Troubleshooting a misclassified workload in Azure Synapse Analytics
This article covers guidance on how to troubleshoot a misclassified workload, and how to identify the reason behind the classification, for workloads in a dedicated SQL pool.
Azure Synapse Analytics provides workload management capabilities like classifying workloads to appropriate workload groups, assigning importance, and isolating resources to meet SLAs.
However, in some scenarios, a combination of these capabilities can lead to workload classification that doesn't reflect user intent. This article lists such common scenarios and how to troubleshoot them. First, you should query basic information for troubleshooting misclassified workload scenarios.
Note
Classifying managed identities (MI) behavior differs between the dedicated SQL pool in Azure Synapse workspaces and the standalone dedicated SQL pool (formerly SQL DW). While the standalone dedicated SQL pool MI maintains the assigned identity, for Azure Synapse workspaces the MI runs as dbo. This cannot be changed. The dbo role, by default, is classified to smallrc. Creating a classifier for the dbo role allows for assigning requests to a workload group other than smallrc. If dbo alone is too generic for classification and has broader impacts, consider using label, session or time-based classification in conjunction with the dbo role classification.
Basic troubleshooting information
To troubleshoot a misclassified workload scenario the following information is needed:
- List of all workload groups
- List of all workload classifiers and associated workload groups
- List of users and mapped workload groups (system and user defined)
- List of workload group and classifier details of a request
Workload groups
Azure portal
To get a list of all workload groups (including system workload groups) and associated details in the Azure portal:
- Go to the Azure Synapse workspace under which the dedicated SQL Pool of interest has been created.
- On the left side pane, all pool types created under the workspace are listed. Select SQL Pools under Analytical Pools section.
- Select the dedicated SQL pool of interest.
- In the left side pane, select Workload management under Settings.
- Under Workload groups section, all workloads are listed. By default only User-Defined Workload groups are listed. To view a list of both user-defined and system-defined workload groups, edit the filter and Select All.
T-SQL
To view workload groups using T-SQL, connect to the dedicated SQL Pool using SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) and issue following query:
SELECT * FROM sys.workload_management_workload_groups;
For more information, see sys.workload_management_workload_groups.
Workload classifiers
Azure portal
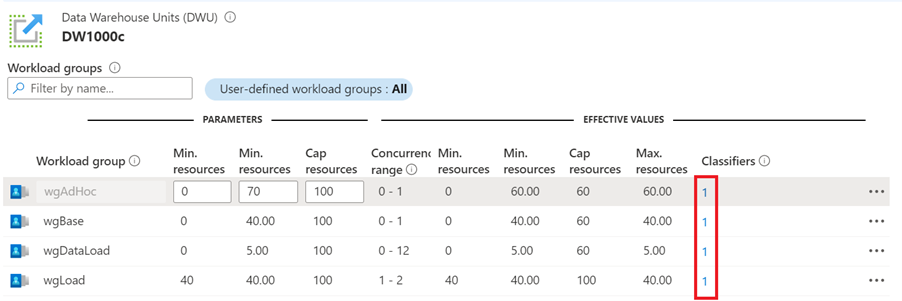
To list all workload classifiers (including system-defined classifiers) by workload group in the Azure portal, see the numbers listed in Classifiers column in Workload group table (see previous section).
T-SQL
To get the list of all workload classifiers (including system-defined classifiers) using T-SQL, use following query:
SELECT * FROM sys.workload_management_workload_classifiers;
For more information, see sys.workload_management_workload_classifiers.
Users and mapped resource classes
To get a list of system defined resource classes and mapped users in T-SQL, use following query:
SELECT r.name AS [Resource Class]
, m.name AS [Member Name]
FROM sys.database_role_members AS rm
JOIN sys.database_principals AS r ON rm.role_principal_id = r.principal_id
JOIN sys.database_principals AS m ON rm.member_principal_id = m.principal_id
WHERE r.name IN ('mediumrc','largerc','xlargerc','staticrc10','staticrc20','staticrc30','staticrc40','staticrc50','staticrc60','staticrc70','staticrc80');
Workload group and classifier details of a request
The first step in troubleshooting a misclassified workload problem is to identify the workload group and workload classifier for a query. Use the dynamic management view sys.dm_pdw_exec_requests to view submitted queries and their classification:
SELECT * FROM sys.dm_pdw_exec_requests;
For more information, see sys.dm_pdw_exec_requests.
