Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Azure Files always stores multiple copies of your data so that it's protected from planned and unplanned events, including transient hardware failures, network or power outages, and natural disasters. Redundancy ensures that your storage account meets its availability and durability targets even in the face of failures.
When deciding which redundancy option is best for your scenario, consider the tradeoffs between lower costs and higher availability. The factors that help determine which redundancy option you should choose include:
- How your data is replicated in the primary region.
- Whether your data is replicated to a second region that's geographically distant to the primary region, to protect against regional disasters (geo-redundancy).
Azure file shares are managed through a common Azure resource called a storage account. The storage account represents a shared pool of storage that can be used to deploy file shares. For more information about storage accounts, see Storage account overview.
When you create a storage account, you choose a redundancy setting for the storage account that's shared for all storage services exposed by that account. Therefore, all file shares deployed in the same storage account have the same redundancy setting. You might want to isolate file shares in separate storage accounts if they have different redundancy requirements.
Applies to
| Management model | Billing model | Media tier | Redundancy | SMB | NFS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microsoft.Storage | Provisioned v2 | HDD (standard) | Local (LRS) | ||
| Microsoft.Storage | Provisioned v2 | HDD (standard) | Zone (ZRS) | ||
| Microsoft.Storage | Provisioned v2 | HDD (standard) | Geo (GRS) | ||
| Microsoft.Storage | Provisioned v2 | HDD (standard) | GeoZone (GZRS) | ||
| Microsoft.Storage | Provisioned v1 | SSD (premium) | Local (LRS) | ||
| Microsoft.Storage | Provisioned v1 | SSD (premium) | Zone (ZRS) | ||
| Microsoft.Storage | Pay-as-you-go | HDD (standard) | Local (LRS) | ||
| Microsoft.Storage | Pay-as-you-go | HDD (standard) | Zone (ZRS) | ||
| Microsoft.Storage | Pay-as-you-go | HDD (standard) | Geo (GRS) | ||
| Microsoft.Storage | Pay-as-you-go | HDD (standard) | GeoZone (GZRS) |
Redundancy in the primary region
Data in an Azure storage account is always replicated three times in the primary region. Azure Files offers two options for how your data is replicated in the primary region:
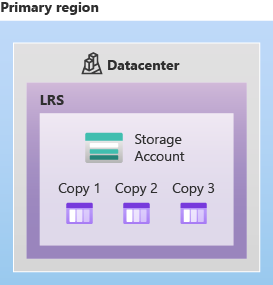
- Locally redundant storage (LRS) copies your data synchronously three times within a single physical location in the primary region. LRS is the least expensive replication option, but isn't recommended for applications requiring high availability or durability.
- Zone-redundant storage (ZRS) copies your data synchronously across three Azure availability zones in the primary region. For applications requiring high availability, we recommend using geo-zone-redundant storage (GZRS), which uses ZRS in the primary region and also geo-replicates your data to a secondary region.
Locally redundant storage
Locally redundant storage (LRS) replicates your storage account three times within a single data center in the primary region. LRS provides at least 99.999999999% (11 nines) durability over a given year.
LRS is the lowest-cost redundancy option and offers the least durability compared to other options. LRS protects your data against server rack and drive failures. However, if a disaster such as fire or flooding occurs within the data center, all replicas of a storage account using LRS could be lost or unrecoverable. To mitigate this risk, we recommend using ZRS, GRS, or GZRS.
A write request to a storage account that's using LRS happens synchronously. The write operation returns successfully only after the data is written to all three replicas.
The following diagram shows how your data is replicated within a single data center with LRS:
LRS is a good choice for the following scenarios:
- If your application stores data that can be easily reconstructed if data loss occurs.
- If your application is restricted to replicating data only within a country or region due to data governance requirements. In some cases, the paired regions across which the data is geo-replicated might be in another country or region. For more information, see Azure region pairs and nonpaired regions.
LRS is supported in all Azure regions for HDD file shares. For a list of regions that support LRS for SSD file shares, see LRS support for SSD file shares.
