Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Many Azure regions provide availability zones, which are separated groups of datacenters within a region. Each availability zone has independent power, cooling, and networking infrastructure, so that if one zone experiences an outage, then regional services, capacity, and high availability are supported by the remaining zones.
Availability zones are typically separated by several kilometers, and usually are within 100 kilometers. This distance means they're close enough to have low-latency connections to other availability zones through a high-performance network. However, they're far enough apart to reduce the likelihood that more than one will be affected by local outages or weather.
Datacenter locations are selected by using rigorous vulnerability risk assessment criteria. This process identifies all significant datacenter-specific risks and considers shared risks between availability zones.
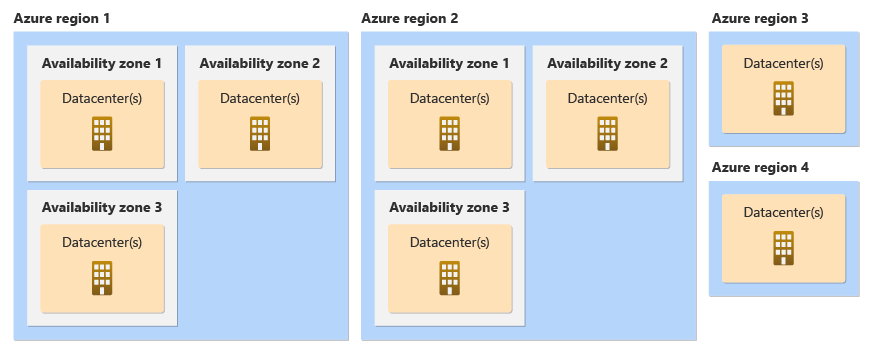
The following diagram shows several example Azure regions. Regions 1 and 2 support availability zones, and regions 3 and 4 don't have availability zones.
Tip
To see which regions support availability zones, see List of Azure regions.
What is the difference between a datacenter and an availability zone?
An availability zone is a logical grouping of one or more physically separate datacenters within a region. Each availability zone is built in a way that if something goes wrong in one (like a power outage or network issue), the others keep working. A single datacenter doesn’t offer this level of protection on its own.
Types of availability zone support
Azure services can provide two types of availability zone support: zone-redundant and zonal. Each service might support one or both types. When designing your reliability strategy, make sure that you understand how each service in your workload supports availability zones.
Zone-redundant deployments: Zone-redundant resources are replicated or distributed across multiple availability zones automatically. For example, zone-redundant data services replicate the data across multiple zones so that a failure in one zone doesn't affect the availability of the data. For some services you can select the set of zones that your resource uses, while in other services Microsoft selects the zones.
With zone-redundant deployments, Microsoft manages spreading requests across zones and the replication of data across zones. If an outage occurs in an availability zone, Microsoft manages failover to another zone automatically.
Zonal deployments: A zonal resource is deployed to a single, self-selected availability zone. This approach doesn't provide a resiliency benefit, but it helps you to achieve more stringent latency or performance requirements. For example, virtual machines, managed disks, and standard IP addresses can be deployed zonally to the same zone.
To improve the resiliency of zonal resources, you need to design an architecture with separate resources in multiple availability zones within the region, but Microsoft doesn't manage the process for you. If an outage occurs in an availability zone, you're responsible for failover to another zone.
When you use configure a resource to be zone redundant, or if you use multiple instances of a zonal resource in different availabilty zones, then your resource is considered to be zone-resilient: that is, it's resilient to the outage of a single availability zone.
Some services don't use availability zones until you configure them to do so. If you don't explicitly configure a service for availability zone support, it's called a nonzonal or regional deployment. Resources configured in this way might be placed in any availability zone in the region, and might be moved. If any availability zone in the region experiences an outage, non-zonal resources might be in the affected zone and could experience downtime.
Important
Some services may have extra requirements to meet for availability zone support. For example, some may only support availability zones for certain tiers or SKUs, or in a subset of Azure regions.
Configuring resources for availability zone support
Each service has its own method for configuring availability zone support. To learn about how each service supports availability zones and how to configure that support, see Azure reliability guides by service.
Physical and logical availability zones
Each datacenter is assigned to a physical zone. Physical zones are mapped to logical zones in your Azure subscription, and different subscriptions might have a different mapping order. Azure subscriptions are automatically assigned their mapping at the time the subscription is created. Because of this, the zone mapping for one subscription could be different for other subscriptions.
For example, subscription A may have physical zone 1 mapped to logical zone 2, while subscription B has physical zone 1 mapped to logical zone 3:
To understand the mapping between logical and physical zones for your subscription, use the List Locations Azure Resource Manager API. You can use the Azure CLI or Azure PowerShell to retrieve the information from the API.
To compare zone mapping for resilient solutions that span multiple subscriptions, use the dedicated ARM API checkZonePeers. To use the checkZonePeers API, the feature "Microsoft.Resources/AvailabilityZonePeering" needs to be enabled. For more information about how to enable features, see Register features in Azure subscription.
az rest --method get \
--uri '/subscriptions/{subscriptionId}/locations?api-version=2022-12-01' \
--query 'value[?availabilityZoneMappings != `null`].{displayName: displayName, name: name, availabilityZoneMappings: availabilityZoneMappings}'
Availability zones and Azure updates
For each region, Microsoft aims to deploy updates to Azure services within a single availability zone at a time. This approach reduces the impact that updates might have on an active workload, allowing the workload to continue to run in other zones while the update is in process. To take advantage of sequenced zone updates, your workload must be already configured to run across multiple zones. For more information about how Azure deploys updates, see Advancing safe deployment practices.
Note
As reported on Azure Updates Blog Azure will not charge for the data transfer across availability zones regardless of using private or public IPs on your Azure resources. With this change, Azure will further encourage and support customers’ efforts in building more resilient and efficient applications and solutions on Azure
Inter-zone latency
Within each region, availability zones are connected through a high-performance network. Microsoft strives to achieve an inter-zone communication with round-trip latency of less than approximately 2 milliseconds. Low latency allows for high-performance communication within a region, and for synchronous replication of data across multiple availability zones.
Note
The target latency refers to the latency of the network links. Depending on the communication protocol you use and the network hops required for any specific network flow, the latency you observe might be different.
In most workloads, you can distribute components of your solution across availability zones without a noticeable effect on your performance. If you have a workload with a high degree of sensitivity to inter-zone latency, it's important to test the latency between your selected availability zones with your actual protocols and configuration. To reduce inter-zone traffic, it's possible to use zonal deployments, but optimally, you should use multiple availability zones in your reliability strategy plan.
Availability zone architectural guidance
To achieve reliable workloads:
- Production workloads should be configured to use multiple availability zones if the region they are in supports availability zones.
- For mission-critical workloads, you should consider a solution that is both multi-region and multi-zone.
For more detailed information on how to use regions and availability zones in a solution architecture, see Recommendations for using availability zones and regions.