Store business-critical blob data with immutable storage in a write once, read many (WORM) state
Immutable storage for Azure Blob Storage enables users to store business-critical data in a WORM (Write Once, Read Many) state. While in a WORM state, data can't be modified or deleted for a user-specified interval. By configuring immutability policies for blob data, you can protect your data from overwrites and deletes.
Immutable storage for Azure Blob Storage supports two types of immutability policies:
Time-based retention policies: With a time-based retention policy, users can set policies to store data for a specified interval. When a time-based retention policy is set, objects can be created and read, but not modified or deleted. After the retention period has expired, objects can be deleted but not overwritten.
Legal hold policies: A legal hold stores immutable data until the legal hold is explicitly cleared. When a legal hold is set, objects can be created and read, but not modified or deleted.
These policies can be set at the same time as one another. For example, a user can have both a time-based retention policy and a legal hold set at the same level and at the same time. In order for a write to succeed, you must either have versioning enabled or have neither a legal hold or time-based retention policy on the data. In order for a delete to succeed, there must not be a legal hold or time-based retention policy on the data as well.
The following diagram shows how time-based retention policies and legal holds prevent write and delete operations while they are in effect.
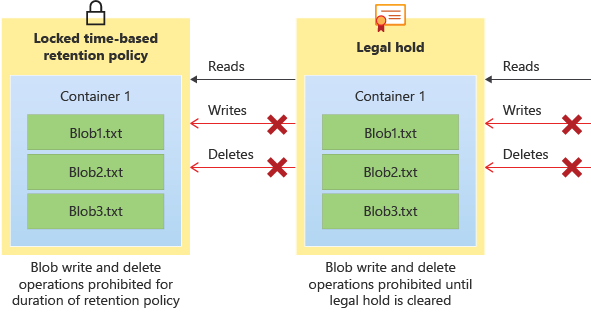
There are two features under the immutable storage umbrella: container-level WORM and version-level WORM. Container-level WORM allows policies to be set at the container level only, while version-level WORM allows policies to be set at the account, container, or version level.
About immutable storage for blobs
Immutable storage helps healthcare organizations, financial institutions, and related industries—particularly broker-dealer organizations—to store data securely. Immutable storage can be used in any scenario to protect critical data against modification or deletion.
Typical applications include:
Regulatory compliance: Immutable storage for Azure Blob Storage helps organizations address SEC 17a-4(f), CFTC 1.31(d), FINRA, and other regulations.
Secure document retention: Immutable storage for blobs ensures that data can't be modified or deleted by any user, not even by users with account administrative privileges.
Legal hold: Immutable storage for blobs enables users to store sensitive information that is critical to litigation or business use in a tamper-proof state for the desired duration until the hold is removed. This feature isn't limited only to legal use cases but can also be thought of as an event-based hold or an enterprise lock, where the need to protect data based on event triggers or corporate policy is required.
Regulatory compliance
Microsoft retained a leading independent assessment firm that specializes in records management and information governance, Cohasset Associates, to evaluate immutable storage for blobs and its compliance with requirements specific to the financial services industry. Cohasset validated that immutable storage, when used to retain blobs in a WORM state, meets the relevant storage requirements of CFTC Rule 1.31(c)-(d), FINRA Rule 4511, and SEC Rule 17a-4(f). Microsoft targeted this set of rules because they represent the most prescriptive guidance globally for records retention for financial institutions.
The Cohasset report is available in the Microsoft Service Trust Center. The Azure Trust Center contains detailed information about Microsoft's compliance certifications. To request a letter of attestation from Microsoft regarding WORM immutability compliance, please contact Azure Support.
Time-based retention policies
A time-based retention policy stores blob data in a WORM format for a specified interval. When a time-based retention policy is set, clients can create and read blobs, but can't modify or delete them. After the retention interval has expired, blobs can be deleted but not overwritten.
Scope
A time-based retention policy can be configured at the following scopes:
- Version-level WORM policy: A time-based retention policy can be configured at the account, container, or version level. If it's configured at the account or container level, it will be inherited by all blobs in the respective account or container.
- Container-level WORM policy: A time-based retention policy configured at the container level applies to all blobs in that container. Individual blobs can't be configured with their own immutability policies.
Retention interval for a time-based policy
The minimum retention interval for a time-based retention policy is one day, and the maximum is 146,000 days (400 years). When you configure a time-based retention policy, the affected objects stay in the immutable state during the effective retention period. The effective retention period for objects is equal to the difference between the blob's creation time and the user-specified retention interval. Because a policy's retention interval can be extended, immutable storage uses the most recent value of the user-specified retention interval to calculate the effective retention period.
