Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This article explains how you can improve performance for network file system (NFS) Azure file shares.
Applies to
| Management model | Billing model | Media tier | Redundancy | SMB | NFS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microsoft.Storage | Provisioned v2 | SSD (premium) | Local (LRS) | ||
| Microsoft.Storage | Provisioned v2 | SSD (premium) | Zone (ZRS) | ||
| Microsoft.Storage | Provisioned v2 | HDD (standard) | Local (LRS) | ||
| Microsoft.Storage | Provisioned v2 | HDD (standard) | Zone (ZRS) | ||
| Microsoft.Storage | Provisioned v2 | HDD (standard) | Geo (GRS) | ||
| Microsoft.Storage | Provisioned v2 | HDD (standard) | GeoZone (GZRS) | ||
| Microsoft.Storage | Provisioned v1 | SSD (premium) | Local (LRS) | ||
| Microsoft.Storage | Provisioned v1 | SSD (premium) | Zone (ZRS) | ||
| Microsoft.Storage | Pay-as-you-go | HDD (standard) | Local (LRS) | ||
| Microsoft.Storage | Pay-as-you-go | HDD (standard) | Zone (ZRS) | ||
| Microsoft.Storage | Pay-as-you-go | HDD (standard) | Geo (GRS) | ||
| Microsoft.Storage | Pay-as-you-go | HDD (standard) | GeoZone (GZRS) |
Increase read-ahead size to improve read throughput
The read_ahead_kb kernel parameter in Linux represents the amount of data that should be "read ahead" or prefetched during a sequential read operation. Linux kernel versions before 5.4 set the read-ahead value to the equivalent of 15 times the mounted file system's rsize, which represents the client-side mount option for read buffer size. This sets the read-ahead value high enough to improve client sequential read throughput in most cases.
However, beginning with Linux kernel version 5.4, the Linux NFS client uses a default read_ahead_kb value of 128 KiB. This small value might reduce the amount of read throughput for large files. Customers upgrading from Linux releases with the larger read-ahead value to releases with the 128 KiB default might experience a decrease in sequential read performance.
For Linux kernels 5.4 or later, we recommend persistently setting the read_ahead_kb to 15 MiB for improved performance.
To change this value, set the read-ahead size by adding a rule in udev, a Linux kernel device manager. Follow these steps:
In a text editor, create the /etc/udev/rules.d/99-nfs.rules file by entering and saving the following text:
SUBSYSTEM=="bdi" \ , ACTION=="add" \ , PROGRAM="/usr/bin/awk -v bdi=$kernel 'BEGIN{ret=1} {if ($4 == bdi) {ret=0}} END{exit ret}' /proc/fs/nfsfs/volumes" \ , ATTR{read_ahead_kb}="15360"In a console, apply the udev rule by running the udevadm command as a superuser and reloading the rules files and other databases. You only need to run this command once, to make udev aware of the new file.
sudo udevadm control --reload
NFS nconnect
NFS nconnect is a client-side mount option for NFS file shares that allows you to use multiple TCP connections between the client and your NFS file share.
Benefits
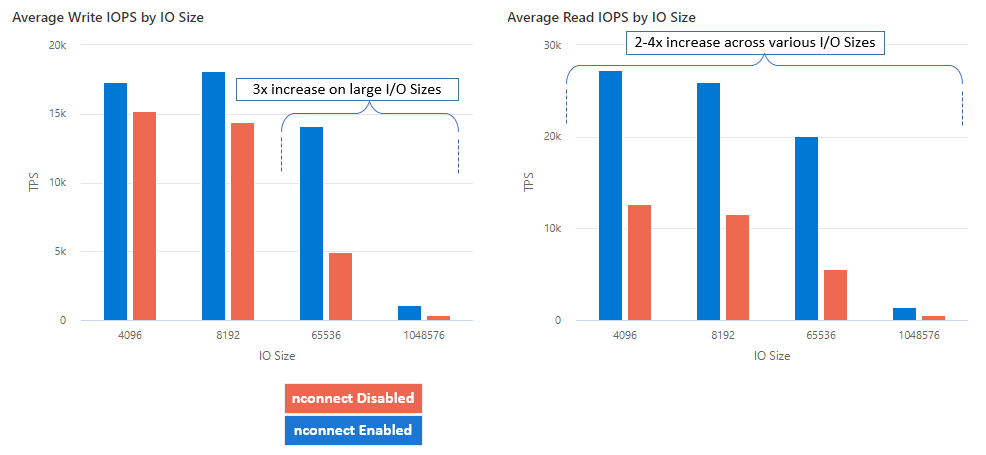
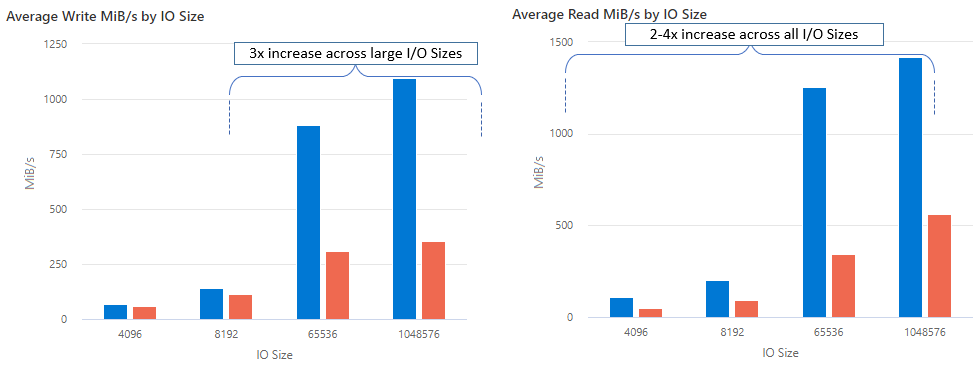
With nconnect, you can increase performance at scale using fewer client machines to reduce total cost of ownership (TCO). The nconnect feature increases performance by using multiple TCP channels on one or more NICs, using single or multiple clients. Without nconnect, you'd need roughly 20 client machines in order to achieve the bandwidth scale limits (10 GiB / sec) offered by the largest SSD file share provisioning size. With nconnect, you can achieve those limits using only 6-7 clients, reducing compute costs by nearly 70% while providing significant improvements in I/O operations per second (IOPS) and throughput at scale. See the following table.
| Metric (operation) | I/O size | Performance improvement |
|---|---|---|
| IOPS (write) | 64 KiB, 1,024 KiB | 3x |
| IOPS (read) | All I/O sizes | 2-4x |
| Throughput (write) | 64 KiB, 1,024 KiB | 3x |
| Throughput (read) | All I/O sizes | 2-4x |
Prerequisites
- The latest Linux distributions fully support nconnect. For older Linux distributions, ensure that the Linux kernel version is 5.3 or higher.
- Per-mount configuration is only supported when a single file share is used per storage account over a private endpoint.
Performance impact
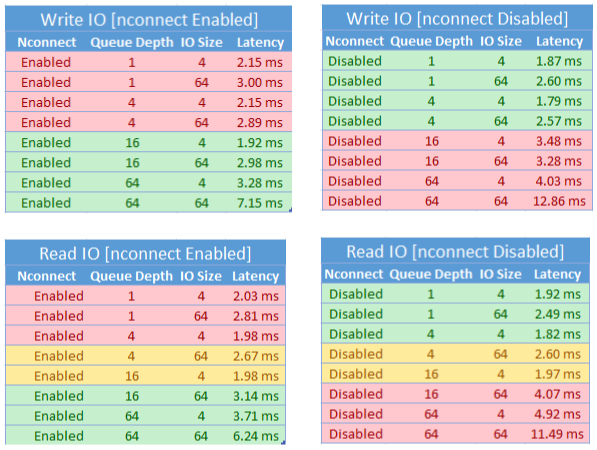
We achieved the following performance results when using the nconnect mount option with NFS Azure file shares on Linux clients at scale. For more information on how we achieved these results, see performance test configuration.
Recommendations
Follow these recommendations to get the best results from nconnect.
Set nconnect=4
While Azure Files supports setting nconnect up to the maximum setting of 16, we recommend configuring the mount options with the optimal setting of nconnect=4. Currently, there are no gains beyond four channels for the Azure Files implementation of nconnect. In fact, exceeding four channels to a single Azure file share from a single client might adversely affect performance due to TCP network saturation.
Size virtual machines carefully
Depending on your workload requirements, it's important to correctly size the client virtual machines (VMs) to avoid being restricted by their expected network bandwidth. You don't need multiple network interface controllers (NICs) in order to achieve the expected network throughput. While it's common to use general purpose VMs with Azure Files, various VM types are available depending on your workload needs and region availability. For more information, see Azure VM Selector.
Keep queue depth less than or equal to 64
Queue depth is the number of pending I/O requests that a storage resource can service. We don't recommend exceeding the optimal queue depth of 64 because you won't see any more performance gains. For more information, see Queue depth.
Per mount configuration
If a workload requires mounting multiple shares with one or more storage accounts with different nconnect settings from a single client, we can't guarantee that those settings persist when mounting over the public endpoint. Per mount configuration is only supported when a single Azure file share is used per storage account over the private endpoint as described in Scenario 1.
