Make outbound connections through a shared private link
This article explains how to configure private, outbound calls from Azure AI Search to an Azure PaaS resource that runs within an Azure virtual network.
Setting up a private connection allows a search service to connect to a virtual network IP address instead of a port that's open to the internet. The object created for the connection is called a shared private link. On the connection, the search service uses the shared private link internally to reach an Azure PaaS resource inside the network boundary.
Shared private link is a premium feature that's billed by usage. When you set up a shared private link, charges for the private endpoint are added to your Azure invoice. As you use the shared private link, data transfer rates for inbound and outbound access are also invoiced. For details, see Azure Private Link pricing.
Note
If you're setting up a private indexer connection to a SQL Managed Instance, see this article instead for steps specific to that resource type.
When to use a shared private link
Azure AI Search makes outbound calls to other Azure PaaS resources in the following scenarios:
- Indexer or search engine connections to Azure OpenAI for text-to-vector embeddings
- Indexer connections to supported data sources
- Indexer (skillset) connections to Azure Storage for caching enrichments, debug session sate, or writing to a knowledge store
- Encryption key requests to Azure Key Vault
- Custom skill requests to Azure Functions or similar resource
Shared private links only work for Azure-to-Azure connections. If you're connecting to OpenAI or another external model, the connection must be over the public internet.
Shared private links are for operations and data accessed through a private endpoint for Azure resources or clients that run in an Azure virtual network.
A shared private link is:
- Created using Azure AI Search tooling, APIs, or SDKs
- Approved by the Azure PaaS resource owner
- Used internally by Azure AI Search on a private connection to a specific Azure resource
Only your search service can use the private links that it creates, and there can be only one shared private link created on your service for each resource and subresource combination.
Once you set up the private link, it's used automatically whenever the search service connects to that PaaS resource. You don't need to modify the connection string or alter the client you're using to issue the requests, although the device used for the connection must connect using an authorized IP in the Azure PaaS resource's firewall.
There are two scenarios for using Azure Private Link and Azure AI Search together.
Scenario one: create a shared private link when an outbound (indexer) connection to Azure PaaS requires a private connection.
Scenario two: configure search for a private inbound connection from clients that run in a virtual network.
Scenario one is covered in this article.
While both scenarios have a dependency on Azure Private Link, they're independent. You can create a shared private link without having to configure your own search service for a private endpoint.
Limitations
When evaluating shared private links for your scenario, remember these constraints.
Several of the resource types used in a shared private link are in preview. If you're connecting to a preview resource (Azure Database for MySQL, Azure Functions, or Azure SQL Managed Instance), use a preview version of the Management REST API to create the shared private link. These versions include
2020-08-01-preview,2021-04-01-preview,2024-03-01-preview, and2024-06-01-preview. We recommend the latest preview API.Indexer execution must use the private execution environment that's specific to your search service. Private endpoint connections aren't supported from the multitenant environment. The configuration setting for this requirement is covered in this article.
Prerequisites
An Azure AI Search at the Basic tier or higher. If you're using AI enrichment and skillsets, the tier must be Standard 2 (S2) or higher. See Service limits for details.
An Azure PaaS resource from the following list of supported resource types, configured to run in a virtual network.
Permissions on both Azure AI Search and the data source:
On the Azure PaaS resource, you must have the permission to approve private endpoint connections. For instance, if you're using an Azure Storage account as your data source (such as Blob container, Azure Files share, Azure table), you need
Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/privateEndpointConnectionsApproval/action.On the search service, you must have read and write permissions on shared private link resources and read operation statuses:
Microsoft.Search/searchServices/sharedPrivateLinkResources/writeMicrosoft.Search/searchServices/sharedPrivateLinkResources/readMicrosoft.Search/searchServices/sharedPrivateLinkResources/operationStatuses/read
Supported resource types
You can create a shared private link for the following resources.
| Resource type | Subresource (or Group ID) |
|---|---|
| Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts 1 | blob, table, dfs, file |
| Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts 2 | Sql |
| Microsoft.Sql/servers 3 | sqlServer |
| Microsoft.KeyVault/vaults | vault |
| Microsoft.DBforMySQL/servers (preview) | mysqlServer |
| Microsoft.Web/sites (preview) 4 | sites |
| Microsoft.Sql/managedInstances (preview) 5 | managedInstance |
| Microsoft.CognitiveServices/accounts (preview) 6 | openai_account |
1 If Azure Storage and Azure AI Search are in the same region, the connection to storage is made over the Microsoft backbone network, which means a shared private link is redundant for this configuration. However, if you already set up a private endpoint for Azure Storage, you should also set up a shared private link or the connection is refused on the storage side. Also, if you're using multiple storage formats for various scenarios in search, make sure to create a separate shared private link for each subresource.
