Trusted Signing resources and roles
Trusted Signing is an Azure-native resource that offers full support for common Azure concepts, such as resources. Like with any other Azure resource, Trusted Signing has its own set of resources and roles that are designed to simplify management of the service.
This article introduces you to the resources and roles that are specific to Trusted Signing.
Trusted Signing resource types
Trusted Signing has the following resource types:
Trusted Signing account: An account is a logical container of all the resources you need to complete signing and manage access controls to sensitive resources.
Identity validations: Identity validation performs verification of your organization or individual identity before you can sign code. The verified organization or individual identity is the source of the attributes for your certificate profile Subject Distinguished Name (subject DN) values (for example,
CN=Microsoft Corporation, O=Microsoft Corporation, L=Redmond, S=Washington, C=US). Identity validation roles are assigned to tenant identities to create these resources.Certificate profiles: A certificate profile is the configuration attributes that generate the certificates you use to sign code. It also defines the trust model and scenario that signed content is consumed under by relying parties. Signing roles are assigned to this resource to authorize tenant identities to request signing. A prerequisite for creating any certificate profile is to have at least one identity validation request completed.
In the following example structure, an Azure subscription has a resource group. Under the resource group, you can have one or many Trusted Signing account resources with one or many identity validations and certificate profiles.
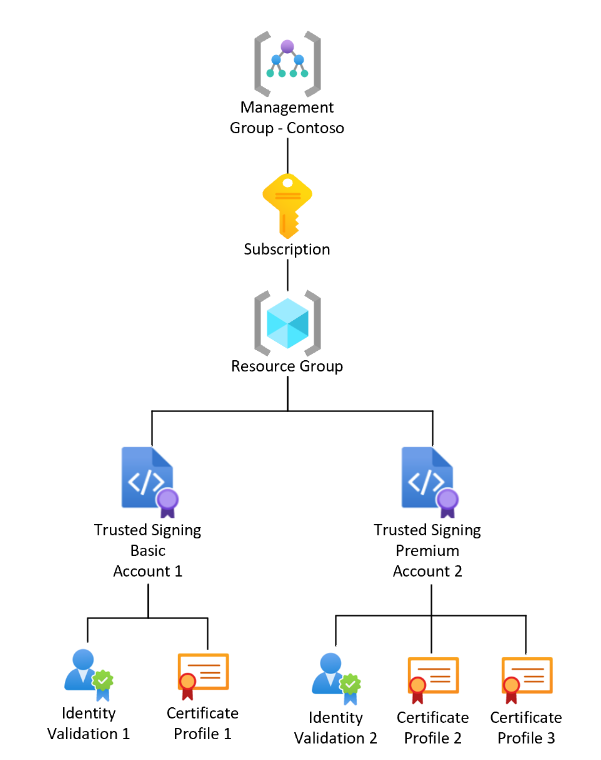
The service supports Public Trust, Private Trust, code integrity (CI) policy, virtualization-based security (VBS) enclave, and Public Trust test signing types, so it's useful to have multiple Trusted Signing accounts and certificate profiles. For more information about the certificate profile types and how they're used, see Trusted Signing certificate types and management.
Note
Identity validations and certificate profiles align with either Public Trust or Private Trust. A Public Trust identity validation is used only for certificate profiles that are used for the Public Trust model. For more information, see Trusted Signing trust models.
Trusted Signing account
A Trusted Signing account is a logical container of the resources that are used to complete certificate signing. Trusted Signing accounts can be used to define boundaries of a project or organization. For most, a single Trusted Signing account can satisfy all the signing needs for an individual or organization. You might want to sign many artifacts that are distributed by the same identity (for example, Contoso News, LLC), but operationally, there might be boundaries that you want to draw in terms of access to signing. You might choose to have a Trusted Signing account per product or per team to isolate how an account is used or to track signing. However, you can also achieve this isolation pattern at the certificate profile level.
Identity validations
Identity validations are all about establishing the identity on the certificates that are used for signing. There are two types: Public Trust and Private Trust. What defines the two types is the level of identity validation required to complete the creation of an identity validation resource.
Public Trust means that all identity values must be validated in accordance to the Microsoft PKI Services Third-Party Certification Practice Statement (CPS). This requirement aligns with the expectations for publicly trusted code signing certificates.
Private Trust is intended for situations in which there's an established trust in a private identity across one or many relying parties (consumers of signatures) or internally in app control or line-of-business (LOB) scenarios. With Private Trust identity validations, there's minimal verification of the identity attributes (for example, the
Organization Unitvalue). Verification is tightly associated with the Azure Tenant of the subscriber (for example,Contoso.onmicrosoft.com). The values in Private Trust certificate profiles aren't validated beyond the Azure Tenant information.
For more information about Public Trust and Private Trust, see Trusted Signing trust models.
Certificate profiles
Trusted Signing provides five total certificate profile types that all subscribers can use with the aligned and completed identity validation resources. These five certificate profiles are aligned to Public Trust or Private Trust identity validations as follows:
- Public Trust
Public Trust: Used for signing code and artifacts that can be publicly distributed. This certificate profile is default-trusted on the Windows platform for code signing.
VBS enclave: Used to sign virtualization-based security enclaves on Windows.
Public Trust Test: Used for test signing only and aren't publicly trusted by default. Consider Public Trust Test certificate profiles as a great option for inner-loop build signing.
Note
All certificates under the Public Trust Test certificate profile type include the lifetime EKU (
1.3.6.1.4.1.311.10.3.13), which forces validation to respect the lifetime of the signing certificate regardless of the presence of a valid time stamp countersignature.
- Private Trust
- Private Trust: Used to sign internal or private artifacts such as LOB applications and containers. You also can use it to sign catalog files in App Control for Business.
- Private Trust CI Policy: The Private Trust CI Policy certificate profile is the only type that doesn't include the code signing EKU (
1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.3). This certificate profile is designed for signing App Control for Business CI policy files.
Supported roles
Role-based access control (RBAC) is a cornerstone concept for all Azure resources. Trusted Signing adds two custom roles to meet subscriber needs for creating an identity validation (the Trusted Signing Identity Verifier role) and signing with certificate profiles (the Trusted Signing Certificate Profile Signer role). These custom roles explicitly must be assigned to perform those two critical functions in using Trusted Signing. The following table contains a complete list of roles that Trusted Signing supports and their capabilities, including all standard Azure roles.
| Role | Manage and view account | Manage certificate profiles | Sign by using a certificate profile | View signing history | Manage role assignment | Manage identity validation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trusted Signing Identity Verifier1 | X | |||||
| Trusted Signing Certificate Profile Signer2 | X | X | ||||
| Owner | X | X | X | |||
| Contributor | X | X | ||||
| Reader | X | |||||
| User Access Admin | X |
1 Required to create or manage identity validation. Available only in the Azure portal.
2 Required to successfully sign by using Trusted Signing.
Related content
- Complete the quickstart to set up Trusted Signing.
- Learn about Trusted Signing trust models.
- Review the Trusted Signing certificates and management concept.