Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Azure Resource Graph is an Azure service that allows you to use the same KQL query language used in log queries to query your Azure resources at scale with complex filtering, grouping, and sorting by resource properties. You can use VM health annotations to Azure Resource Graph (ARG) for detailed failure attribution and downtime analysis including the following:
- Query the latest snapshot of VM availability together across all your Azure subscriptions.
- Assess the impact to business SLAs and trigger decisive mitigation actions, in response to disruptions and type of failure signature.
- Set up custom dashboards to supervise the comprehensive health of applications by joining VM availability information with additional resource metadata in Resource Graph.
- Track relevant changes in VM availability across a rolling 14 days window, by using the change tracking mechanism for conducting detailed investigations.
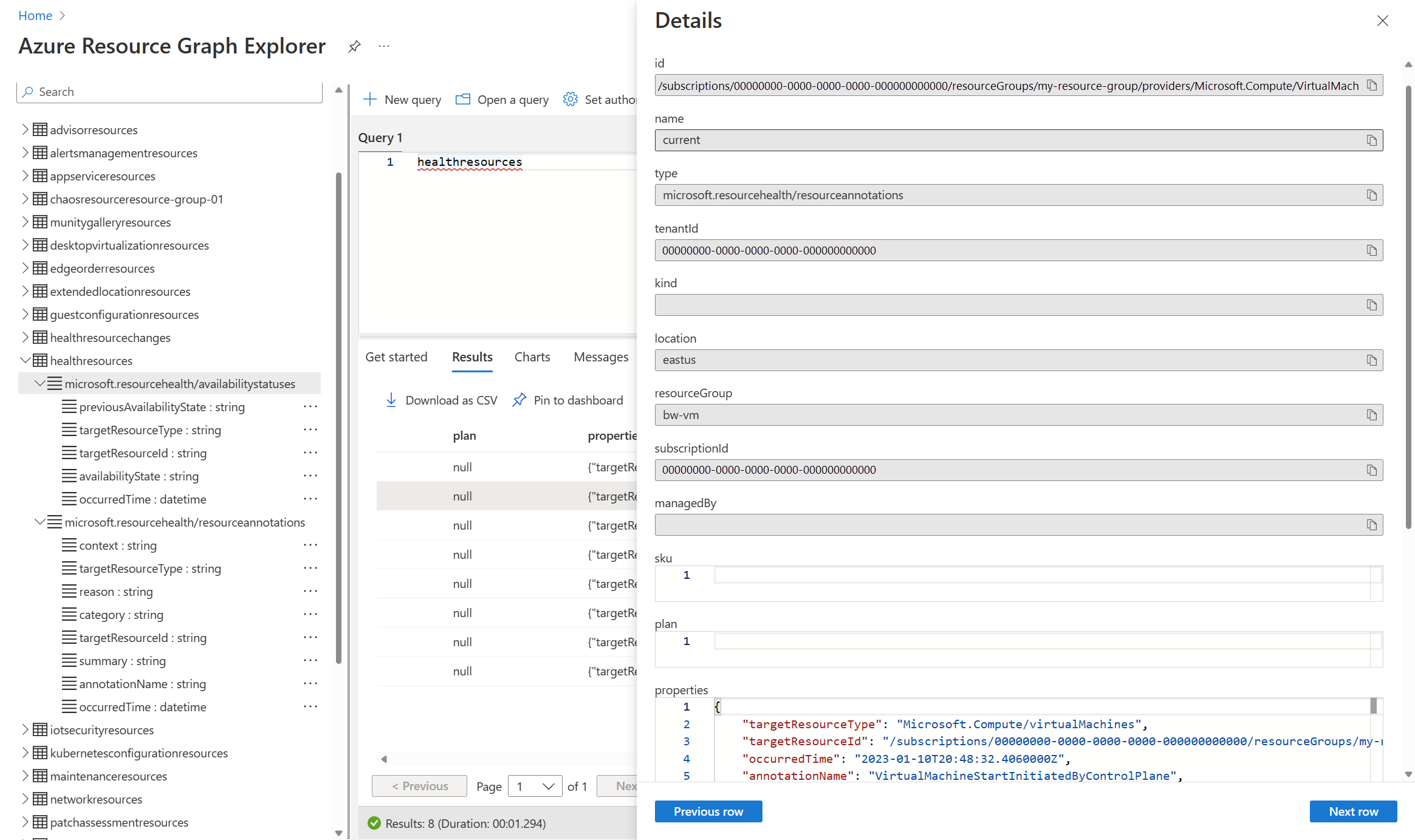
To get started with Resource Graph, open Resource Graph Explorer in the Azure portal. Select the Table tab and have a look at the microsoft.resourcehealth/availabilitystatuses and microsoft.resourcehealth/resourceannotations tables which are described below. Click on healthresources to create a simple query and then click Run to return the records.