Zone-redundant storage
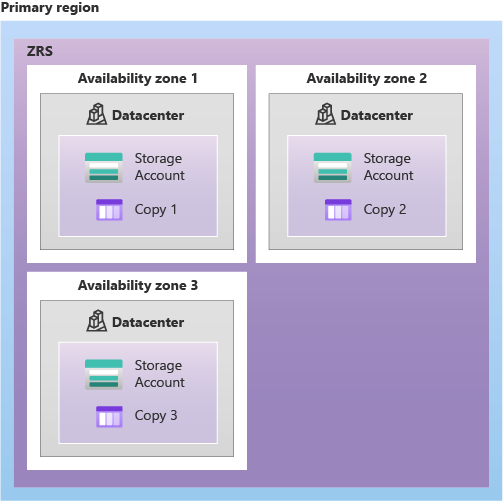
Zone-redundant storage (ZRS) replicates your storage account synchronously across three Azure availability zones in the primary region. Each availability zone is a separate physical location with independent power, cooling, and networking. ZRS offers durability of at least 99.9999999999% (12 9's) over a given year.
With ZRS, your data is still accessible for both read and write operations even if a zone becomes unavailable. If a zone becomes unavailable, Azure undertakes networking updates, such as DNS repointing. These updates may affect your application if you access data before the updates have completed. When designing applications for ZRS, follow practices for transient fault handling, including implementing retry policies with exponential back-off.
A write request to a storage account that is using ZRS happens synchronously. The write operation returns successfully only after the data is written to all replicas across the three availability zones.
An advantage of using ZRS for Azure Files workloads is that if a zone becomes unavailable, no remounting of Azure file shares from the connected clients is required. We recommend using ZRS in the primary region for scenarios that require high availability. We also recommend ZRS for restricting replication of data to a particular country or region to meet data governance requirements.
Note
Azure File Sync is zone-redundant in all regions that support availability zones except US Gov Virginia. In most cases, we recommend that Azure File Sync users configure storage accounts to use ZRS or GZRS.
The following diagram shows how your data is replicated across availability zones in the primary region with ZRS:
ZRS provides excellent performance, low latency, and resiliency for your data if it becomes temporarily unavailable. However, ZRS by itself might not protect your data against a regional disaster where multiple zones are permanently affected. For protection against regional disasters, we recommend using GZRS.
ZRS support by region
To understand which regions support ZRS for standard file shares, see the Azure regions list and refer to the availability zone support column. ZRS is supported in standard general-purpose v2 storage accounts for all three standard tiers: transaction optimized, hot, and cool.
ZRS is supported for SSD file shares through the FileStorage storage account kind. For a list of regions that support ZRS for SSD file share accounts, see ZRS support for SSD file shares.
Redundancy in a secondary region
For applications requiring high durability for SMB file shares, you can choose geo-redundant storage to copy the data in your storage account to a secondary region that is hundreds of miles away from the primary region. If your storage account is copied to a secondary region, then your data is durable even in the case of a complete regional outage or a disaster in which the primary region isn't recoverable.
Important
Azure Files only supports geo-redundancy (GRS or GZRS) for HDD file shares. SSD file shares must use LRS or ZRS.
When you create a storage account, you select the primary region for the account. The paired secondary region is determined based on the primary region, and can't be changed. For more information about regions supported by Azure, see the Azure regions list.
Azure Files offers two options for copying your data to a secondary region. Currently, geo-redundant storage options are only available for standard SMB file shares.
- Geo-redundant storage (GRS) copies your data synchronously three times within a single physical location in the primary region using LRS. It then copies your data asynchronously to a single physical location in the secondary region. Within the secondary region, your data is copied synchronously three times using LRS.
- Geo-zone-redundant storage (GZRS) copies your data synchronously across three Azure availability zones in the primary region using ZRS. It then copies your data asynchronously to a single physical location in the secondary region. Within the secondary region, your data is copied synchronously three times using LRS.
The primary difference between GRS and GZRS is how data is replicated in the primary region. Within the secondary region, data is always replicated synchronously three times using LRS. LRS in the secondary region protects your data against hardware failures.