2 The Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts resource type is used for indexer connections to Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL. The provider name and group ID are case-sensitive.
3 The Microsoft.Sql/servers resource type is used for connections to Azure SQL database. There's currently no support for a shared private link to Azure Synapse SQL.
4 The Microsoft.Web/sites resource type is used for App service and Azure functions. In the context of Azure AI Search, an Azure function is the more likely scenario. An Azure function is commonly used for hosting the logic of a custom skill. Azure Function has Consumption, Premium, and Dedicated App Service hosting plans. The App Service Environment (ASE), Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) and Azure API Management aren't supported at this time.
5 See Create a shared private link for a SQL Managed Instance for instructions.
6 The Microsoft.CognitiveServices/accounts resource type is used for vectorizer and indexer connections to Azure OpenAI when implementing integrated Vectorization. There's currently no support for shared private link to embedding models in the Azure AI Studio model catalog or to the Azure AI Vision multimodal API.
1 - Create a shared private link
Use the Azure portal, Management REST API, the Azure CLI, or Azure PowerShell to create a shared private link.
Here are a few tips:
- Give the private link a meaningful name. In the Azure PaaS resource, a shared private link appears alongside other private endpoints. A name like "shared-private-link-for-search" can remind you how it's used.
When you complete the steps in this section, you have a shared private link that's provisioned in a pending state. It takes several minutes to create the link. Once it's created, the resource owner must approve the request before it's operational.
Sign in to the Azure portal and find your search service.
Under Settings on the left navigation pane, select Networking.
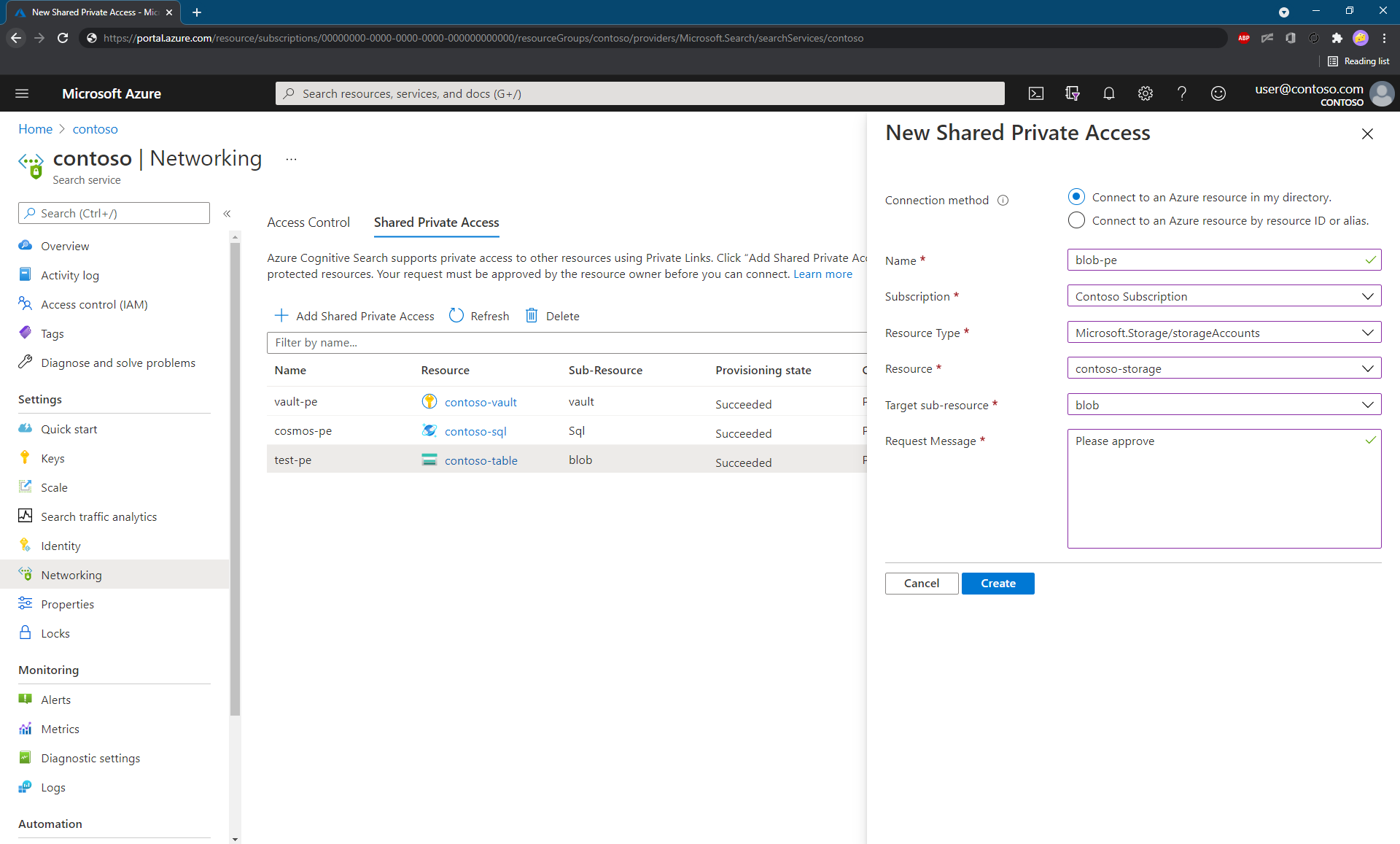
On the Shared Private Access page, select + Add Shared Private Access.
