Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
In this tutorial, you learn how to use client-side encryption to encrypt and decrypt blobs using a key stored with Azure Key Vault.
Azure Blob Storage supports both service-side and client-side encryption. For most scenarios, Microsoft recommends using service-side encryption features for ease of use in protecting your data. To learn more about service-side encryption, see Azure Storage encryption for data at rest.
The Azure Blob Storage client library for .NET supports client-side data encryption within applications before uploading to Azure Storage, and decrypting data while downloading to the client. The library also supports integration with Azure Key Vault for key management.
This tutorial shows you how to:
- Configure permissions for an Azure Key Vault resource
- Create a console application to interact with resources using .NET client libraries
- Add a key to a key vault
- Configure client-side encryption options using a key stored in a key vault
- Create a blob service client object with client-side encryption enabled
- Upload an encrypted blob, then download and decrypt the blob
Prerequisites
- Azure subscription - create an account for free
- Azure storage account - create a storage account
- Key vault - create one using Azure portal, Azure CLI, or PowerShell
- Visual Studio 2022 installed
Assign a role to your Microsoft Entra user
When developing locally, make sure that the user account that is accessing the key vault has the correct permissions. You'll need the Key Vault Crypto Officer role to create a key and perform actions on keys in a key vault. You can assign Azure RBAC roles to a user using the Azure portal, Azure CLI, or Azure PowerShell. You can learn more about the available scopes for role assignments on the scope overview page.
In this scenario, you'll assign permissions to your user account, scoped to the key vault, to follow the Principle of Least Privilege. This practice gives users only the minimum permissions needed and creates more secure production environments.
The following example shows how to assign the Key Vault Crypto Officer role to your user account, which provides the access you'll need to complete this tutorial.
Important
In most cases it will take a minute or two for the role assignment to propagate in Azure, but in rare cases it may take up to eight minutes. If you receive authentication errors when you first run your code, wait a few moments and try again.
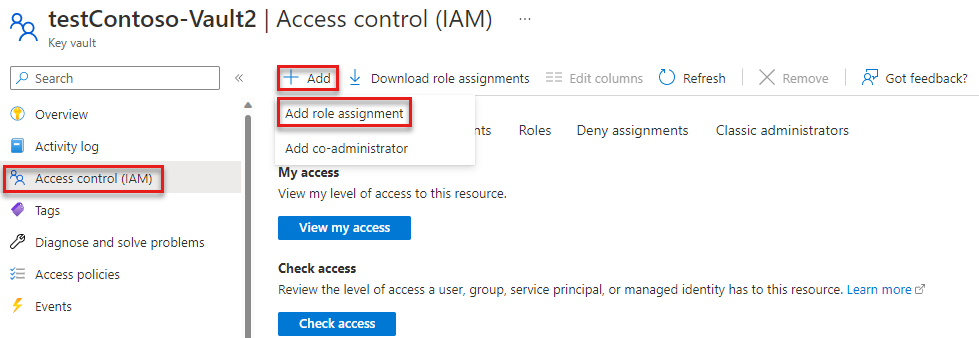
In the Azure portal, locate your key vault using the main search bar or left navigation.
On the key vault overview page, select Access control (IAM) from the left-hand menu.
On the Access control (IAM) page, select the Role assignments tab.
Select + Add from the top menu and then Add role assignment from the resulting drop-down menu.
Use the search box to filter the results to the desired role. For this example, search for Key Vault Crypto Officer and select the matching result and then choose Next.
Under Assign access to, select User, group, or service principal, and then choose + Select members.
In the dialog, search for your Microsoft Entra username (usually your user@domain email address) and then choose Select at the bottom of the dialog.
Select Review + assign to go to the final page, and then Review + assign again to complete the process.
