository PSGallery -Force
# Login into the subscription
Connect-AzAccount -Subscription <SubscriptionID>
# Register the feature
Register-AzProviderFeature -FeatureName AllowPurviewPolicyEnforcement -ProviderNamespace Microsoft.Storage
If the output of the last command shows RegistrationState as Registered, then your subscription is enabled for access policies. If the output is Registering, wait at least 10 minutes, and then retry the command. Do not continue unless the RegistrationState shows as Registered.
Microsoft Purview configuration
Register the data source in Microsoft Purview
Before a policy can be created in Microsoft Purview for a data resource, you must register that data resource in Microsoft Purview Studio. You will find the instructions related to registering the data resource later in this guide.
Note
Microsoft Purview policies rely on the data resource ARM path. If a data resource is moved to a new resource group or subscription it will need to be de-registered and then registered again in Microsoft Purview.
Configure permissions to enable Data policy enforcement on the data source
Once a resource is registered, but before a policy can be created in Microsoft Purview for that resource, you must configure permissions. A set of permissions are needed to enable the Data policy enforcement. This applies to data sources, resource groups, or subscriptions. To enable Data policy enforcement, you must have both specific Identity and Access Management (IAM) privileges on the resource as well as specific Microsoft Purview privileges:
You must have either one of the following IAM role combinations on the resource's Azure Resource Manager path or any parent of it (that is, using IAM permission inheritance):
- IAM Owner
- Both IAM Contributor and IAM User Access Administrator
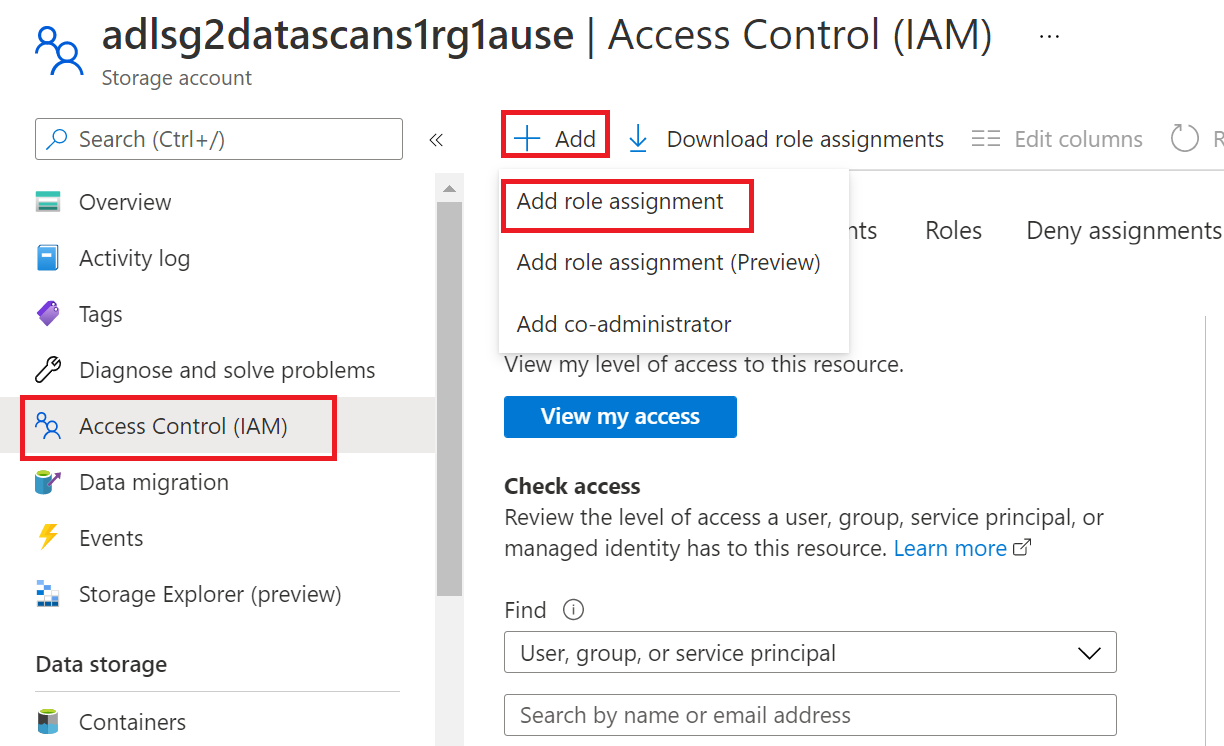
To configure Azure role-based access control (RBAC) permissions, follow this guide. The following screenshot shows how to access the Access Control section in the Azure portal for the data resource to add a role assignment.