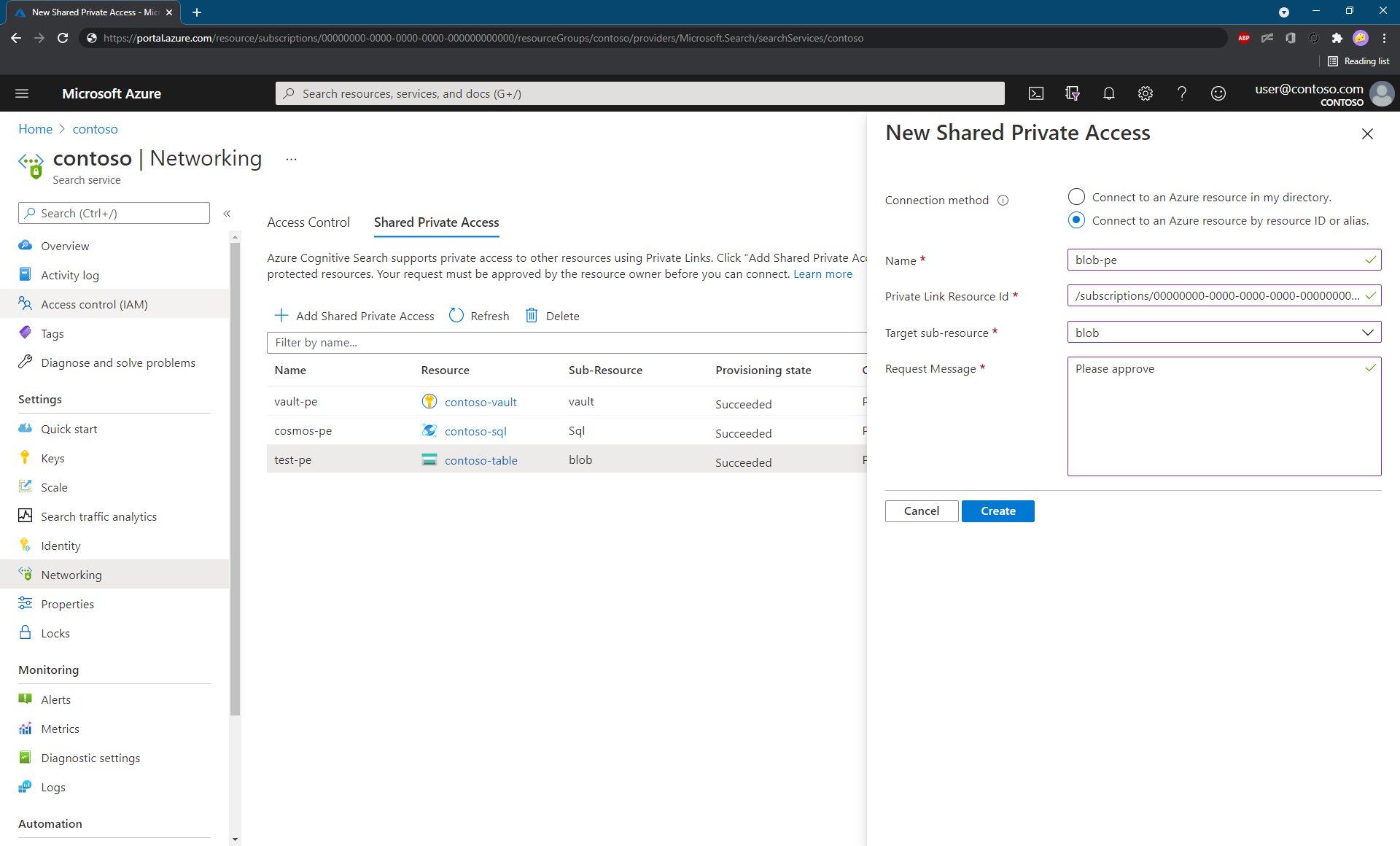
Select either Connect to an Azure resource in my directory or Connect to an Azure resource by resource ID.