For example, suppose that a user creates a time-based retention policy with a retention interval of five years. An existing blob in that container, testblob1, was created one year ago, so the effective retention period for testblob1 is four years. When a new blob, testblob2, is uploaded to the container, the effective retention period for testblob2 is five years from the time of its creation.
Locked versus unlocked policies
When you first configure a time-based retention policy, the policy is unlocked for testing purposes. When you finish testing, you can lock the policy so that it's fully compliant with SEC 17a-4(f) and other regulatory compliance.
Both locked and unlocked policies protect against deletes and overwrites. However, you can modify an unlocked policy by shortening or extending the retention period. You can also delete an unlocked policy. You can't delete a locked time-based retention policy. You can extend the retention period, but you can't decrease it. A maximum of five increases to the effective retention period is allowed over the lifetime of a locked policy that is defined at the container level. For a policy configured for a blob version, there's no limit to the number of increases to the effective period.
Important
A time-based retention policy must be locked for the blob to be in a compliant immutable (write and delete protected) state for SEC 17a-4(f) and other regulatory compliance. Microsoft recommends that you lock the policy in a reasonable amount of time, typically less than 24 hours. While the unlocked state provides immutability protection, using the unlocked state for any purpose other than short-term testing is not recommended.
Retention policy audit logging
Each container with a time-based retention policy enabled provides a policy audit log. The audit log includes up to seven time-based retention commands for locked time-based retention policies. Logging typically starts once you have locked the policy. Log entries include the user ID, command type, time stamps, and retention interval. The audit log is retained for the policy's lifetime in accordance with the SEC 17a-4(f) regulatory guidelines.
The Azure Activity log provides a more comprehensive log of all management service activities. Azure resource logs retain information about data operations. It's the user's responsibility to store those logs persistently, as might be required for regulatory or other purposes.
Changes to time-based retention policies at the version level aren't audited.
Legal holds
A legal hold is a temporary immutability policy that can be applied for legal investigation purposes or general protection policies. A legal hold stores blob data in a Write-Once, Read-Many (WORM) format until the hold is explicitly cleared. When a legal hold is in effect, blobs can be created and read, but not modified or deleted. Use a legal hold when the period of time that the data must be kept in a WORM state is unknown.
Scope
A legal hold policy can be configured at either of the following scopes:
Version-level WORM policy: A legal hold can be configured on an individual blob version level for granular management of sensitive data.
Container-level WORM policy: A legal hold that is configured at the container level applies to all blobs in that container. Individual blobs can't be configured with their own immutability policies.
Tags
A container-level legal hold must be associated with one or more user-defined alphanumeric tags that serve as identifier strings. For example, a tag may include a case ID or event name.
Audit logging
Each container with a legal hold in effect provides a policy audit log. The log contains the user ID, command type, time stamps, and legal hold tags. The audit log is retained for the policy's lifetime in accordance with the SEC 17a-4(f) regulatory guidelines.
The Azure Activity log provides a more comprehensive log of all management service activities. Azure resource logs retain information about data operations. It's the user's responsibility to store those logs persistently, as might be required for regulatory or other purposes.
Changes to legal holds at the version level aren't audited.
Immutable storage feature options
The following table shows a breakdown of the differences between container-level WORM and version-level WORM:
| Category | Container-level WORM | Version-level WORM |
|---|---|---|
| Policy granularity level | Policies can be configured only at the container level. Each object that is uploaded into the container inherits the immutable policy set. | Policies can be configured at the account, container, or blob level. If a policy is set at the account level, all blobs that are uploaded into that account inherits the policy. The same logic follows with containers. If a policy is set at multiple levels, the order of precedence is always Blob -> Container -> Account. |
| Types of policies available | Two different types of policies can be set at the container level: Time-based retention policies and legal holds. | At the account and container level, only time-based retention policies can be set. At the blob level, both time-based retention policies and legal holds can be set. |
| Feature dependencies | No other features are a prerequisite or requirement for this feature to function. | Versioning is a prerequisite for this feature to be used. |
| Enablement for existing accounts/container | This feature can be enabled at any time for existing containers. | Depending on the level of granularity, this feature might not be enabled for all existing accounts/containers. |
| Account/container deletion | Once a time-based retention policy is locked on a container, containers may only be deleted if they're empty. | Once version-level WORM is enabled on an account or container level, they may only be deleted if they're empty. |
| Support for Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 (storage accounts that have a hierarchical namespace enabled) | Container-level WORM policies are supported in accounts that have a hierarchical namespace. | Version-level WORM policies are not yet supported in accounts that have a hierarchical namespace. |
To learn more about container-level WORM, see Container-Level WORM policies. To learn more about version-level WORM, please visit version-Level WORM policies.
