Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Running in a secure sandbox, SRE Agent allows you to execute Python code with access to common Python libraries to add custom logic to the agent.
This article shows you how to create, configure, and test Python tools in Azure SRE Agent.
Prerequisites
- Access to an Azure SRE Agent instance
- Familiarity with Python programming
Create a Python tool
In the Azure portal, go to your Azure SRE Agent.
Select Builder > Subagent builder from the left navigation.
Select Create > Tool.
Select Python tool.
In the Python tool creation dialog, configure the following fields:
Field Description Tool Name A unique identifier using alphanumeric characters and hyphens (maximum 64 characters). Description A description of what the tool does. Timeout (seconds) Execution timeout between 5 and 900 seconds. Default is 120. Python Code Your function code. Must contain a def mainfunction.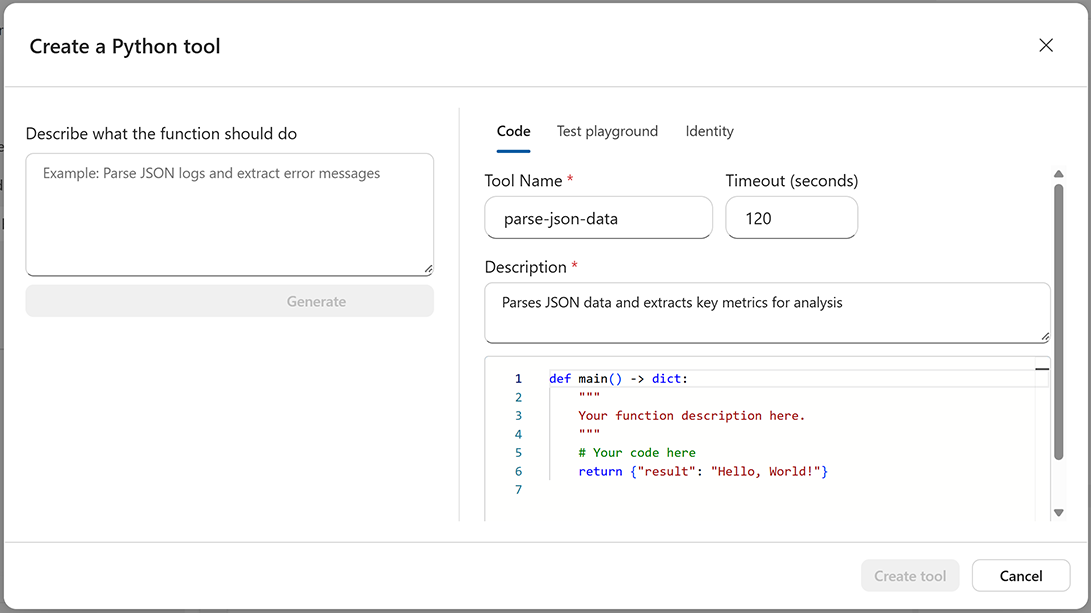
Select the Test playground tab to validate your code.
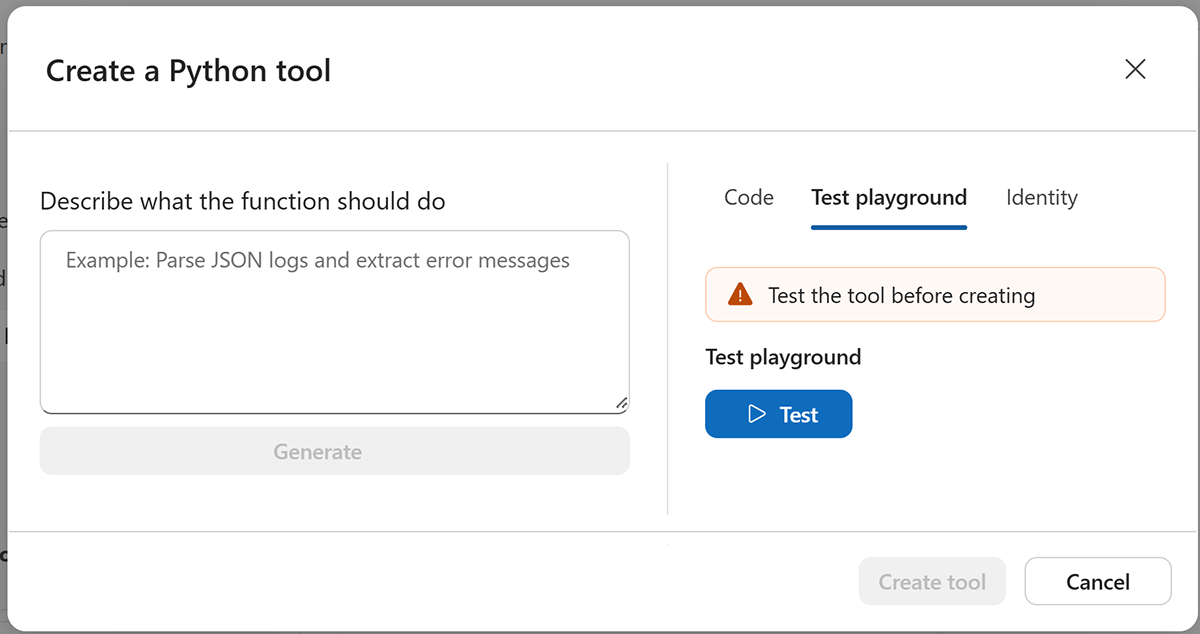
Enter test values for your parameters and select Test.
After testing succeeds, select Create tool.
