Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Azure Elastic SAN uses server-side encryption (SSE) to automatically encrypt data stored in an Elastic SAN. SSE protects your data and helps you meet your organizational security and compliance requirements.
Data in Azure Elastic SAN volumes is encrypted and decrypted transparently using 256-bit AES encryption, one of the strongest block ciphers available, and is FIPS 140-2 compliant. For more information about the cryptographic modules underlying Azure data encryption, see Cryptography API: Next Generation.
SSE is enabled by default and can't be disabled. SSE can't be disabled, doesn't impact the performance of your Elastic SAN, and has no extra cost associated with it.
About encryption key management
There are two kinds of encryption keys available: platform-managed keys and customer-managed keys. Data written to an Elastic SAN volume is encrypted with platform-managed (Microsoft-managed) keys by default. If you prefer, you can use Customer-managed keys instead, if you have specific organizational security and compliance requirements.
When you configure a volume group, you can choose to use either platform-managed or customer-managed keys. All volumes in a volume group inherit the volume group's configuration. You can switch between customer-managed and platform-managed keys at any time. If you switch between these key types, the Elastic SAN service re-encrypts the data encryption key with the new KEK. The protection of the data encryption key changes, but the data in your Elastic SAN volumes always remains encrypted. There's no extra action required on your part to ensure that your data is protected.
Customer-managed keys
If you use customer-managed keys, you must use either an Azure Key Vault to store it.
You can either create and import your own RSA keys and store them in your Azure Key Vault, or you can generate new RSA keys using Azure Key Vault. You can use the Azure Key Vault APIs or management interfaces to generate your keys. The Elastic SAN and the key vault can be in different regions and subscriptions, but they must be in the same Microsoft Entra ID tenant.
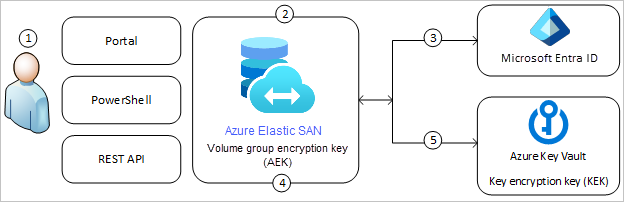
The following diagram shows how Azure Elastic SAN uses Microsoft Entra ID and a key vault to make requests using the customer-managed key:
The following list explains the numbered steps in the diagram:
- An Azure Key Vault admin grants permissions to a managed identity to access the key vault that contains the encryption keys. The managed identity can be either a user-assigned identity that you create and manage, or a system-assigned identity that is associated with the volume group.
- An Azure Elastic SAN Volume Group Owner configures encryption with a customer-managed key for the volume group.
- Azure Elastic SAN uses the managed identity granted permissions in step 1 to authenticate access to the key vault via Microsoft Entra ID.
- Azure Elastic SAN wraps the data encryption key with the customer-managed key from the key vault.
- For read/write operations, Azure Elastic SAN sends requests to Azure Key Vault to unwrap the account encryption key to perform encryption and decryption operations.