Set up your project
In a console window (such as PowerShell or Bash), use the
dotnet newcommand to create a new console app with the name BlobEncryptionKeyVault. This command creates a simple "Hello World" C# project with a single source file: Program.cs.dotnet new console -n BlobEncryptionKeyVaultSwitch to the newly created BlobEncryptionKeyVault directory.
cd BlobEncryptionKeyVaultOpen the project in your desired code editor. To open the project in:
- Visual Studio, locate and double-click the
BlobEncryptionKeyVault.csprojfile. - Visual Studio Code, run the following command:
code .- Visual Studio, locate and double-click the
To interact with Azure services in this example, install the following client libraries using dotnet add package.
dotnet add package Azure.Identity
dotnet add package Azure.Security.KeyVault.Keys
dotnet add package Azure.Storage.Blobs
Add the following using directives and make sure to add a reference to System.Configuration to the project.
using Azure;
using Azure.Core;
using Azure.Identity;
using Azure.Security.KeyVault.Keys;
using Azure.Security.KeyVault.Keys.Cryptography;
using Azure.Storage;
using Azure.Storage.Blobs;
using Azure.Storage.Blobs.Models;
using Azure.Storage.Blobs.Specialized;
Set environment variable
This application looks for an environment variable called KEY_VAULT_NAME to retrieve the name of your key vault. To set the environment variable, open a console window and follow the instructions for your operating system. Replace <your-key-vault-name> with the name of your key vault.
Windows:
You can set environment variables for Windows from the command line. However, when using this approach the values are accessible to all applications running on that operating system and may cause conflicts if you aren't careful. Environment variables can be set at either user or system level:
setx KEY_VAULT_NAME "<your-key-vault-name>"
After you add the environment variable in Windows, you must start a new instance of the command window. If you're using Visual Studio on Windows, you may need to relaunch Visual Studio after creating the environment variable for the change to be detected.
Linux:
export KEY_VAULT_NAME=<your-key-vault-name>
Add a key in Azure Key Vault
In this example, we create a key and add it to the key vault using the Azure Key Vault client library. You can also create and add a key to a key vault using Azure CLI, Azure portal, or PowerShell.
In the sample below, we create a KeyClient object for the specified vault. The KeyClient object is then used to create a new RSA key in the specified vault.
var keyName = "testRSAKey";
var keyVaultName = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("KEY_VAULT_NAME");
// URI for the key vault resource
var keyVaultUri = $"https://{keyVaultName}.vault.azure.net";
TokenCredential tokenCredential = new DefaultAzureCredential();
// Create a KeyClient object
var keyClient = new KeyClient(new Uri(keyVaultUri), tokenCredential);
// Add a key to the key vault
var key = await keyClient.CreateKeyAsync(keyName, KeyType.Rsa);
Create key and key resolver instances
Next, we'll use the key we just added to the vault to create the cryptography client and key resolver instances. CryptographyClient implements IKeyEncryptionKey and is used to perform cryptographic operations with keys stored in Azure Key Vault. KeyResolver implements IKeyEncryptionResolver and retrieves key encryption keys from the key identifier and resolves the key.
// Cryptography client and key resolver instances using Azure Key Vault client library
CryptographyClient cryptoClient = keyClient.GetCryptographyClient(key.Value.Name, key.Value.Properties.Version);
KeyResolver keyResolver = new (tokenCredential);
If you have an existing key in the vault that you'd like to encrypt with, you can create the key and key resolver instances by passing in the URI:
var keyVaultKeyUri = $"https://{keyVaultName}.vault.azure.net/keys/{keyName}";
CryptographyClient cryptoClient = new CryptographyClient(new Uri(keyVaultKeyUri), tokenCredential);
Configure encryption options
Now we need to configure the encryption options to be used for blob upload and download. To use client-side encryption, we first create a ClientSideEncryptionOptions object and set it on client creation with SpecializedBlobClientOptions.
The ClientSideEncryptionOptions class provides the client configuration options for connecting to Blob Storage using client-side encryption. KeyEncryptionKey is required for upload operations and is used to wrap the generated content encryption key. KeyResolver is required for download operations and fetches the correct key encryption key to unwrap the downloaded content encryption key. KeyWrapAlgorithm is required for uploads and specifies the algorithm identifier to use when wrapping the content encryption key.
Important
Due to a security vulnerability in version 1, it's recommended to construct the ClientSideEncryptionOptions object using ClientSideEncryptionVersion.V2_0 for the version parameter. To learn more about mitigating the vulnerability in your apps, see Mitigate the security vulnerability in your applications. For more information about this security vulnerability, see Azure Storage updating client-side encryption in SDK to address security vulnerability.