Geo-redundant storage
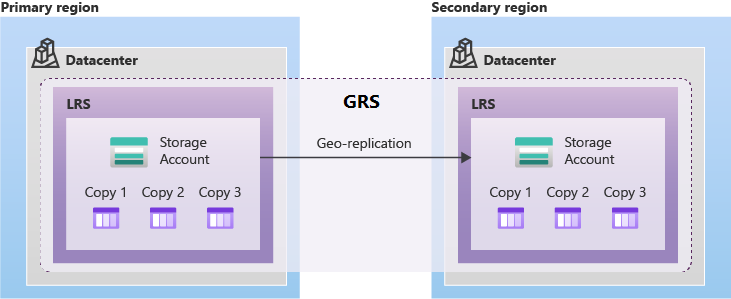
Geo-redundant storage (GRS) copies your data synchronously three times within a single physical location in the primary region using LRS. It then copies your data asynchronously to a single physical location in a secondary region that is hundreds of miles away from the primary region. GRS offers durability of at least 99.99999999999999% (16 9's) over a given year.
A write operation is first committed to the primary location and replicated using LRS. The update is then replicated asynchronously to the secondary region. When data is written to the secondary location, it's also replicated within that location using LRS.
The following diagram shows how your data is replicated with GRS:
Geo-zone-redundant storage
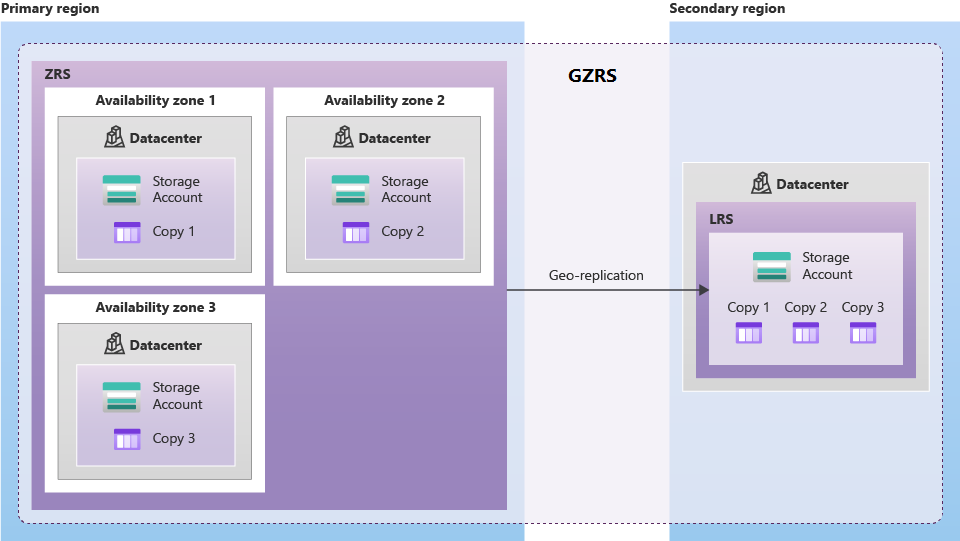
Geo-zone-redundant storage (GZRS) combines the high availability provided by redundancy across availability zones with protection from regional outages provided by geo-replication. Data in a GZRS storage account is copied across three Azure availability zones in the primary region and is also replicated to a secondary geographic region for protection from regional disasters. We recommend using GZRS for applications requiring maximum consistency, durability, and availability, excellent performance, and resilience for disaster recovery.
With a GZRS storage account, you can continue to read and write data if an availability zone becomes unavailable or is unrecoverable. Additionally, your data is also durable in the case of a complete regional outage or a disaster in which the primary region isn't recoverable. GZRS is designed to provide at least 99.99999999999999% (16 9's) durability over a given year.
The following diagram shows how your data is replicated with GZRS:
Only standard general-purpose v2 storage accounts support GZRS.
To determine if a region supports GZRS, see the Azure regions list. To support GZRS, a region must support availability zones and have a paired region.
Snapshot and sync frequency
To ensure Geo and GeoZone redundant file shares are in a consistent state when a failover occurs, a system snapshot is created in the primary region every 15 minutes and is replicated to the secondary region. When a failover occurs to the secondary region, the share state is based on the latest system snapshot in the secondary region. Due to geo-lag or other issues, the latest system snapshot in the secondary region may be older than 15 minutes.
The Last Sync Time (LST) property on the storage account indicates the last time that data from the primary region was written successfully to the secondary region. For Azure Files, the Last Sync Time is based on the latest system snapshot in the secondary region. You can use PowerShell or Azure CLI to check the Last Sync Time for a storage account.
It's important to understand the following about the Last Sync Time property:
- The Last Sync Time property on the storage account is based on the service (Files, Blobs, Tables, Queues) in the storage account that's the furthest behind.
