Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Monitoring the performance and availability of SAP systems on Azure is simplified through Azure Monitor for SAP. It collects and analyzes metrics and logs from your applications, databases, operating systems, and Azure resources. Customers use Azure Monitor for SAP to visualize and troubleshoot issues, set alerts and notifications, and optimize SAP workloads on Azure.
By integrating Azure Monitor for SAP and SAP Deployment Automation Framework, you can achieve a faster, easier, and more reliable deployment and operation of your SAP systems on Azure. You can use the automation framework to provision and configure the SAP systems, and Azure Monitor for SAP to monitor and optimize the performance and availability of those SAP systems.
This integration with SAP on Azure Deployment Automation Framework enables you to reduce the complexity and deployment cost of running your SAP environments on Azure, by helping to automate the monitoring of different components of an SAP landscape.
Overview
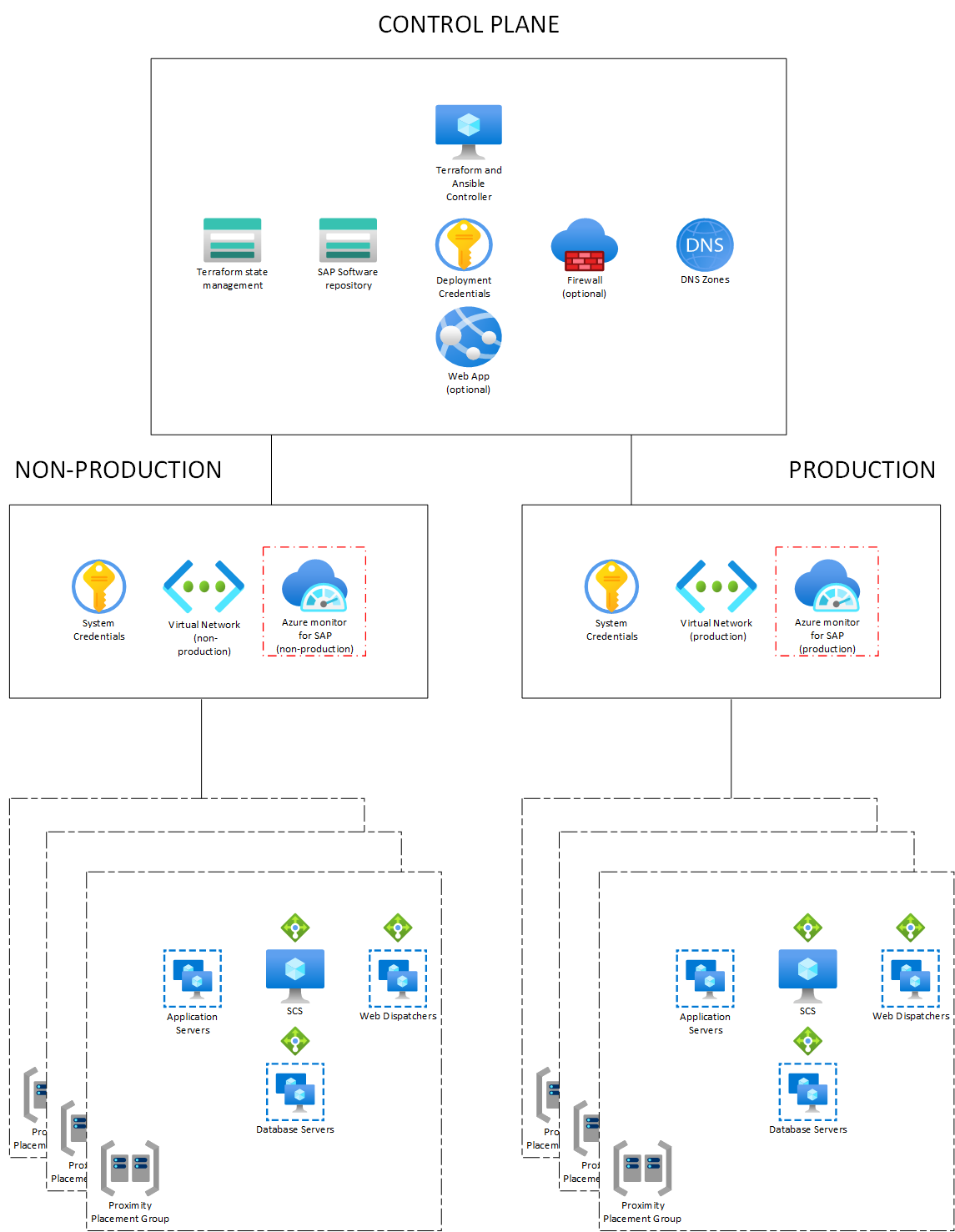
As described in the overview document, the automation framework has two main components:
- Deployment infrastructure (control plane, typically deployed in the hub)
- SAP infrastructure (SAP workload zone, typically deployed in a spoke)
Deployment of Azure Monitor for SAP (AMS) and the providers can be automated from the SAP Deployment Automation Framework (SDAF) to simplify the monitoring process. In this architecture, one Azure Monitor for SAP resource is deployed in each workload zone, which represents the environment. This resource is responsible for monitoring the performance and availability of different components of the SAP systems in that environment.