Note
The IAM Owner role for a data resource can be inherited from a parent resource group, a subscription, or a subscription management group. Check which Microsoft Entra users, groups, and service principals hold or are inheriting the IAM Owner role for the resource.
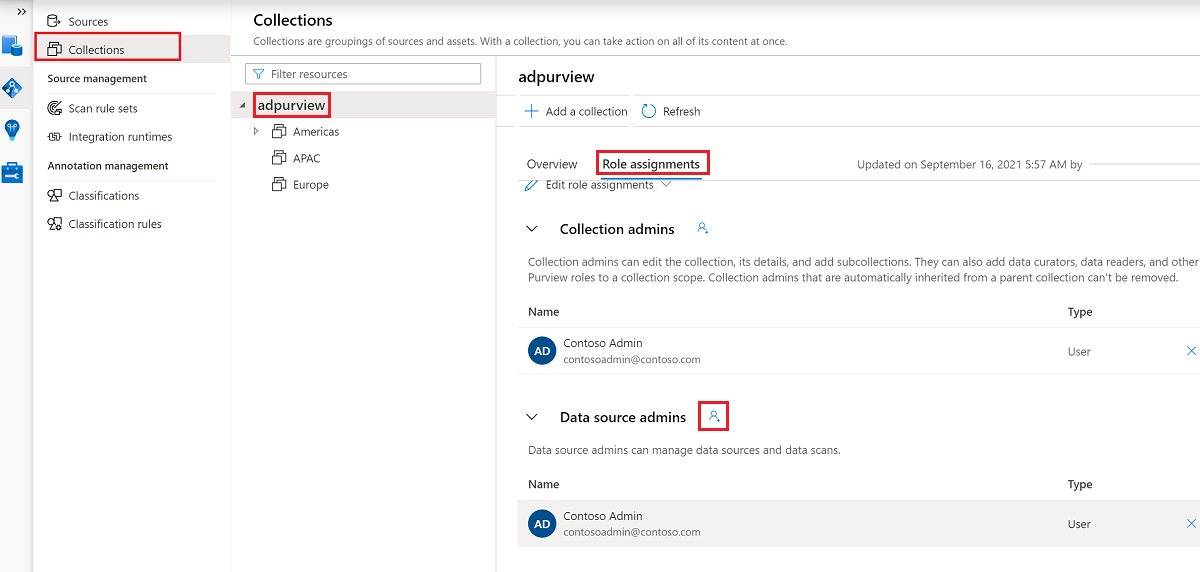
You also need to have the Microsoft Purview Data source admin role for the collection or a parent collection (if inheritance is enabled). For more information, see the guide on managing Microsoft Purview role assignments.
The following screenshot shows how to assign the Data source admin role at the root collection level.
Configure Microsoft Purview permissions to create, update, or delete access policies
To create, update or delete policies, you need to get the Policy author role in Microsoft Purview at root collection level:
- The Policy author role can create, update, and delete DevOps and Data Owner policies.
- The Policy author role can delete self-service access policies.
For more information about managing Microsoft Purview role assignments, see Create and manage collections in the Microsoft Purview Data Map.
Note
Policy author role must be configured at the root collection level.
In addition, to easily search Microsoft Entra users or groups when creating or updating the subject of a policy, you can greatly benefit from getting the Directory Readers permission in Microsoft Entra ID. This is a common permission for users in an Azure tenant. Without the Directory Reader permission, the Policy Author will have to type the complete username or email for all the principals included in the subject of a data policy.