// Configure the encryption options to be used for upload and download
ClientSideEncryptionOptions encryptionOptions = new (ClientSideEncryptionVersion.V2_0)
{
KeyEncryptionKey = cryptoClient,
KeyResolver = keyResolver,
// String value that the client library will use when calling IKeyEncryptionKey.WrapKey()
KeyWrapAlgorithm = "RSA-OAEP"
};
// Set the encryption options on the client options.
BlobClientOptions options = new SpecializedBlobClientOptions() { ClientSideEncryption = encryptionOptions };
Configure client object to use client-side encryption
In this example, we apply the client-side encryption configuration options to a BlobServiceClient object. When applied at the service client level, these encryption options are passed from the service client to container clients, and from container clients to blob clients. When the BlobClient object performs an upload or download operation, the Azure Blob Storage client libraries use envelope encryption to encrypt and decrypt blobs on the client side. Envelope encryption encrypts a key with one or more additional keys.
// Create a blob client with client-side encryption enabled.
// Attempting to construct a BlockBlobClient, PageBlobClient, or AppendBlobClient from a BlobContainerClient
// with client-side encryption options present will throw, as this functionality is only supported with BlobClient.
Uri blobUri = new (string.Format($"https://{accountName}.blob.core.windows.net"));
BlobClient blob = new BlobServiceClient(blobUri, tokenCredential, options).GetBlobContainerClient("test-container").GetBlobClient("testBlob");
Encrypt blob and upload
When the BlobClient object calls an upload method, several steps occur to perform the client-side encryption:
- The Azure Storage client library generates a random initialization vector (IV) of 16 bytes and a random content encryption key (CEK) of 32 bytes, and performs envelope encryption of the blob data using this information.
- Blob data is encrypted using the CEK.
- The CEK is then wrapped (encrypted) using the key encryption key (KEK) we specified in
ClientSideEncryptionOptions. In this example, the KEK is an asymmetric key pair stored in the specified Azure Key Vault resource. The blob client itself never has access to the KEK, it just invokes the key wrapping algorithm that is provided by Key Vault. - The encrypted blob data is then uploaded to the storage account.
Add the following code to encrypt a blob and upload it to your Azure storage account:
// Upload the encrypted contents to the blob
Stream blobContent = BinaryData.FromString("Ready for encryption, Captain.").ToStream();
await blob.UploadAsync(blobContent);
Once the blob is uploaded, you can view the blob in your storage account to see the encrypted contents along with the encryption metadata.
Decrypt blob and download
The Azure Storage client library assumes that the user is managing the KEK either locally or in a key vault. The user doesn't need to know the specific key that was used for encryption. The key resolver specified in ClientSideEncryptionOptions will be used to resolve key identifiers when blob data is downloaded and decrypted.
When the BlobClient object calls a download method, several steps occur to decrypt the encrypted blob data:
- The client library downloads the encrypted blob data, including encryption metadata, from the storage account.
- The wrapped CEK is then unwrapped (decrypted) using the KEK. The client library doesn't have access to the KEK during this process, but only invokes the key unwrapping algorithm specified in
ClientSideEncryptionOptions. The private key of they RSA key pair remains in the key vault, so the encrypted key from the blob metadata that contains the CEK is sent to the key vault for decryption. - The client library uses the CEK to decrypt the encrypted blob data.
Add the following code to download and decrypt the blob that you previously uploaded.
// Download and decrypt the encrypted contents from the blob
Response<BlobDownloadInfo> response = await blob.DownloadAsync();
BlobDownloadInfo downloadInfo = response.Value;
Console.WriteLine((await BinaryData.FromStreamAsync(downloadInfo.Content)).ToString());
Next steps
In this tutorial, you learned how to use .NET client libraries to perform client-side encryption for blob upload and download operations.
For a broad overview of client-side encryption for blobs, including instructions for migrating encrypted data to version 2, see Client-side encryption for blobs.
For more information about Azure Key Vault, see the Azure Key Vault overview page