Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Azure routing preference enables you to choose how your traffic routes between Azure and the Internet. You can choose to route traffic either via the Microsoft network, or, via the ISP network (public internet). These options are also referred to as cold potato routing and hot potato routing respectively. Egress data transfer price varies based on the routing selection. You can choose the routing option while creating a public IP address. The public IP address can be associated with resources such as virtual machine, virtual machine scale sets, internet-facing load balancer, etc. You can also set the routing preference for Azure storage resources such as blobs, files, web, and Azure Data Lake. By default, traffic is routed via the Microsoft global network for all Azure services.
Routing via Microsoft global network
Routing your traffic via the Microsoft global network delivers your traffic over one of the largest networks in the world, spanning over 160,000 miles of fiber with over 165 edge Point of Presence (POP). The network is well provisioned with multiple redundant fiber paths to ensure exceptionally high reliability and availability. The software-defined WAN controller manages traffic engineering, ensuring low-latency path selection for your traffic and offering premium network performance.
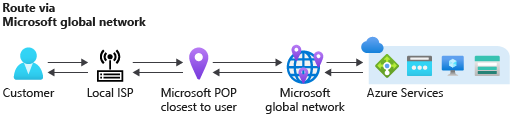
Ingress traffic: The global BGP Anycast announcement ensures ingress traffic enters Microsoft network closest to the user. When a user from Singapore accesses Azure resources hosted in Chicago, the traffic enters the Microsoft global network at the Singapore edge POP. The traffic then travels on the Microsoft network to the service hosted in Chicago.
Egress traffic: The egress traffic follows the same principle. Traffic travels most of its journey on Microsoft global network and exits closest to the user. For example, if traffic from Azure in Chicago is destined to a user from Singapore, then traffic travels on the Microsoft network from Chicago to Singapore, and exits the Microsoft network at Singapore edge POP.
Both ingress and egress traffic remain on the Microsoft global network whenever possible. This process is also known as cold potato routing.
Routing over public Internet (ISP network)
The new routing choice Internet routing minimizes travel on the Microsoft global network, and uses the transit ISP network to route your traffic. This cost-optimized routing option offers network performance that is comparable to other cloud providers.
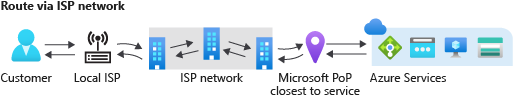
Ingress traffic: The ingress path uses hot potato routing, which means that traffic enters the Microsoft network that is closest to the hosted service region. For example, if a user from Singapore accesses Azure resources hosted in Chicago then traffic travels over the public internet and enters the Microsoft global network in Chicago.
Egress traffic: The egress traffic follows the same principle. Traffic exits Microsoft network in the same region that the service is hosted. For example, if traffic from your service in Azure in Chicago is destined to a user in Singapore, the traffic exits the Microsoft network in Chicago. It then travels over the public internet to the user in Singapore.
Note
Even when using a public IP with routing preference Internet, all traffic that is bound for a destination within Azure continues to use the direct path within the Microsoft Wide Area Network.
Supported services
Public IP with routing preference choice Microsoft Global Network can be associated with any Azure services. However, a public IP with routing preference choice Internet can be associated with the following Azure resources:
Virtual machine
Virtual Machine Scale Set
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
Public load balancer (NIC-based backend only)
Application Gateway
Azure Firewall
For storage, primary endpoints always use the Microsoft global network. You can enable secondary endpoints with Internet as your choice for traffic routing. Supported storage services are:
Blobs
Files
Web
Azure Data Lake
Pricing
The price difference between both options is reflected in the internet egress data transfer pricing. Routing via Microsoft global network data transfer price is same as current internet egress price. Visit Azure bandwidth pricing page for the latest pricing information.
Limitations
Internet routing preference is only compatible with zone-redundant standard SKU of public IP address. Basic SKU of public IP address isn't supported.
Internet routing preference currently supports only IPv4 public IP addresses. IPv6 public IP addresses aren't supported.
Internet routing preference public IP addresses are not compatible with NAT Gateways or IP-based Public Load Balancers.
Regional availability
Internet routing preference is available in all regions listed below:
- Australia Central
- Australia Central 2
- Australia East
- Australia Southeast
- Brazil South
- Brazil Southeast
- Canada Central
- Canada East
- Central India
- Central US
- Central US EUAP
- East Asia
- East US
- East US 2
- East US 2 EUAP
- France Central
- France South
- Germany North
- Germany West Central
- Japan East
- Japan West
- Korea Central
- Korea South
- North Central US
- North Europe
- Norway East
- Norway West
- South Africa North
- South Africa West
- South Central US
- South India
- Southeast Asia
- Sweden Central
- Switzerland North
- Switzerland West
- UAE Central
- UAE North
- UK South
- UK West
- West Central US
- West Europe
- West India
- West US
- West US 2
- West US 3