Configure Microsoft Purview permissions for publishing Data Owner policies
Data Owner policies allow for checks and balances if you assign the Microsoft Purview Policy author and Data source admin roles to different people in the organization. Before a Data owner policy takes effect, a second person (Data source admin) must review it and explicitly approve it by publishing it. This does not apply to DevOps or Self-service access policies as publishing is automatic for them when those policies are created or updated.
To publish a Data owner policy you need to get the Data source admin role in Microsoft Purview at root collection level.
For more information about managing Microsoft Purview role assignments, see Create and manage collections in the Microsoft Purview Data Map.
Note
To publish Data owner policies, the Data source admin role must be configured at the root collection level.
Delegate access provisioning responsibility to roles in Microsoft Purview
After a resource has been enabled for Data policy enforcement, any Microsoft Purview user with the Policy author role at the root collection level can provision access to that data source from Microsoft Purview.
Note
Any Microsoft Purview root Collection admin can assign new users to root Policy author roles. Any Collection admin can assign new users to a Data source admin role under the collection. Minimize and carefully vet the users who hold Microsoft Purview Collection admin, Data source admin, or Policy author roles.
If a Microsoft Purview account with published policies is deleted, such policies will stop being enforced within an amount of time that depends on the specific data source. This change can have implications on both security and data access availability. The Contributor and Owner roles in IAM can delete Microsoft Purview accounts. You can check these permissions by going to the Access control (IAM) section for your Microsoft Purview account and selecting Role Assignments. You can also use a lock to prevent the Microsoft Purview account from being deleted through Resource Manager locks.
Register the data sources in Microsoft Purview for Data Policy Enforcement
The Azure Storage resources need to be registered first with Microsoft Purview to later define access policies.
To register your resources, follow the Prerequisites and Register sections of these guides:
After you've registered your resources, you'll need to enable Data Policy Enforcement. Data Policy Enforcement needs certain permissions and can affect the security of your data, as it delegates to certain Microsoft Purview roles to manage access to the data sources. Go through the secure practices related to Data Policy Enforcement in this guide: How to enable Data Policy Enforcement
Once your data source has the Data Policy Enforcement toggle Enabled, it will look like this screenshot:

Create and publish a data owner policy
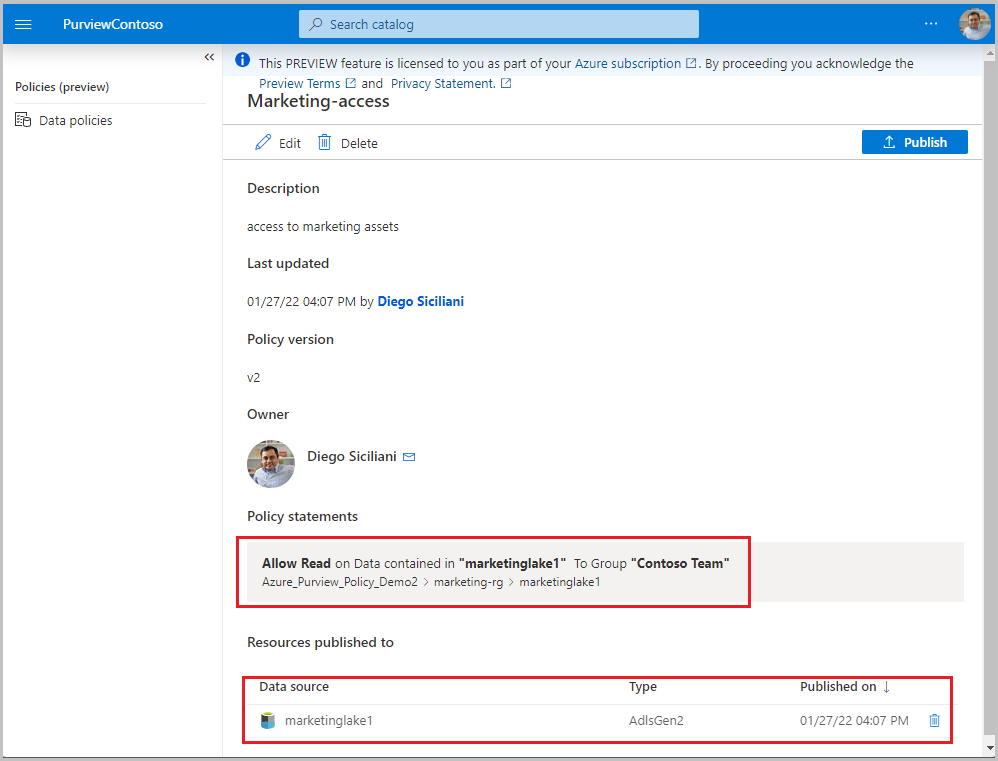
Execute the steps in the Create a new policy and Publish a policy sections of the data-owner policy authoring tutorial. The result will be a data owner policy similar to the example shown in the image: a policy that provides group Contoso Team read access to Storage account marketinglake1:
Important
- Publish is a background operation. Azure Storage accounts can take up to 2 hours to reflect the changes.