If you select the first option (recommended), the portal helps you pick the appropriate Azure resource and fills in other properties, such as the group ID of the resource and the resource type.
If you select the second option, enter the Azure resource ID manually and choose the appropriate group ID from the list at the beginning of this article.
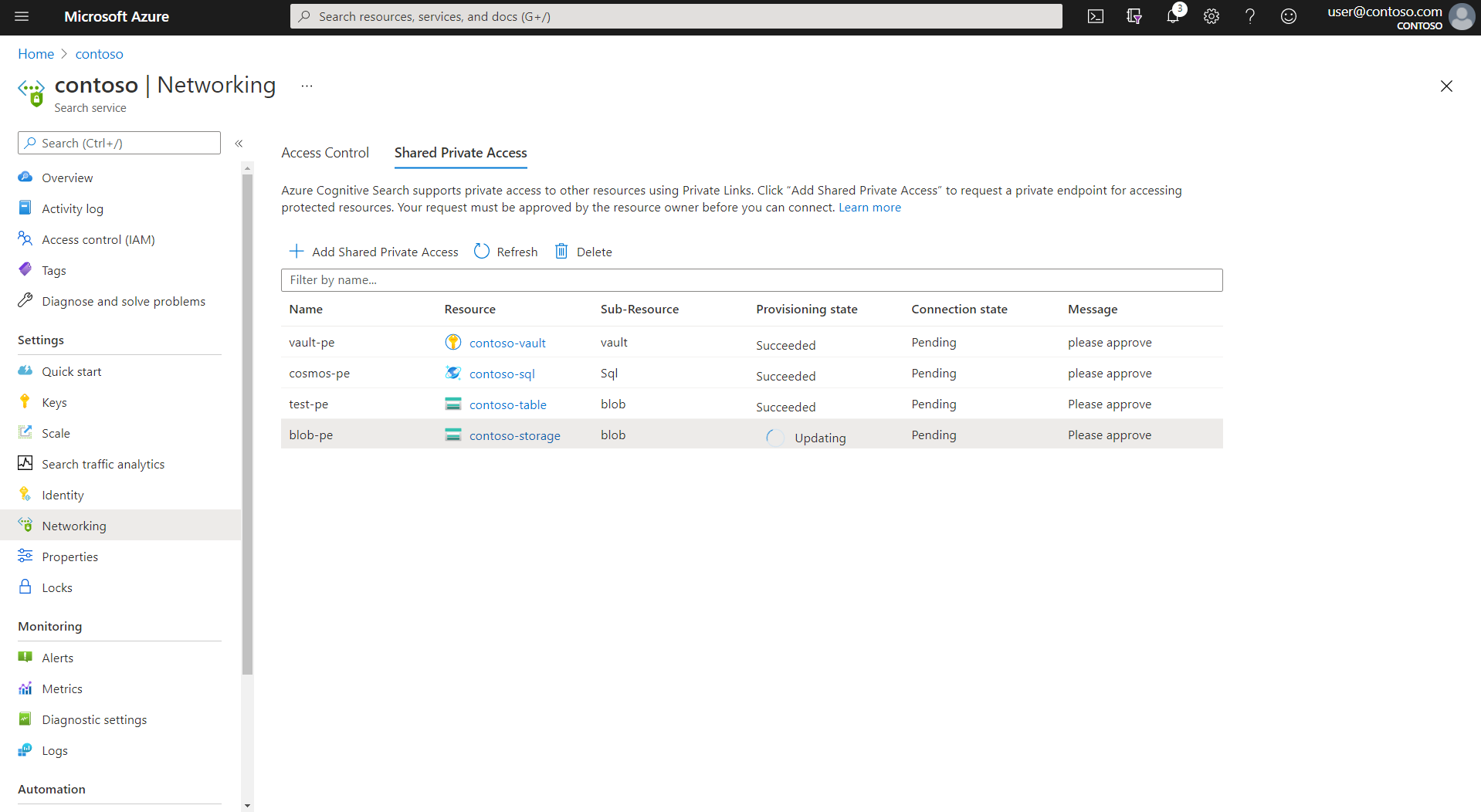
Confirm the provisioning status is "Updating".
Once the resource is successfully created, the provisioning state of the resource changes to "Succeeded".
Shared private link creation workflow
A 202 Accepted response is returned on success. The process of creating an outbound private endpoint is a long-running (asynchronous) operation. It involves deploying the following resources:
A private endpoint, allocated with a private IP address in a
"Pending"state. The private IP address is obtained from the address space that's allocated to the virtual network of the execution environment for the search service-specific private indexer. Upon approval of the private endpoint, any communication from Azure AI Search to the Azure resource originates from the private IP address and a secure private link channel.A private DNS zone for the type of resource, based on the group ID. By deploying this resource, you ensure that any DNS lookup to the private resource utilizes the IP address that's associated with the private endpoint.
