Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Get started with the Azure Blob Storage client library for C++. Azure Blob Storage is Microsoft's object storage solution for the cloud. Follow these steps to install the package and try out example code for basic tasks.
| API reference documentation | Library source code | Samples |
Prerequisites
- Azure subscription - create one for free
- Azure storage account - create a storage account
- C++ compiler
- CMake
- vcpkg - C and C++ package manager
Setting up
This section walks you through preparing a project to work with the Azure Blob Storage client library for C++. The easiest way to acquire the Azure SDK for C++ is to use the vcpkg package manager.
Install the packages
Use the vcpkg install command to install the Azure Blob Storage library for C++ and necessary dependencies:
vcpkg.exe install azure-storage-blobs-cpp
The Azure Identity library is needed for passwordless connections to Azure services:
vcpkg.exe install azure-identity-cpp
For more information on project setup and working with the Azure SDK for C++, see the Azure SDK for C++ readme.
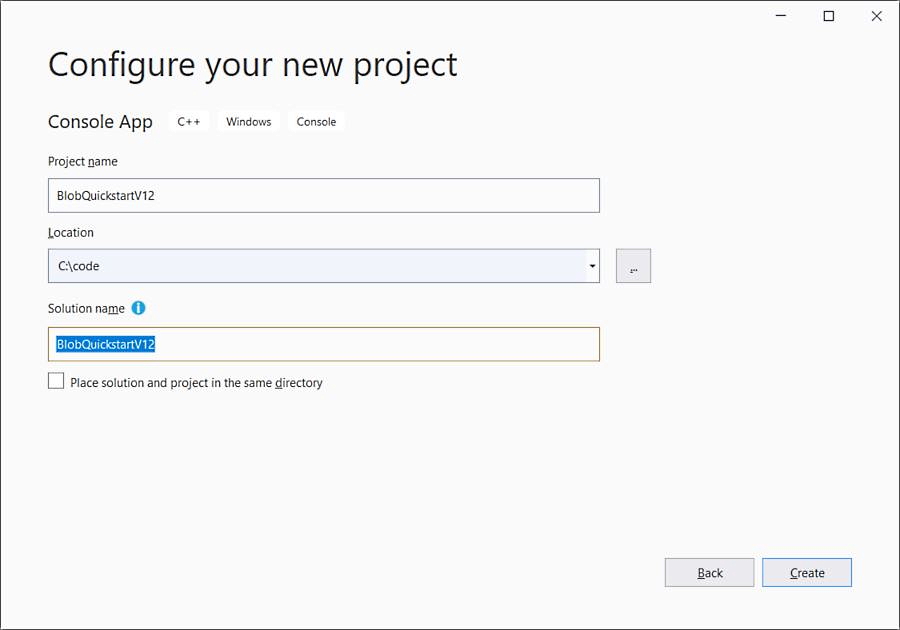
Create the project
In Visual Studio, create a new C++ console application for Windows called BlobQuickstart.
Object model
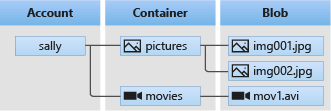
Azure Blob Storage is optimized for storing massive amounts of unstructured data. Unstructured data is data that doesn't adhere to a particular data model or definition, such as text or binary data. Blob Storage offers three types of resources:
- The storage account
- A container in the storage account
- A blob in the container
The following diagram shows the relationship between these resources.
Use these C++ classes to interact with these resources:
- BlobServiceClient: The
BlobServiceClientclass allows you to manipulate Azure Storage resources and blob containers. - BlobContainerClient: The
BlobContainerClientclass allows you to manipulate Azure Storage containers and their blobs. - BlobClient: The
BlobClientclass allows you to manipulate Azure Storage blobs. It's the base class for all specialized blob classes. - BlockBlobClient: The
BlockBlobClientclass allows you to manipulate Azure Storage block blobs.
Code examples
These example code snippets show you how to do the following tasks with the Azure Blob Storage client library for C++:
- Add include files
- Authenticate to Azure and authorize access to blob data
- Create a container
- Upload blobs to a container
- List the blobs in a container
- Download blobs
- Delete a container
Add include files
From the project directory:
- Open the BlobQuickstart.sln solution file in Visual Studio
- Inside Visual Studio, open the BlobQuickstart.cpp source file
- Remove any code inside
mainthat was autogenerated - Add
#includeandusing namespacestatements
#include <iostream>
#include <azure/core.hpp>
#include <azure/identity/default_azure_credential.hpp>
#include <azure/storage/blobs.hpp>
using namespace Azure::Identity;
using namespace Azure::Storage::Blobs;
Authenticate to Azure and authorize access to blob data
Application requests to Azure Blob Storage must be authorized. Using the DefaultAzureCredential class provided by the Azure Identity client library is the recommended approach for implementing passwordless connections to Azure services in your code, including Blob Storage.