Unpublish a data owner policy
Follow this link for the steps to unpublish a data owner policy in Microsoft Purview.
Update or delete a data owner policy
Follow this link for the steps to update or delete a data owner policy in Microsoft Purview.
Data Consumption
- Data consumer can access the requested dataset using tools such as Power BI or Azure Synapse Analytics workspace.
- The Copy and Clone commands in Azure Storage Explorer require other IAM permissions to work in addition to the Allow Modify policy from Purview. Provide Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/blobServices/generateUserDelegationKey/action permission in IAM to the Microsoft Entra principal.
- Subcontainer access: Policy statements set below container level on a Storage account are supported. However, users won't be able to browse to the data asset using Azure portal's Storage Browser or Microsoft Azure Storage Explorer tool if access is granted only at file or folder level of the Azure Storage account. This is because these apps attempt to crawl down the hierarchy starting at container level, and the request fails because no access has been granted at that level. Instead, the App that requests the data must execute a direct access by providing a fully qualified name to the data object. The following documents show examples of how to perform a direct access. See also the blogs in the Next steps section of this how-to-guide.
Additional information
- Creating a policy at Storage account level enables the Subjects to access system containers, for example $logs. If this is undesired, first scan the data sources and then create finer-grained policies for each (that is, at container or subcontainer level).
- The root blob in a container will be accessible to the Microsoft Entra principals in a Microsoft Purview allow-type RBAC policy if the scope of such policy is either subscription, resource group, Storage account or container in Storage account.
- The root container in a Storage account will be accessible to the Microsoft Entra principals in a Microsoft Purview allow-type RBAC policy if the scope of such policy is either subscription, resource group, or Storage account.
Limits
- The limit for Microsoft Purview policies that can be enforced by Storage accounts is 100 MB per subscription, which roughly equates to 5,000 policies.
Known issues
Known issues related to Policy creation
- Don't create policy statements based on Microsoft Purview resource sets. Even if displayed in Microsoft Purview policy authoring UI, they aren't yet enforced. Learn more about resource sets.
Policy action mapping
This section contains a reference of how actions in Microsoft Purview data policies map to specific actions in Azure Storage.
| Microsoft Purview policy action | Data source specific actions |
|---|---|
| Read | Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/blobServices/containers/read |
| Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/blobServices/containers/blobs/read | |
| Modify | Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/blobServices/containers/blobs/read |
| Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/blobServices/containers/blobs/write | |
| Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/blobServices/containers/blobs/add/action | |
| Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/blobServices/containers/blobs/move/action | |
| Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/blobServices/containers/blobs/delete | |
| Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/blobServices/containers/read | |
| Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/blobServices/containers/write | |
| Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/blobServices/containers/delete | |
Next steps
Check blog, demo, and related tutorials:
- Demo of access policy for Azure Storage
- Doc: Concepts for Microsoft Purview data owner policies
- Doc: Provision access to all data sources in a subscription or a resource group
- Blog: What's New in Microsoft Purview at Microsoft Ignite 2021
- Blog: Accessing data when folder level permission is granted
- Blog: Accessing data when file level permission is granted
- Blog: Grant users access to data assets in your enterprise via API
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for