Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Azure Route Server is a fully managed Azure service that simplifies dynamic routing between network virtual appliances (NVAs) and Azure virtual networks. It enables automatic route exchange through Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) between NVAs and the Azure Software Defined Network (SDN), eliminating the need for manual route table configuration and maintenance.
With Azure Route Server, you can deploy sophisticated network topologies that automatically adapt to changes, support multiple NVAs for high availability, and maintain centralized routing control—all backed by Azure's managed infrastructure.
Important
Route servers created before November 1, 2021, without an associated public IP address, were deployed with the public preview offering. The public preview offering doesn't include General Availability SLA and support. To deploy a route server with the General Availability offering and qualify for the General Availability SLA and support, delete and recreate your route server.
Key capabilities
Azure Route Server provides essential capabilities for modern cloud networking:
- Dynamic route exchange: Automatically exchange routes between NVAs and Azure virtual networks using BGP
- Simplified management: Eliminate manual route table configuration and maintenance
- High availability: Built-in redundancy and fault tolerance through Azure's managed infrastructure
- Standard protocol support: Works with any NVA that supports BGP routing
- Flexible deployment: Deploy in new or existing virtual networks without infrastructure changes
How Azure Route Server works
Azure Route Server acts as a BGP route reflector within your virtual network, automatically managing route distribution between NVAs and Azure's routing infrastructure.
In the following diagram, Route Server receives:
- An on-premises route (10.250.0.0/16) from the SD-WAN appliance
- A default route (0.0.0.0/0) from the security appliance
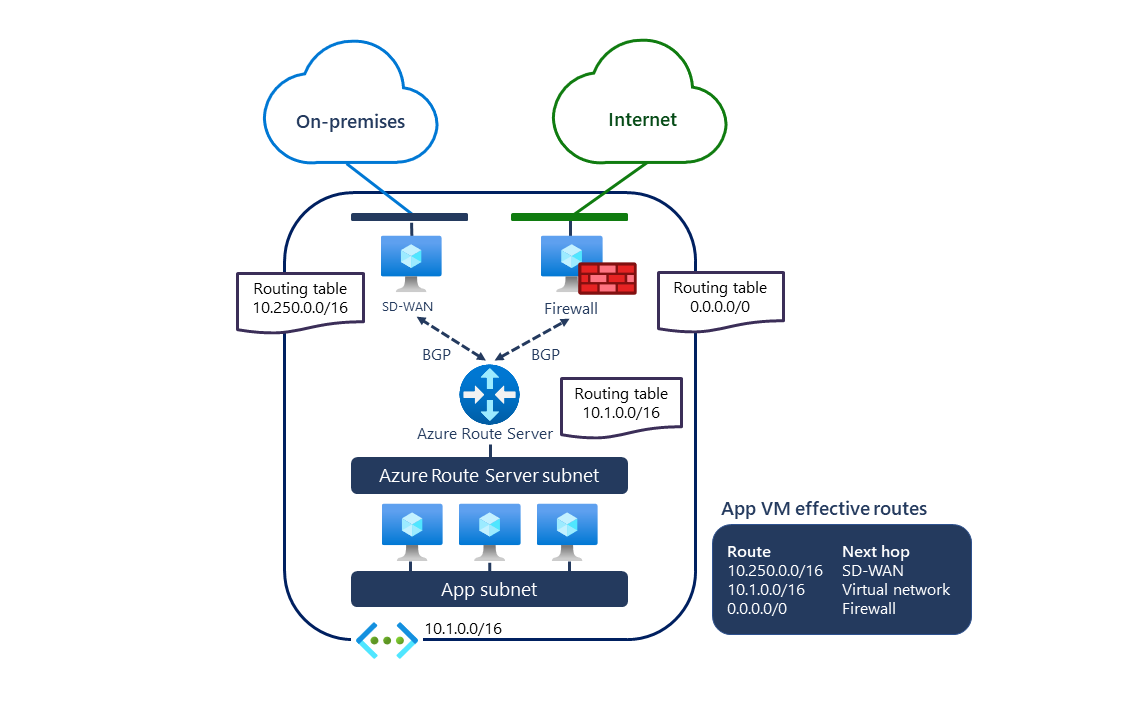
These routes are automatically configured on all virtual machines in the network. Traffic destined for on-premises networks flows through the SD-WAN appliance, while internet-bound traffic routes through the security appliance. The SD-WAN appliance can propagate the virtual network address (10.1.0.0/16) to on-premises networks.