Write the main function
Your code must contain a main function. The agent calls this function as the entry point.
def main(param1, param2="default"):
"""
Your tool's main function.
Args:
param1: Required parameter
param2: Optional parameter with default
Returns:
Result to return to the agent
"""
# Your logic here
return {"result": "success"}
Note
You can also name the function execute, but main is recommended.
Return values
The system automatically serializes return values to JSON. The following types are supported:
- Dictionaries → JSON objects
- Lists → JSON arrays
- Strings, numbers, booleans → primitives
None→ null
def main():
return {
"status": "complete",
"count": 42,
"items": ["a", "b", "c"],
"nested": {"key": "value"}
}
Handle errors
Raise exceptions to indicate errors. The agent receives the error message.
def main(resource_id):
if not resource_id:
raise ValueError("resource_id is required")
if not resource_id.startswith("/subscriptions/"):
raise ValueError(f"Invalid resource ID format: {resource_id}")
return {"valid": True}
Use AI-assisted code generation
You can use the AI assistant to generate Python code automatically.
In the Describe what the function should do text box, enter a natural language description.
Select Generate to create the initial code.
Review and modify the generated code as needed.
Example prompts:
- "Parse JSON logs and extract error messages"
- "Calculate average response time from metrics data"
- "Format Azure resource IDs into readable names"
Configure dependencies
Specify Python packages your tool requires in the Dependencies configuration.
The runtime includes common packages like json, re, datetime, collections, and itertools.
Common dependencies you might add:
| Package | Use case |
|---|---|
requests |
HTTP requests |
pandas |
Data analysis |
numpy |
Numerical computing |
Tip
Only include packages you actually use. Avoid packages with native dependencies when possible.
Set the timeout
Set appropriate timeouts based on your function's complexity.
| Scenario | Recommended timeout |
|---|---|
| Simple calculations | 5-30 seconds |
| API calls | 30-120 seconds |
| Data processing | 120-300 seconds |
| Large batch operations | 300-900 seconds |
Warning
If a function runs longer than the timeout, the system terminates the function and returns an error.
Configure tool mode
Control how the agent invokes your tool.
| Mode | Description |
|---|---|
| Auto | Agent automatically decides when to use the tool based on context. |
| Manual | User must explicitly request the tool. |
| Hidden | Tool is available but not shown in tool listings. |
Configure identity
For tools that need to access Azure resources, configure managed identity access in the Identity tab.
Select the Identity tab.
Configure the managed identity permissions.
Use the Azure SDK in your code to authenticate.
def main(resource_group):
"""List resources using managed identity."""
from azure.identity import DefaultAzureCredential
from azure.mgmt.resource import ResourceManagementClient
credential = DefaultAzureCredential()
# Use credential to access Azure resources
return {"authenticated": True}
Examples
Data transformation
def main(metrics_data):
"""Transform metrics into summary statistics."""
import json
data = json.loads(metrics_data) if isinstance(metrics_data, str) else metrics_data
values = [m.get("value", 0) for m in data]
return {
"count": len(values),
"sum": sum(values),
"avg": sum(values) / len(values) if values else 0,
"min": min(values) if values else 0,
"max": max(values) if values else 0,
}
HTTP request
def main(url, method="GET", headers=None):
"""Fetch data from an external URL."""
import requests
import json
request_headers = json.loads(headers) if headers else {}
response = requests.request(method, url, headers=request_headers, timeout=30)
response.raise_for_status()
return {
"status_code": response.status_code,
"content_type": response.headers.get("Content-Type"),
"data": response.json() if "application/json" in response.headers.get("Content-Type", "") else response.text
}
Text processing
def main(log_line):
"""Parse a log line into structured components."""
import re
pattern = r'\[(\d{4}-\d{2}-\d{2}T[\d:]+Z?)\]\s*(\w+):\s*(.*)'
match = re.match(pattern, log_line)
if not match:
return {"error": "Unable to parse log format", "raw": log_line}
timestamp, level, message = match.groups()
return {
"timestamp": timestamp,
"level": level.upper(),
"message": message.strip(),
"parsed": True
}
Azure resource parser
def main(resource_id, include_tags=True):
"""Parse Azure resource ID into components."""
parts = resource_id.split('/')
result = {
"subscription": parts[2] if len(parts) > 2 else None,
"resource_group": parts[4] if len(parts) > 4 else None,
"resource_type": parts[6] if len(parts) > 6 else None,
"resource_name": parts[8] if len(parts) > 8 else None,
}
if include_tags:
result["tags"] = {}
return result
Test your tool
Use the Test playground to validate your code before deploying.
Select the Test playground tab in the tool creation dialog.
Enter test values for each parameter.
Select Test to run your function.
Review the results and fix any errors.
Repeat until the test passes.
Debugging tips
- Start with minimal code and add complexity gradually.
- Use
print()statements for debugging. Output appears in test results. - Wrap risky code in try/except blocks.
- Validate inputs before processing.
- Test with empty inputs, invalid data, and boundary values.
Troubleshoot common errors
| Error | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
Function must contain a 'def main' function |
Missing main function | Add def main(...): to your code. |
Timeout must be between 5 and 900 |
Invalid timeout value | Set timeout within 5-900 seconds. |
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'xxx' |
Missing dependency | Add the package to dependencies. |
SyntaxError |
Invalid Python syntax | Check for typos, missing colons, or indentation errors. |
Security considerations
Keep the following security considerations in mind:
- Python code runs in a sandboxed environment.
- Network access is available for external API calls.
- File system access is restricted.
- Don't hardcode sensitive data. Use secure parameters instead.
- Review third-party packages before adding them as dependencies.