You can also authorize requests to Azure Blob Storage by using the account access key. However, this approach should be used with caution. Developers must be diligent to never expose the access key in an unsecure location. Anyone who has the access key is able to authorize requests against the storage account, and effectively has access to all the data. DefaultAzureCredential offers improved management and security benefits over the account key to allow passwordless authentication. Both options are demonstrated in the following example.
The Azure Identity library provides Microsoft Entra token authentication support across the Azure SDK. It provides a set of TokenCredential implementations which can be used to construct Azure SDK clients which support Microsoft Entra token authentication. DefaultAzureCredential supports multiple authentication methods and determines which method should be used at runtime.
Assign roles to your Microsoft Entra user account
When developing locally, make sure that the user account that is accessing blob data has the correct permissions. You'll need Storage Blob Data Contributor to read and write blob data. To assign yourself this role, you'll need to be assigned the User Access Administrator role, or another role that includes the Microsoft.Authorization/roleAssignments/write action. You can assign Azure RBAC roles to a user using the Azure portal, Azure CLI, or Azure PowerShell. For more information about the Storage Blob Data Contributor role, see Storage Blob Data Contributor. For more information about the available scopes for role assignments, see Understand scope for Azure RBAC.
In this scenario, you'll assign permissions to your user account, scoped to the storage account, to follow the Principle of Least Privilege. This practice gives users only the minimum permissions needed and creates more secure production environments.
The following example will assign the Storage Blob Data Contributor role to your user account, which provides both read and write access to blob data in your storage account.
Important
In most cases it will take a minute or two for the role assignment to propagate in Azure, but in rare cases it may take up to eight minutes. If you receive authentication errors when you first run your code, wait a few moments and try again.
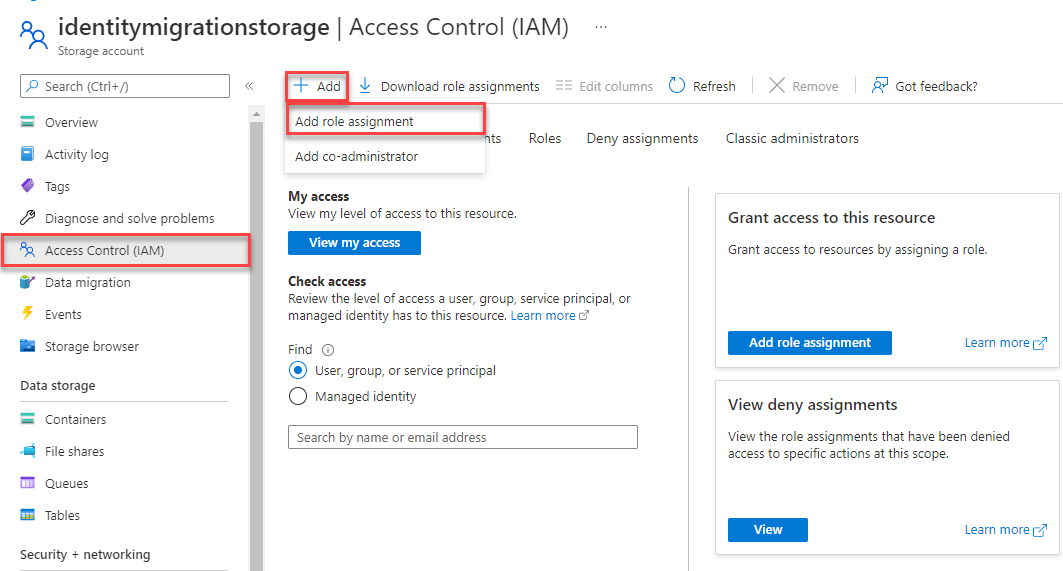
In the Azure portal, locate your storage account using the main search bar or left navigation.
On the storage account overview page, select Access control (IAM) from the left-hand menu.
On the Access control (IAM) page, select the Role assignments tab.
Select + Add from the top menu and then Add role assignment from the resulting drop-down menu.
Use the search box to filter the results to the desired role. For this example, search for Storage Blob Data Contributor and select the matching result and then choose Next.
Under Assign access to, select User, group, or service principal, and then choose + Select members.
In the dialog, search for your Microsoft Entra username (usually your user@domain email address) and then choose Select at the bottom of the dialog.
Select Review + assign to go to the final page, and then Review + assign again to complete the process.