2 - Approve the private endpoint connection
Approval of the private endpoint connection is granted on the Azure PaaS side. Explicit approval by the resource owner is required. The following steps cover approval using the Azure portal, but here are some links to approve the connection programmatically from the Azure PaaS side:
- On Azure Storage, use Private Endpoint Connections - Put
- On Azure Cosmos DB, use Private Endpoint Connections - Create Or Update
- On Azure OpenAI, use Private Endpoint Connections - Create Or Update
Using the Azure portal, perform the following steps:
Open the Networking page of the Azure PaaS resource.text
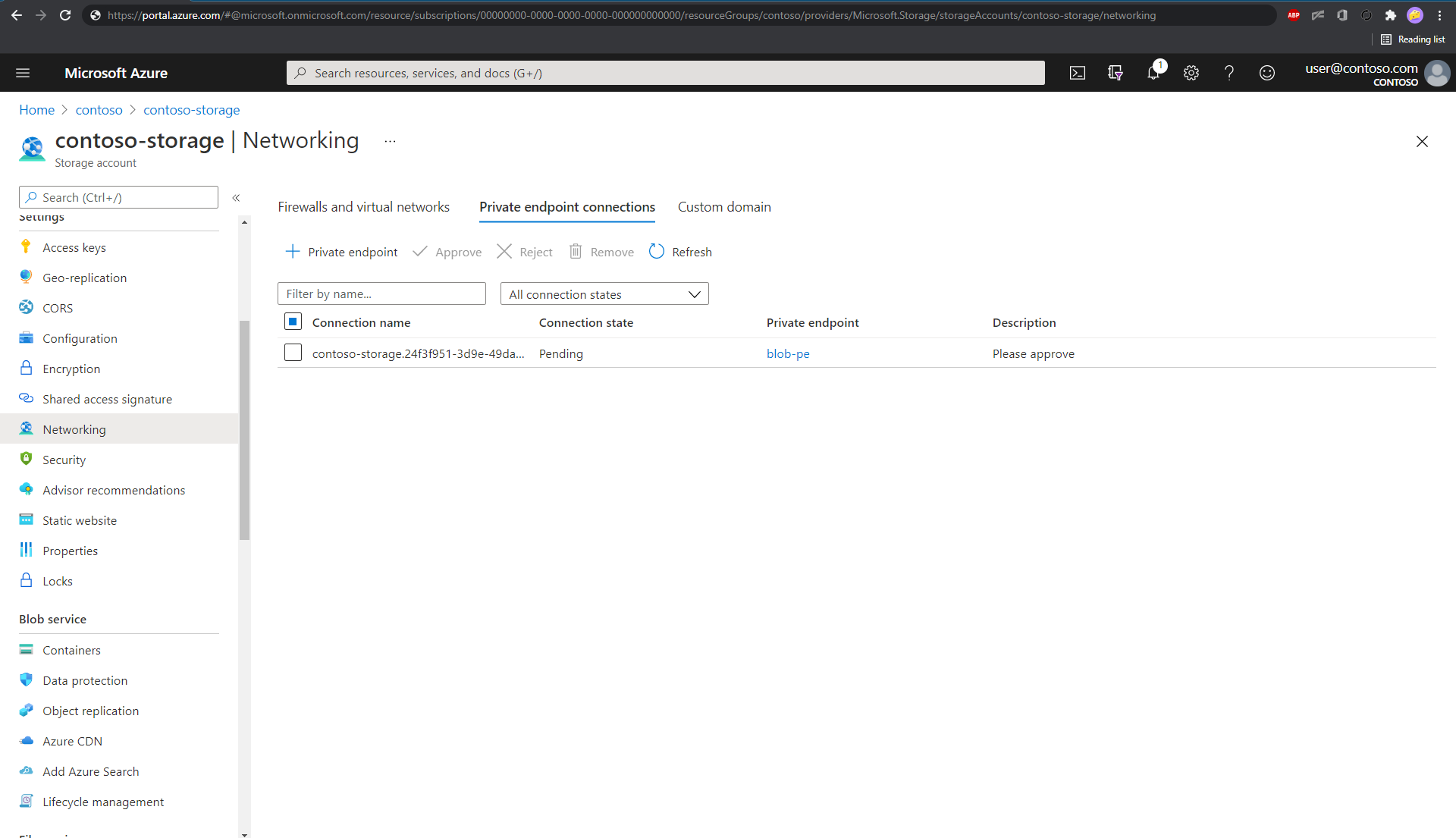
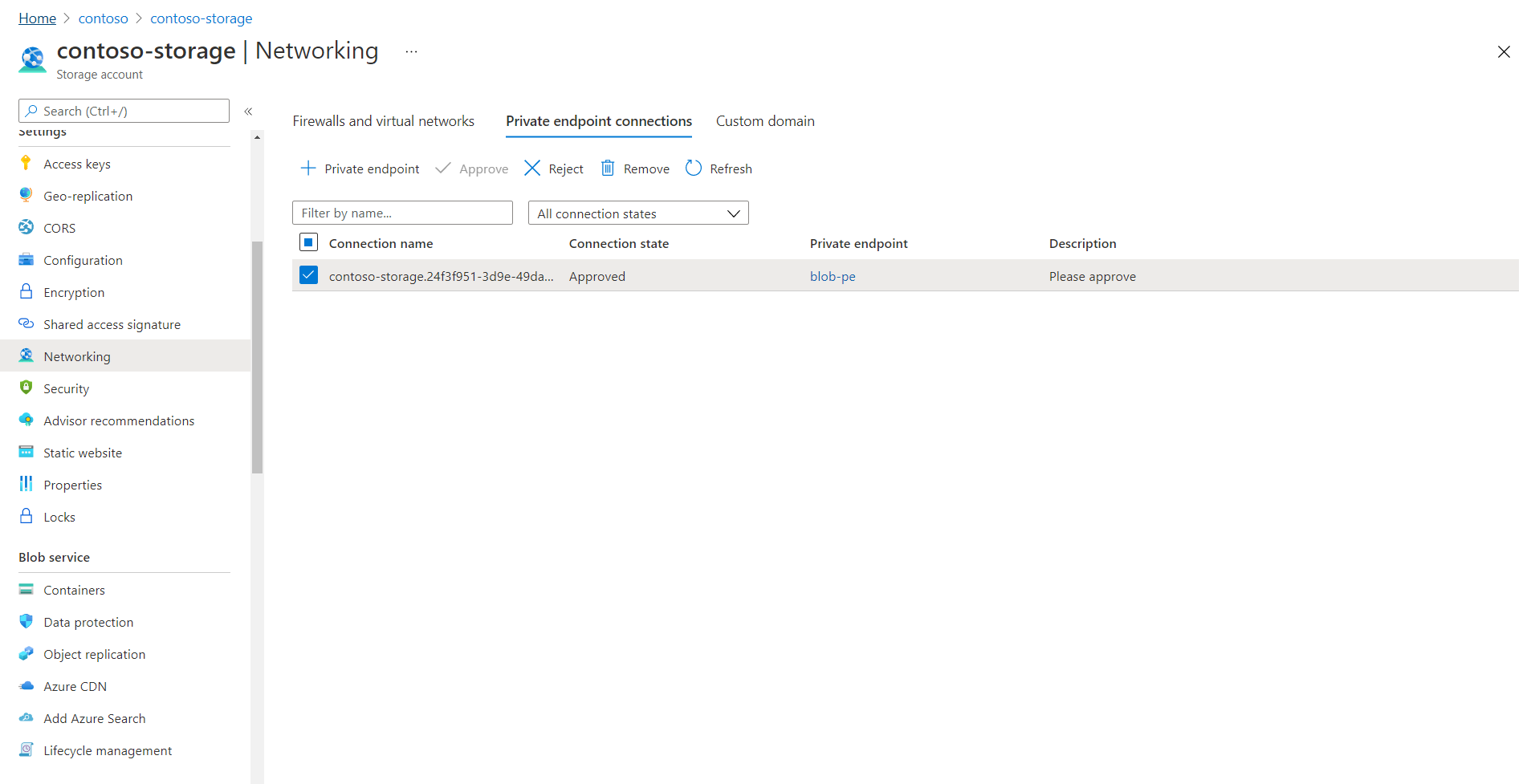
Find the section that lists the private endpoint connections. The following example is for a storage account.
Select the connection, and then select Approve. It can take a few minutes for the status to be updated in the portal.
After the private endpoint is approved, Azure AI Search creates the necessary DNS zone mappings in the DNS zone that's created for it.
Although the private endpoint link on the Networking page is active, it won't resolve.