Container-level vs version-level WORM
The following table helps you decide which type of WORM policy to use.
| Criteria | Container-level WORM Usage | Version-level WORM Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Organization of data | You want to set policies for specific data sets, which can be categorized by container. All the data in that container needs to be kept in a WORM state for the same amount of time. | You can't group objects by retention periods. All blobs must be stored with an individual retention time based on that blob’s scenarios, or user has a mixed workload so that some groups of data can be clustered into containers while other blobs can't. You might also want to set container-level policies and blob-level policies within the same account. |
| Amount of data that requires an immutable policy | You don't need to set policies on more than 10,000 containers per account. | You want to set policies on all data or large amounts of data that can be delineated by account. You know that if you use container-level WORM, you'll have to exceed the 10,000-container limit. |
| Interest in enabling versioning | You don't want to deal with enabling versioning either because of the cost, or because the workload would create numerous extra versions to deal with. | You either want to use versioning, or don't mind using it. You know that if they don’t enable versioning, you can't keep edits or overwrites to immutable blobs as separate versions. |
| Storage location (Blob Storage vs Data Lake Storage Gen2) | Your workload is entirely focused on Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2. You have no immediate interest or plan to switch to using an account that doesn't have the hierarchical namespace feature enabled. | Your workload is either on Blob Storage in an account that doesn't have the hierarchical namespace feature enabled, and can use version-level WORM now, or you're willing to wait for versioning to be available for accounts that do have a hierarchical namespace enabled (Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2). |
Access tiers
All blob access tiers support immutable storage. You can change the access tier of a blob with the Set Blob Tier operation. For more information, see Access tiers for blob data.
Redundancy configurations
All redundancy configurations support immutable storage. For more information about redundancy configurations, see Azure Storage redundancy.
Recommended blob types
Microsoft recommends that you configure immutability policies mainly for block blobs and append blobs. Configuring an immutability policy for a page blob that stores a VHD disk for an active virtual machine is discouraged as writes to the disk will be blocked, or if versioning is enabled, each write is stored as a new version. Microsoft recommends that you thoroughly review the documentation and test your scenarios before locking any time-based policies. Microsoft recommends that you thoroughly review the documentation and test your scenarios before locking any time-based policies.
Immutable storage with blob soft delete
When blob soft delete is configured for a storage account, it applies to all blobs within the account regardless of whether a legal hold or time-based retention policy is in effect. Microsoft recommends enabling soft delete for extra protection before any immutability policies are applied.
If you enable blob soft delete and then configure an immutability policy, any blobs that have already been soft deleted are permanently deleted once the soft delete retention policy is expired. Soft-deleted blobs can be restored during the soft delete retention period. A blob or version that hasn't yet been soft deleted is protected by the immutability policy and can't be soft deleted until after the time-based retention policy is expired or the legal hold is removed.
Use blob inventory to track immutability policies
Azure Storage blob inventory provides an overview of the containers in your storage accounts and the blobs, snapshots, and blob versions within them. You can use the blob inventory report to understand the attributes of blobs and containers, including whether a resource has an immutability policy configured.
When you enable blob inventory, Azure Storage generates an inventory report daily. The report provides an overview of your data for business and compliance requirements.
For more information about blob inventory, see Azure Storage blob inventory.
Note
You can't configure an inventory policy in an account if support for version-level immutability is enabled on that account, or if support for version-level immutability is enabled on the destination container that is defined in the inventory policy.
Configuring policies at scale
You can use a storage task to configure a immutability policies at scale across multiple storage accounts based on a set of conditions that you define. A storage task is a resource available in Azure Storage Actions; a serverless framework that you can use to perform common data operations on millions of objects across multiple storage accounts. To learn more, see What is Azure Storage Actions?.
Pricing
There's no extra capacity charge for using immutable storage. Immutable data is priced in the same way as mutable data. If you're using version-level WORM, the bill might be higher because you've enabled versioning, and there's a cost associated with extra versions being stored. Review the versioning pricing policy for more information. For pricing details on Azure Blob Storage, see the Azure Storage pricing page.
Creating, modifying, or deleting a time-based retention policy or legal hold on a blob version results in a write transaction charge.
If you fail to pay your bill and your account has an active time-based retention policy in effect, normal data retention policies apply as stipulated in the terms and conditions of your contract with Microsoft. For general information, see Data management at Microsoft.
Feature support
This feature is incompatible with point in time restore and last access tracking. Immutability policies aren't supported in accounts that have Network File System (NFS) 3.0 protocol or the SSH File Transfer Protocol (SFTP) enabled on them.
Some workloads, such as SQL Backup to URL, create a blob and then add to it. If a container has an active time-based retention policy or legal hold in place, this pattern won't succeed. See the Allow protected append blob writes for more detail.
For more information, see Blob Storage feature support in Azure Storage accounts.
Next steps
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for