Common scenarios of misclassified workloads
Here are some common scenarios where unintended misclassified workloads can occur:
Mixed usage of resource classes and user-defined workload management
In scenarios where resource classes and workload groups are used together, user role to resource class mappings can conflict with workload classifier rules, and lead to unintended query classification.
Consider following scenario:
- A database user, DBAUser, is assigned to largerc resource class role using
sp_addrolememberprocedure. - DBAUser has created a new workload group and classifier using workload management.
- A newly-created workload classifier maps database role DBARole to mediumrc resource class with high importance.
- DBAUser is a made a member of the DBARole database role.
- When DBAUser runs a query, the query is expected to run on mediumrc based on workload classifier. Instead it will be assigned to largerc, as user mapping takes precedence over role membership mapping to a classifier.
It's best to avoid mixing usage of resource classes and workload management groups to do workload management. For more information on steps to convert resource classes to workloads, see Convert Resource Classes to Workload Groups.
However, there can be situations where both resource classes and workload management need to be used together. In such scenarios, to simplify troubleshooting misclassification, we recommend you remove resource class role mappings as you create workload classifiers. The code below returns existing resource class role memberships. Run sp_droprolemember for each member name returned from the corresponding resource class.
SELECT r.name AS [Resource Class]
, m.name AS membername
FROM sys.database_role_members AS rm
JOIN sys.database_principals AS r ON rm.role_principal_id = r.principal_id
JOIN sys.database_principals AS m ON rm.member_principal_id = m.principal_id
WHERE r.name IN ('mediumrc','largerc','xlargerc','staticrc10','staticrc20','staticrc30','staticrc40','staticrc50','staticrc60','staticrc70','staticrc80');
--for each row returned run
EXEC sp_droprolemember '[Resource Class]', membername;
Some administrative users are always mapped to smallrc workload group
Consider a scenario for the Azure Synapse Workspace SQL Admin login, the Azure Synapse Microsoft Entra admin (user or group member), or a database owner. These users may still have a workload classifier or have been added to a resource class role other than smallrc. All queries executed by these user will still run on smallrc resource class, even though the user is mapped to a different resource class or workload group.
Recommendation: These administrative users can't change their default workload group. For more information, see workload management with resource classes. It is recommended that critical or performance-sensitive workloads not run as one of these administrative users in the dedicated SQL pool.
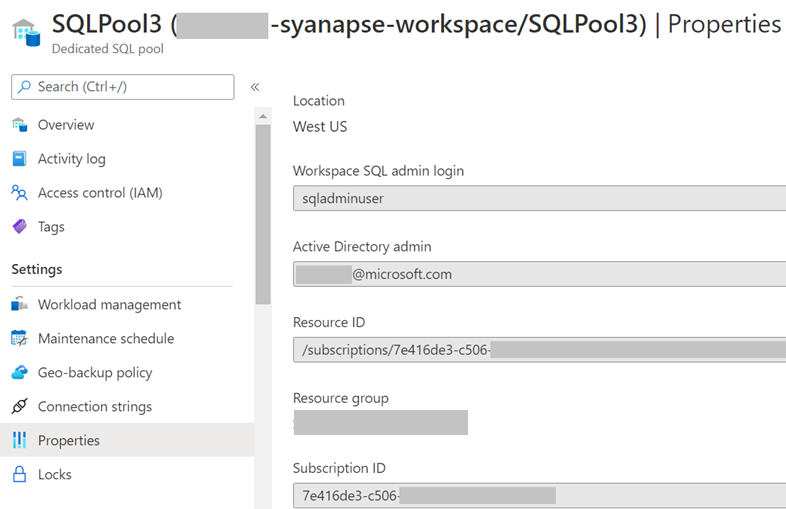
The Azure Synapse Workspace SQL Admin login and the Azure Synapse Microsoft Entra admin (user or group member) are specified in the Azure portal:
Similarly, the database owner (dbo) and db_owner database roles are not allowed to change their default resource class. If a user is either the database owner or added under db_owner database role, all queries executed by the user go to smallrc by default. These roles can't be added to a resource class other than smallrc. However, if a user who is part of this role would like to classify their queries to a different workload group, they can use MEMBERNAME option in workload classifier definition.