- The Last Sync Time isn't updated if no changes have been made on the storage account.
- The Last Sync Time calculation can time out if the number of file shares exceeds 100 per storage account. Less than 100 file shares per storage account is recommended.
Failover considerations
With GRS or GZRS, the file shares won't be accessible in the secondary region unless a failover occurs. If the primary region becomes unavailable, you can choose to fail over to the secondary region. The failover process updates the DNS entry provided by Azure Files so that the secondary endpoint becomes the new primary endpoint for your storage account. During the failover process, your data is inaccessible. After the failover is complete, you can read and write data to the new primary region. After the failover has completed, the secondary region becomes the primary region, and you can again read and write data. For more information, see Azure Files disaster recovery and failover.
Important
Azure Files doesn't support read-access geo-redundant storage (RA-GRS) or read-access geo-zone-redundant storage (RA-GZRS). If a storage account is configured to use RA-GRS or RA-GZRS, the file shares will be configured and billed as GRS or GZRS.
The following items might impact your ability to fail over to the secondary region:
- Storage account failover is blocked if a system snapshot doesn't exist in the secondary region.
- Storage account failover is blocked if the storage account contains more than 100,000 file shares. To fail over the storage account, open a support request.
- File handles and leases aren't retained on failover, and clients must unmount and remount the file shares.
- File share quota might change after failover. The file share quota in the secondary region will be based on the quota that was configured when the system snapshot was taken in the primary region.
- Copy operations in progress are aborted when a failover occurs. When the failover to the secondary region completes, retry the copy operation.
To fail over a storage account, see initiate an account failover.
Geo-redundancy for SSD file shares
As previously mentioned, geo-redundancy options (GRS and GZRS) aren't supported for SSD file shares. However, you can achieve geo-redundancy in other ways.
For Azure File Sync scenarios, you can sync between your Azure file share (your cloud endpoint), an on-premises Windows file server, and a mounted file share running on a virtual machine in another Azure region (your server endpoint for disaster recovery purposes). You must disable cloud tiering to ensure all data is present locally, and provision enough storage on the Azure VM to hold the entire dataset. To ensure changes will replicate quickly to the secondary region, files should only be accessed and modified on the server endpoint rather than in Azure.
You can also create your own script to copy data to a storage account in a secondary region using tools such as AzCopy (use version 10.4 or later to preserve ACLs and timestamps).
Summary of redundancy options
The tables in the following sections summarize the redundancy options available for Azure Files.
Durability and availability parameters
The following table describes key parameters for each redundancy option:
| Parameter | LRS | ZRS | GRS | GZRS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Percent durability of over a given year | at least 99.999999999% (11 9's) | at least 99.9999999999% (12 9's) | at least 99.99999999999999% (16 9's) | at least 99.99999999999999% (16 9's) |
| Availability for read requests | At least 99.9% (99% for Cool tier) | At least 99.9% (99% for Cool tier) | At least 99.9% (99% for Cool tier) | At least 99.9% (99% for Cool tier) |
| Availability for write requests | At least 99.9% (99% for Cool tier) | At least 99.9% (99% for Cool tier) | At least 99.9% (99% for Cool tier) | At least 99.9% (99% for Cool tier) |
| Number of copies of data maintained on separate nodes | Three copies within a single region | Three copies across separate availability zones within a single region | Six copies total, including three in the primary region and three in the secondary region | Six copies total, including three across separate availability zones in the primary region and three locally redundant copies in the secondary region |
For more information, see the SLA for Storage Accounts.
Durability and availability by outage scenario
The following table indicates whether your data is durable and available in a given scenario, depending on which type of redundancy is in effect for your storage account. Azure Files doesn't support read access to the secondary region if the primary region becomes unavailable, unless a failover occurs.
| Outage scenario | LRS | ZRS | GRS | GZRS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A node within a data center becomes unavailable | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| An entire data center (zonal or non-zonal) becomes unavailable | No | Yes | Yes1 | Yes |
| A region-wide outage occurs in the primary region | No | No | Yes1 | Yes1 |
1 Account failover is required to restore write availability if the primary region becomes unavailable.
For pricing information for each redundancy option, see Azure Files pricing.
Region supportability based on different billing models
You can verify region supportability for various billing models using the following commands.
To view region supportability based on different billing models, use Azure PowerShell or Azure CLI.