To view the details for a record, scroll to the right and select See details.
There will be two types of events populated in the HealthResources table:
microsoft.resourcehealth/availabilitystatuses
This event denotes the latest availability status of a VM, based on the health checks performed by the underlying Azure platform. The availability states currently emitted for VMs are as follows:
- Available: The VM is up and running as expected.
- Unavailable: A disruption to the normal functioning of the VM has been detected.
- Unknown: The platform is unable to accurately detect the health of the VM. Check back in a few minutes.
The availability state is in the properties field of the record which includes the following properties:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| targetResourceType | Type of resource for which health data is flowing |
| targetResourceId | Resource ID |
| occurredTime | Timestamp when the latest availability state is emitted by the platform |
| previousAvailabilityState | Previous availability state of the VM |
| availabilityState | Current availability state of the VM |
A sample properties value looks similar to the following:
{
"targetResourceType": "Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines",
"targetResourceId": "/subscriptions/<subscriptionId>/resourceGroups/<ResourceGroupName>/providers/Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines/<VMName>",
"occurredTime": "2022-10-11T11:13:59.9570000Z",
"previousAvailabilityState": "Available",
"availabilityState": "Unavailable"
}
microsoft.resourcehealth/resourceannotations
This event contextualizes any changes to VM availability, by detailing necessary failure attributes to help you investigate and mitigate the disruption as needed. The full list of VM health annotations are listed at [Resource Health virtual machine Health Annotations] (../service-health/resource-health-vm-annotation.md).
These annotations can be broadly classified into the following:
- Downtime Annotations: Emitted when the platform detects VM availability transitioning to Unavailable. Examples include host crashes or reboot operations.
- Informational Annotations: Emitted during control plane activities with no impact to VM availability. Examples include VM allocation, stop, delete, start. Usually, no additional customer action is required in response.
- Degraded Annotations: Emitted when VM availability is detected to be at risk. Examples include when failure prediction models predict a degraded hardware component that can cause the VM to reboot at any given time. You should redeploy by the deadline specified in the annotation message to avoid any unanticipated loss of data or downtime.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| targetResourceType | Type of resource for which health data is flowing |
| targetResourceId | Resource ID |
| occurredTime | Timestamp when the latest availability state is emitted by the platform |
| annotationName | Name of the Annotation emitted |
| reason | Brief overview of the availability impact observed by the customer |
| category | Denotes whether the platform activity triggering the annotation was either planned maintenance or unplanned repair. This field is not applicable to customer/VM-initiated events. Possible values: Planned | Unplanned | Not Applicable | Null |
| context | Denotes whether the activity triggering the annotation was due to an authorized user or process (customer initiated), due to the Azure platform (platform initiated), or due to activity in the guest OS that has resulted in availability impact (VM initiated). Possible values: Platform-Initiated | User-initiated | VM-initiated | Not Applicable | Null |
| summary | Statement detailing the cause for annotation emission, along with remediation steps that can be taken by users |
See Azure Resource Graph sample queries by table for sample queries using this data.