Use workload group precedence for better classification
In scenarios where workload classifiers are mapped to multiple workload groups, or a user is mapped to multiple resource classes, precedence order determines chosen workload group and Resource class. List of precedence rules:
Note
As mentioned in Mixing Resource Classes and user-defined Workload Management section, it isn't recommended to combine usage of Resource classes and user-defined workload groups/classes.
If resource classes are being used:
In scenarios where resource classes are being used it's best to create a dedicated user for each type of workload being run. However, if a user is a member of multiple resource classes, then precedence rules documented in Resource Class Precedence take effect:
- Dynamic resource class takes precedence over static resource class. For example, if a user is member of mediumrc (dynamic) and staticrc80(static), user queries run with mediumrc.
- Bigger resource classes are preferred over smaller resource classes. For example, if a user is member of staticrc20 and staticrc80, then user queries will run with staticrc80.
If Workload Management Capabilities are used
WLM provides capability to create multiple workload classifiers for same user or workload group. Classifier definition statement has multiple parameters based on which incoming requests are assigned to workloads. These parameters have a weight score as shown below and this score determines order of precedence:
| Classifier parameter | Weight |
|---|---|
| MEMBERNAME:USER | 64 |
| MEMBERNAME:ROLE | 32 |
| WLM_LABEL | 16 |
| WLM_CONTEXT | 8 |
| START_TIME/END_TIME | 4 |
Let us see these precedence rules in action using an example. If a user creates two workload classifiers as follows:
CREATE WORKLOAD CLASSIFIER CLASSIFIER-1 WITH
( WORKLOAD_GROUP = 'wgDataLoad'
,MEMBERNAME = 'USER-1'
,WLM_LABEL = 'dimension_loads'
,IMPORTANCE = 'High');
CREATE WORKLOAD CLASSIFIER CLASSIFIER-2 WITH
( WORKLOAD_GROUP = 'wgUserqueries'
,MEMBERNAME = 'USER-1'
,START_TIME = '18:00'
,END_TIME = '07:30'
,IMPORTANCE = 'Low')
Queries submitted by User-1 can be submitted via both classifiers. Query run by User-1 with the 'dimension_loads' label between 6PM and 7AM UTC will be assigned to wgDashboards as weight score of WLM_LABEL is higher than START_TIME/END_TIME. The weighting of CLASSIFIER-1 is 80 (64 for user, plus 16 for WLM_LABEL). The weighting of CLASSIFIER-2 is 68 (64 for user, 4 for START_TIME/END_TIME).
For more information on workload classification, see classification weighting and query labels.
What happens if precedence in workload classification leads to a tie?
Even after workload classifier precedence is applied, it is possible for a query to be classified to multiple workload groups. For example, consider following classifiers:
CREATE WORKLOAD CLASSIFIER CLASSIFIER-1 WITH
( WORKLOAD_GROUP = 'wgDataLoad'
,MEMBERNAME = 'USER-1'
,WLM_LABEL = 'dimension_loads'
,IMPORTANCE = 'High');
CREATE WORKLOAD CLASSIFIER CLASSIFIER-2 WITH
( WORKLOAD_GROUP = 'wgUserqueries'
,MEMBERNAME = 'USER-1'
,WLM_LABEL = 'dimension_loads'
,IMPORTANCE = 'Low');
If a user runs a query with OPTION (LABEL = 'dimension_loads'), it can be classified to either wgDataLoad or wgUserqueries based on precedence rules. But which workload group is chosen?