Route exchange process
- BGP peering establishment: Route Server establishes BGP sessions with NVAs in your virtual network
- Route learning: NVAs advertise their routes to Route Server (for example, on-premises prefixes from SD-WAN appliances)
- Route propagation: Route Server automatically programs learned routes into Azure's SDN
- Traffic direction: Virtual machines automatically use the programmed routes to reach advertised destinations
- Bidirectional routing: Route Server also advertises virtual network prefixes back to NVAs
Benefits of Azure Route Server
Azure Route Server eliminates common networking complexities and provides significant operational benefits:
Automated route management - No need to manually update routing tables when virtual network addresses change or when NVAs announce new routes
Simplified NVA deployment - Deploy network virtual appliances without complex routing configuration or ongoing maintenance overhead
Multiple NVA support - Connect multiple NVA instances with configurable BGP attributes for active-active performance or active-passive resilience scenarios
Standards-based integration - Works with any BGP-capable network virtual appliance using industry-standard protocols
Flexible deployment options - Deploy in new virtual networks or integrate seamlessly into existing network infrastructure
Reduced operational overhead - Eliminate manual user-defined route updates and streamline network change management
Common use cases
Azure Route Server enables several important networking scenarios:
Hub-and-spoke architectures - Deploy Route Server in hub virtual networks to manage routing for multiple spokes with centralized routing control and simplified connectivity between spokes through hub-based NVAs.
Hybrid connectivity - Connect Azure virtual networks to on-premises networks through SD-WAN appliances, combine multiple connection types like ExpressRoute and VPN with intelligent path selection, and implement automatic failover between connectivity paths.
Network security - Route traffic through security appliances like firewalls and intrusion detection systems, implement granular security policies with centralized enforcement, and meet regulatory requirements for traffic inspection and logging.
Service limits and considerations
Understanding Azure Route Server limits helps you plan your network architecture:
| Resource | Limit |
|---|---|
| Number of BGP peers | 8 |
| Number of routes each BGP peer can advertise to Azure Route Server 1 | 4,000 |
| Number of VMs in the virtual network (including peered virtual networks) that Azure Route Server can support | 50,000 |
| Number of virtual networks that Azure Route Server can support | 500 |
| Number of total on-premises and Azure Virtual Network prefixes that Azure Route Server can support | 10,000 |
1 If your NVA advertises more routes than the limit, the BGP session gets dropped.
Note
The total number of routes advertised from virtual network address space and Route Server towards ExpressRoute circuit, when Branch-to-branch enabled, must not exceed 1,000. For more information, see Route advertisement limits of ExpressRoute.
Integration with Azure services
Azure Route Server works seamlessly with other Azure networking components:
- ExpressRoute gateways: Exchange routes between ExpressRoute circuits and NVAs for enhanced hybrid connectivity
- VPN gateways: Integrate site-to-site VPN connections with dynamic routing capabilities
- Virtual network peering: Support hub-and-spoke topologies with automatic route propagation to spoke networks
- Load balancers: Use with internal load balancers through next hop IP support for NVA high availability
For detailed integration scenarios, see Azure Route Server support for ExpressRoute and VPN.
Pricing
Azure Route Server uses a simple hourly pricing model:
- Deployment-based pricing: Pay for the time Route Server is deployed, regardless of traffic volume
- No data transfer costs: Route Server doesn't charge for routes processed or BGP sessions maintained
- Cost optimization: Consider regional deployment patterns for cost efficiency
For current pricing details, see Azure Route Server pricing.
Service Level Agreement (SLA)
For complete SLA details, see Service Level Agreements (SLA) for Online Services.
Frequently asked questions (FAQ)
For answers to frequently asked questions about Azure Route Server, see Azure Route Server FAQ.
Next steps
Get started with Azure Route Server and explore advanced scenarios:
- Quickstart: Create an Azure Route Server using the Azure portal
- Tutorial: Configure BGP peering between Azure Route Server and network virtual appliance (NVA)
- Multi-region networking with Azure Route Server
- Training module: Introduction to Azure Route Server
- Azure Architecture Center: Update route tables by using Azure Route Server