Sign in and connect your app code to Azure using DefaultAzureCredential
You can authorize access to data in your storage account using the following steps:
Make sure you're authenticated with the same Microsoft Entra account you assigned the role to on your storage account. You can authenticate via Azure CLI. Sign in to Azure through the Azure CLI using the following command:
az loginTo use
DefaultAzureCredential, make sure that the azure-identity-cpp package is installed and the following#includeis added:#include <azure/identity/default_azure_credential.hpp>Add this code to the end of
main(). When the code runs on your local workstation,DefaultAzureCredentialuses the developer credentials for Azure CLI to authenticate to Azure.// Initialize an instance of DefaultAzureCredential auto defaultAzureCredential = std::make_shared<DefaultAzureCredential>(); auto accountURL = "https://<storage-account-name>.blob.core.windows.net"; BlobServiceClient blobServiceClient(accountURL, defaultAzureCredential);Make sure to update the storage account name in the URI of your
BlobServiceClientobject. The storage account name can be found on the overview page of the Azure portal.
Note
When using the C++ SDK in a production environment, it's recommended that you only enable credentials that you know your application will use. Instead of using
DefaultAzureCredential, you should authorize using a specific credential type, or by usingChainedTokenCredentialwith the supported credentials.
Create a container
Decide on a name for the new container. Then create an instance of BlobContainerClient and create the container.
Important
Container names must be lowercase. For more information about naming containers and blobs, see Naming and Referencing Containers, Blobs, and Metadata.
Add this code to the end of main():
std::string containerName = "myblobcontainer";
auto containerClient = blobServiceClient.GetBlobContainerClient("myblobcontainer");
// Create the container if it does not exist
std::cout << "Creating container: " << containerName << std::endl;
containerClient.CreateIfNotExists();
Upload blobs to a container
The following code snippet:
- Declares a string containing "Hello Azure!"
- Gets a reference to a BlockBlobClient object by calling GetBlockBlobClient on the container from the Create a container section.
- Uploads the string to the blob by calling the UploadFrom function. This function creates the blob if it doesn't already exist, or updates it if it does.
Add this code to the end of main():
std::string blobName = "blob.txt";
uint8_t blobContent[] = "Hello Azure!";
// Create the block blob client
BlockBlobClient blobClient = containerClient.GetBlockBlobClient(blobName);
// Upload the blob
std::cout << "Uploading blob: " << blobName << std::endl;
blobClient.UploadFrom(blobContent, sizeof(blobContent));
List the blobs in a container
List the blobs in the container by calling the ListBlobs function. Only one blob has been added to the container, so the operation returns just that blob.
Add this code to the end of main():
std::cout << "Listing blobs..." << std::endl;
auto listBlobsResponse = containerClient.ListBlobs();
for (auto blobItem : listBlobsResponse.Blobs)
{
std::cout << "Blob name: " << blobItem.Name << std::endl;
}
Download blobs
Get the properties of the uploaded blob. Then, declare and resize a new std::vector<uint8_t> object by using the properties of the uploaded blob. Download the previously created blob into the new std::vector<uint8_t> object by calling the DownloadTo function in the BlobClient base class. Finally, display the downloaded blob data.
Add this code to the end of main():
auto properties = blobClient.GetProperties().Value;
std::vector<uint8_t> downloadedBlob(properties.BlobSize);
blobClient.DownloadTo(downloadedBlob.data(), downloadedBlob.size());
std::cout << "Downloaded blob contents: " << std::string(downloadedBlob.begin(), downloadedBlob.end()) << std::endl;
Delete a Blob
The following code deletes the blob from the Azure Blob Storage container by calling the BlobClient.Delete function.
std::cout << "Deleting blob: " << blobName << std::endl;
blobClient.Delete();
Delete a container
The following code cleans up the resources the app created by deleting the entire container by using BlobContainerClient.Delete.
Add this code to the end of main():
std::cout << "Deleting container: " << containerName << std::endl;
containerClient.Delete();
Run the code
This app creates a container and uploads a text file to Azure Blob Storage. The example then lists the blobs in the container, downloads the file, and displays the file contents. Finally, the app deletes the blob and the container.
The output of the app is similar to the following example:
Azure Blob Storage - C++ quickstart sample
Creating container: myblobcontainer
Uploading blob: blob.txt
Listing blobs...
Blob name: blob.txt
Downloaded blob contents: Hello Azure!
Deleting blob: blob.txt
Deleting container: myblobcontainer
Next steps
In this quickstart, you learned how to upload, download, and list blobs using C++. You also learned how to create and delete an Azure Blob Storage container.
To see a C++ Blob Storage sample, continue to: