Replace or extend Windows file servers with Azure Files and Azure File Sync
This article explains how you can use Azure Files and Azure File Sync to replace or extend your on-premises Windows file servers to reduce total cost of ownership (TCO), increase flexibility, and simplify data protection and access control. Azure Files has its origins in the Windows file server role, making it an excellent choice when migrating Windows file servers to the cloud.
Most customers take one of two deployment approaches:
- Cloud-only deployment: Migrate on-premises file servers to a fully managed SMB Azure file share (or multiple file shares).
- Hybrid deployment: Use Azure File Sync to synchronize existing Windows file servers with an SMB Azure file share. Optionally use cloud tiering to scale file data in the cloud while turning on-premises servers into local caches for hot files.
Applies to
| File share type | SMB | NFS |
|---|---|---|
| Standard file shares (GPv2), LRS/ZRS | ||
| Standard file shares (GPv2), GRS/GZRS | ||
| Premium file shares (FileStorage), LRS/ZRS |
Reduce TCO with fully managed file shares
There's more to file share TCO than the price per GiB of storage. By centralizing your file shares in Azure, you can reduce TCO in many ways:
Achieve better storage utilization by not having to over-provision file share capacity. With Azure Files, you can quickly resize your share without downtime.
Eliminate the work associated with hardware procurement, setup, and maintenance. With Azure Files, storage resiliency, redundancy, and maintenance are included, and there are no patches or upgrades to manage.
Customers relying on full-share replication technologies like DFS-R can reduce costs by centralizing one full copy in an Azure file share and using Azure File Sync to cache hot files locally.
Differential snapshots and integration with Azure Backup offer economical data protection.
Choose between multiple storage tiers, from premium low latency SSD to cost-effective cool storage, allowing you to choose the tier that best fits your workload.
Azure Files Reservations discounts enable up to 36% savings for pre-committed storage.
To learn more about how Azure file shares are billed and how you can reduce TCO, see Understand Azure Files billing.
Broad compatibility with Windows file servers
Most of the core file system and SMB capabilities in the Windows file server role also exist in Azure Files, such as:
- Access control lists (Windows ACLs)
- Active Directory integration
- SMB encryption
- Transparent failover
- File locks
- SMB multichannel
Only a limited set of features supported by SMB and NTFS aren't currently supported by Azure Files.
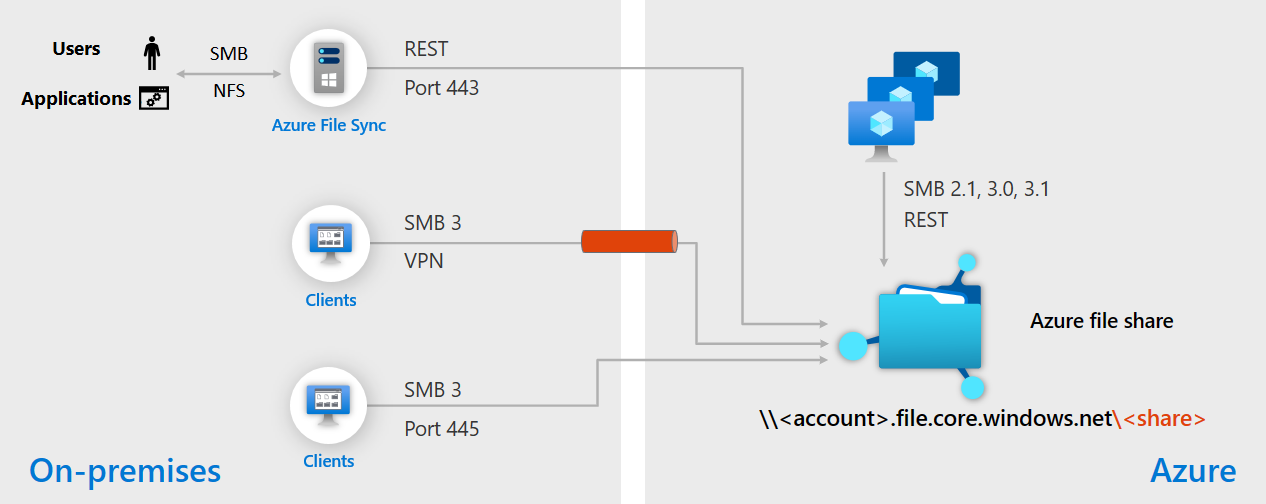
Flexible deployment and hybrid access
Azure Files is built for hybrid access and offers flexible deployment options, including zero downtime migration from Windows file servers. You can connect to an Azure file share from a variety of clients, or from within virtual machines (VMs) or containers. You can connect from anywhere via encrypted SMB 3.x traffic, either over the internet or through VPN/ExpressRoute. If you want to maintain local performance, you can use Azure File Sync to cache hot files or a full copy of your Azure file share.
Moving data from Windows file servers to Azure Files is easy, and you can do it in the background without interrupting user access. Just install Azure File Sync on your file server, connect to an Azure file share, and start the synchronization.
When you migrate to Azure Files, none of your file path links need to break. You can use DFS Namespaces and redirect users to Azure Files. If you're extending an existing Windows file server to Azure using Azure File Sync, users continue to access their files using the same file paths.
Azure File Sync can synchronize and cache your Azure file share anywhere you can install Windows Server. As the diagram shows, you can create regional caches of your file servers in different Azure regions. You can cache files on-premises, in your data centers, or on a VM in third-party clouds. Learn more in the tutorial Extend Windows file servers with Azure File Sync.
Simplified data protection and access control
With Azure Files you benefit from multi-layered security provided by Microsoft across physical data centers, infrastructure, and operations in Azure. We provide several data redundancy options including local, regional, or global. Differential snapshots and snapshot management from Azure Backup simplify data protection, while Azure File Sync offers a variety of disaster recovery options. You can even protect users from accidentally deleting a file or share via soft delete.
Access control works just like your Windows file servers. You can use identity-based authentication and integrate SMB Azure file shares with your on-premises Active Directory environment or Microsoft Entra ID, and control share-level and directory/file-level access as well as administrator privileges.
See also
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for