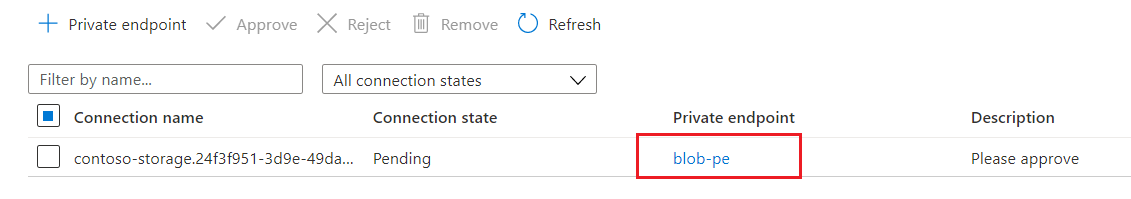
Selecting the link produces an error. A status message of "The access token is from the wrong issuer" and must match the tenant associated with this subscription appears because the backend private endpoint resource is provisioned by Microsoft in a Microsoft-managed tenant, while the linked resource (Azure AI Search) is in your tenant. It's by design you can't access the private endpoint resource by selecting the private endpoint connection link.
Follow the instructions in the next section to check the status of your shared private link.
3 - Check shared private link status
On the Azure AI Search side, you can confirm request approval by revisiting the Shared Private Access page of the search service Networking page. Connection state should be approved.
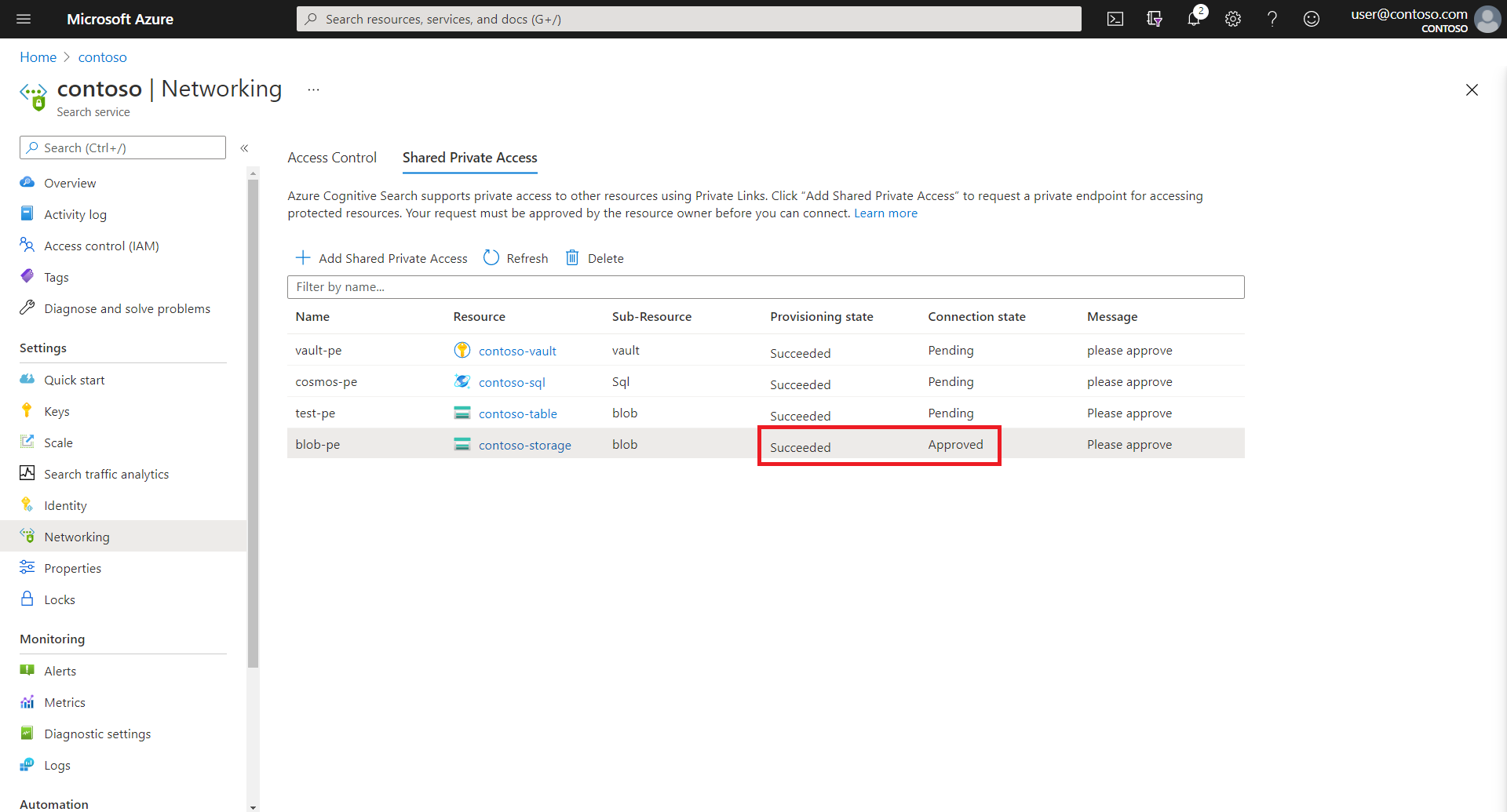
Alternatively, you can also obtain connection state by using the Shared Private Link Resources - Get.
az rest --method get --uri https://management.azure.com/subscriptions/00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000/resourceGroups/contoso/providers/Microsoft.Search/searchServices/contoso-search/sharedPrivateLinkResources/blob-pe?api-version=2023-11-01
This would return a JSON, where the connection state shows up as "status" under the "properties" section. Following is an example for a storage account.