Scenario 1: per mount configuration over private endpoint with multiple storage accounts (supported)
- StorageAccount.file.core.windows.net = 10.10.10.10
- StorageAccount2.file.core.windows.net = 10.10.10.11
Mount StorageAccount.file.core.windows.net:/StorageAccount/FileShare1 nconnect=4Mount StorageAccount2.file.core.windows.net:/StorageAccount2/FileShare1
Scenario 2: per mount configuration over public endpoint (not supported)
- StorageAccount.file.core.windows.net = 52.239.238.8
- StorageAccount2.file.core.windows.net = 52.239.238.7
Mount StorageAccount.file.core.windows.net:/StorageAccount/FileShare1 nconnect=4Mount StorageAccount.file.core.windows.net:/StorageAccount/FileShare2Mount StorageAccount2.file.core.windows.net:/StorageAccount2/FileShare1
Note
Even if the storage account resolves to a different IP address, we can't guarantee that address persist because public endpoints aren't static addresses.
Scenario 3: per mount configuration over private endpoint with multiple shares on single storage account (not supported)
- StorageAccount.file.core.windows.net = 10.10.10.10
Mount StorageAccount.file.core.windows.net:/StorageAccount/FileShare1 nconnect=4Mount StorageAccount.file.core.windows.net:/StorageAccount/FileShare2Mount StorageAccount.file.core.windows.net:/StorageAccount/FileShare3
Performance test configuration
We used the following resources and benchmarking tools to achieve and measure the results outlined in this article.
- Single client: Azure VM (DSv4-Series) with single NIC
- OS: Linux (Ubuntu 20.40)
- NFS storage: SSD file share (provisioned 30 TiB, set
nconnect=4)
| Size | vCPU | Memory | Temp storage (SSD) | Max data disks | Max NICs | Expected network bandwidth |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard_D16_v4 | 16 | 64 GiB | Remote storage only | 32 | 8 | 12,500 Mbps |
Benchmarking tools and tests
We used Flexible I/O Tester (FIO), a free, open-source disk I/O tool used both for benchmark and stress/hardware verification. To install FIO, follow the Binary Packages section in the FIO README file to install for the platform of your choice.
While these tests focus on random I/O access patterns, you get similar results when using sequential I/O.
High IOPS: 100% reads
4k I/O size - random read - 64 queue depth
fio --ioengine=libaio --direct=1 --nrfiles=4 --numjobs=1 --runtime=1800 --time_based --bs=4k --iodepth=64 --filesize=4G --rw=randread --group_reporting --ramp_time=300
8k I/O size - random read - 64 queue depth
fio --ioengine=libaio --direct=1 --nrfiles=4 --numjobs=1 --runtime=1800 --time_based --bs=8k --iodepth=64 --filesize=4G --rw=randread --group_reporting --ramp_time=300
High throughput: 100% reads
64 KiB I/O size - random read - 64 queue depth
fio --ioengine=libaio --direct=1 --nrfiles=4 --numjobs=1 --runtime=1800 --time_based --bs=64k --iodepth=64 --filesize=4G --rw=randread --group_reporting --ramp_time=300
1,024 KiB I/O size - 100% random read - 64 queue depth
fio --ioengine=libaio --direct=1 --nrfiles=4 --numjobs=1 --runtime=1800 --time_based --bs=1024k --iodepth=64 --filesize=4G --rw=randread --group_reporting --ramp_time=300
High IOPS: 100% writes
4 KiB I/O size - 100% random write - 64 queue depth
fio --ioengine=libaio --direct=1 --nrfiles=4 --numjobs=1 --runtime=1800 --time_based --bs=4k --iodepth=64 --filesize=4G --rw=randwrite --group_reporting --ramp_time=300
8 KiB I/O size - 100% random write - 64 queue depth
fio --ioengine=libaio --direct=1 --nrfiles=4 --numjobs=1 --runtime=1800 --time_based --bs=8k --iodepth=64 --filesize=4G --rw=randwrite --group_reporting --ramp_time=300
High throughput: 100% writes
64 KiB I/O size - 100% random write - 64 queue depth
fio --ioengine=libaio --direct=1 --nrfiles=4 --numjobs=1 --runtime=1800 --time_based --bs=64k --iodepth=64 --filesize=4G --rw=randwrite --group_reporting --ramp_time=300
1024 KiB I/O size - 100% random write - 64 queue depth
fio --ioengine=libaio --direct=1 --nrfiles=4 --numjobs=1 --runtime=1800 --time_based --bs=1024k --iodepth=64 --filesize=4G --rw=randwrite --group_reporting --ramp_time=300
Performance considerations for nconnect
When using the nconnect mount option, you should closely evaluate workloads that have the following characteristics:
- Latency sensitive write workloads that are single threaded and/or use a low queue depth (less than 16)
- Latency sensitive read workloads that are single threaded and/or use a low queue depth in combination with smaller I/O sizes
Not all workloads require high-scale IOPS or throughout performance. For smaller scale workloads, nconnect might not make sense. Use the following table to decide whether nconnect is advantageous for your workload. Scenarios highlighted in green are recommended, while scenarios highlighted in red aren't. Scenarios highlighted in yellow are neutral.