Workload group and classifier tie-breakers
If there was a tie in workload groups or classifiers, following precedence takes effect:
- The workload group with the highest resource allocation is chosen. This behavior optimizes for performance in scenarios where logins are members of multiple resource classes. This behavior also ensures backward compatibility.
Consider the following two workload groups and workload classifiers:
-- Workload Groups
CREATE WORKLOAD GROUP wgDataLoad
WITH
( MIN_PERCENTAGE_RESOURCE = 26
,REQUEST_MIN_RESOURCE_GRANT_PERCENT = 2
,CAP_PERCENTAGE_RESOURCE = 100 )
CREATE WORKLOAD GROUP wgUserqueries
WITH
( MIN_PERCENTAGE_RESOURCE = 15
,REQUEST_MIN_RESOURCE_GRANT_PERCENT = 5
,CAP_PERCENTAGE_RESOURCE = 50 );
--Workload Classifiers
CREATE WORKLOAD CLASSIFIER CLASSIFIER-1 WITH
( WORKLOAD_GROUP = 'wgDataLoad'
,MEMBERNAME = 'USER-1'
,WLM_LABEL = 'dimension_loads'
,IMPORTANCE = 'High');
CREATE WORKLOAD CLASSIFIER CLASSIFIER-2 WITH
( WORKLOAD_GROUP = 'wgUserqueries'
,MEMBERNAME = 'USER-1'
,WLM_LABEL = 'dimension_loads'
,IMPORTANCE = 'High');
If a user runs a query with OPTION (LABEL = 'dimension_loads'), the query meets criteria for both the classifiers. However, the user request will be routed to wgUserQueries workload group as it has higher minimum resource allocation per request.
- Next, concurrency setting and available concurrency for respective workload groups is considered for tie-breakers. The workload group with the highest available concurrency at a time when request arrived will give the query best chance of executing.
Consider following two workload groups and workload classifiers:
--Workload Groups
CREATE WORKLOAD GROUP wgDataLoad
WITH
( MIN_PERCENTAGE_RESOURCE = 30
,REQUEST_MIN_RESOURCE_GRANT_PERCENT = 2 (concurrency of 15)
,REQUEST_MIN_RESOURCE_GRANT_PERCENT = 2
,CAP_PERCENTAGE_RESOURCE = 100 );
CREATE WORKLOAD GROUP wgUserqueries
WITH
( MIN_PERCENTAGE_RESOURCE = 30
,REQUEST_MIN_RESOURCE_GRANT_PERCENT = 2 (concurrency of 15)
,REQUEST_MIN_RESOURCE_GRANT_PERCENT = 2
,CAP_PERCENTAGE_RESOURCE = 100 );
-- Workload Classifiers
CREATE WORKLOAD CLASSIFIER CLASSIFIER-1 WITH
( WORKLOAD_GROUP = 'wgDataLoad'
,MEMBERNAME = 'USER-1'
,WLM_LABEL = 'dimension_loads'
,IMPORTANCE = 'High');
CREATE WORKLOAD CLASSIFIER CLASSIFIER-2 WITH
( WORKLOAD_GROUP = 'wgUserqueries'
,MEMBERNAME = 'USER-1'
,WLM_LABEL = 'dimension_loads'
,IMPORTANCE = 'High');
If a user runs a query with OPTION (LABEL = 'dimension_loads'), both the classifiers have a tie as the query meets criteria for both. When user submits the query, consider the scenario where five concurrent queries are getting executed in the wgUserqueries group and ten queries are getting executed in the wgDataLoad group. The user request will be routed to wgUserqueries group using CLASSIFIER-2, as the wgUserqueries workload group has higher available concurrency at the time the user submitted a query.
Next, the importance setting of the request is considered for tie-breakers. If there was a tie in workload classification using precedence rules, the request will be routed to workload group that has highest importance. For more information, see workload importance.
Finally, the creation time of the workload group is considered for tie-breakers. The user request will be routed to the workload group that was created most recently.
Next steps
- For more information on workload classification, see Workload Classification.
- For more information on workload importance, see Workload Importance
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for