{
"name": "blob-pe",
"properties": {
"privateLinkResourceId": "/subscriptions/00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000/resourceGroups/contoso/providers/Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/contoso-storage",
"groupId": "blob",
"requestMessage": "please approve",
"status": "Approved",
"resourceRegion": null,
"provisioningState": "Succeeded"
}
}
If the provisioning state (properties.provisioningState) of the resource is "Succeeded" and connection state(properties.status) is "Approved", it means that the shared private link resource is functional and the indexer can be configured to communicate over the private endpoint.
4 - Configure the indexer to run in the private environment
Indexer execution occurs in either a private environment that's specific to the search service, or a multitenant environment that's used internally to offload expensive skillset processing for multiple customers.
The execution environment is transparent, but once you start building firewall rules or establishing private connections, you must take indexer execution into account. For a private connection, configure indexer execution to always run in the private environment.
This step shows you how to configure the indexer to run in the private environment using the REST API. You can also set the execution environment using the JSON editor in the portal.
Note
You can perform this step before the private endpoint connection is approved. However, until the private endpoint connection shows as approved, any existing indexer that tries to communicate with a secure resource (such as the storage account) will end up in a transient failure state and new indexers will fail to be created.
Create the data source definition, index, and skillset (if you're using one) as you would normally. There are no properties in any of these definitions that vary when using a shared private endpoint.
Create an indexer that points to the data source, index, and skillset that you created in the preceding step. In addition, force the indexer to run in the private execution environment by setting the indexer
executionEnvironmentconfiguration property toprivate.{ "name": "indexer", "dataSourceName": "blob-datasource", "targetIndexName": "index", "parameters": { "configuration": { "executionEnvironment": "private" } }, "fieldMappings": [] }
After the indexer is created successfully, it should connect to the Azure resource over the private endpoint connection. You can monitor the status of the indexer by using the Indexer Status API.
Note
If you already have existing indexers, you can update them via the PUT API by setting the executionEnvironment to private or using the JSON editor in the portal.
5 - Test the shared private link
If you haven't done so already, verify that your Azure PaaS resource refuses connections from the public internet. If connections are accepted, review the DNS settings in the Networking page of your Azure PaaS resource.
Choose a tool that can invoke an outbound request scenario, such as an indexer connection to a private endpoint. An easy choice is using the Import data wizard, but you can also try a REST client and REST APIs for more precision. Assuming that your search service isn't also configured for a private connection, the REST client connection to search can be over the public internet.
Set the connection string to the private Azure PaaS resource. The format of the connection string doesn't change for shared private link. The search service invokes the shared private link internally.
For indexer workloads, the connection string is in the data source definition. An example of a data source might look like this:
{ "name": "my-blob-ds", "type": "azureblob", "subtype": null, "credentials": { "connectionString": "DefaultEndpointsProtocol=https;AccountName=<YOUR-STORAGE-ACCOUNT>;AccountKey=..." }For indexer workloads, remember to set the execution environment in the indexer definition. An example of an indexer definition might look like this:
"name": "indexer", "dataSourceName": "my-blob-ds", "targetIndexName": "my-index", "parameters": { "configuration": { "executionEnvironment": "private" } }, "fieldMappings": [] }Run the indexer. If the indexer execution succeeds and the search index is populated, the shared private link is working.
Troubleshooting
If your indexer creation fails with "Data source credentials are invalid," check the approval status of the shared private link before debugging the connection. If the status is
Approved, check theproperties.provisioningStateproperty. If it'sIncomplete, there might be a problem with underlying dependencies. In this case, reissue thePUTrequest to re-create the shared private link. You might also need to repeat the approval step.If indexers fail consistently or intermittently, check the
executionEnvironmentproperty on the indexer. The value should be set toprivate. If you didn't set this property, and indexer runs succeeded in the past, it's because the search service used a private environment of its own accord. A search service moves processing out of the standard environment if the system is under load.If you get an error when creating a shared private link, check service limits to verify that you're under the quota for your tier.
Next steps
Learn more about private endpoints and other secure connection methods:
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for