To monitor different components of each SAP system, there are corresponding providers and all these providers are deployed in the Azure Monitor for SAP resource of that environment. This setup allows for efficient monitoring and management of the SAP systems, as all the providers for a particular system are located in the same Azure Monitor for SAP resource. The automation framework automates the following steps:
- Creates Azure Monitor for SAP resource in workload zone.
- Performs prerequisites steps required to enable monitoring.
- Creates providers for each component of SAP landscape in Azure Monitor for SAP resource created.
Note
This automation framework currently supports deployment automation of Azure monitor for SAP resource, OS (Linux) provider to monitor the Azure VMs, and HA Pacemaker cluster provider to monitor the high availability clusters in the SAP system.
The key components of the Azure monitor for SAP resource created in the workload zone resource group would include:
- Azure monitor for SAP resource
- Managed Resource group with in the Azure monitor for SAP that includes:
- Azure functions resource
- Azure Key Vault
- Log analytics workspace (optional)
- Storage account
Workload zone configuration for Azure Monitor for SAP resource
The example shows the parameters that are required for the deployment of Azure Monitor for SAP resource in the workload zone. Optionally, you can choose to use an existing log analytics workspace that exists in the same subscription as your workload zone.
#########################################################################################
# AMS Subnet variables #
#########################################################################################
# If defined these parameters control the subnet name and the subnet prefix
# ams_subnet_name is an optional parameter and should only be used if the default naming is not acceptable
# ams_subnet_name = ""
# ams_subnet_address_prefix is a mandatory parameter if the subnets are not defined in the workload or if existing subnets are not used
ams_subnet_address_prefix = "10.242.25.0/24"
# ams_subnet_arm_id is an optional parameter that if provided specifies Azure resource identifier for the existing subnet to use
#ams_subnet_arm_id = ""
# ams_subnet_nsg_name is an optional parameter and should only be used if the default naming is not acceptable for the network security group name
# ams_subnet_nsg_name = ""
# ams_subnet_nsg_arm_id is an optional parameter that if provided specifies Azure resource identifier for the existing network security group to use
# ams_subnet_nsg_arm_id = ""
#########################################################################################
# AMS instance variables #
#########################################################################################
# If defined these parameters control the ams instance (Azure monitor for SAP)
# create_ams_instance is an optional parameter, and should be set true is the AMS instance is to be created.
create_ams_instance = true
# ams_instance_name is an optional parameter and should only be used if the default naming is not acceptable
ams_instance_name = "AMS-RESOURCE"
# ams_laws_arm_id is a optional parameter to use an existing log analytics for the AMS instance
ams_laws_arm_id = "/subscriptions/0000000-000000-0000000-0000000000/resourcegroups/rg-name/providers/microsoft.operationalinsights/workspaces/workspacename"
System configuration for AMS providers
The following example shows the parameter that is required for the automation of provider prerequisites and provider creation in the Azure monitor for SAP.
# enable_os_monitoring is an optional parameter and should be set to true if you want to monitor the Azure VMs of your SAP system.
enable_os_monitoring = true
# enable_ha_monitoring is an optional parameter and should be set to true if you want to monitor the HA clusters of your SAP system.
enable_ha_monitoring = true